This repository contains the Back-End micro-service of the Ascent tool.
Ascent is a tool created by the IBM Ecosystem Lab to accelerate the adoption of IBM Software on Hybrid Cloud. Through automation and integration, Ascent enables enterprises to deliver compliant cloud architectures which can be clearly evidenced and communicated with Governance, Risk and Compliance teams.
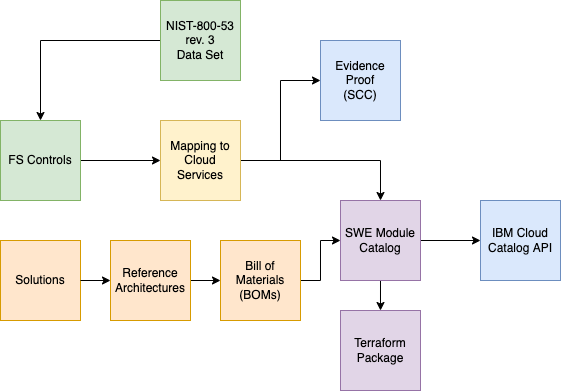
This application backend will enable a collection of APIs that will support the relationship between a Reference Architecture and its Bill of Materials(BOM) (list of comprising services). The BOM relationship to the list of FS Ready services. The mapping between the cloud services and the FS Controls. Finally you can view the FS Controls mapping to the Cloud Services and the supporting reference Architectures.
Once we have this data model in place, we will be able to link it to the Automation Catalog that is being built by Asset team, we will be able to take the BOM and input it into the Solution Builder API they have built and output a package of consistent terraform.
This will enable the Ecosystem teams including ISVs to have a consistent way of describing reference archtiectures and having their automation packaged consistently.
This application is generated using LoopBack 4 CLI with the initial project layout.
List of reference documentation that will support the APIs
The Architecture builder's goal is to simplify the complexity of the data attributes that surround a reference architecture for the FS Cloud. When we review the Financial Controls the number of cloud services and the possible reference architectures these can be assembled in. It has become clear a tool will help manage this wide range of attributes.
The following diagram helps describes the key entities and their relationships.
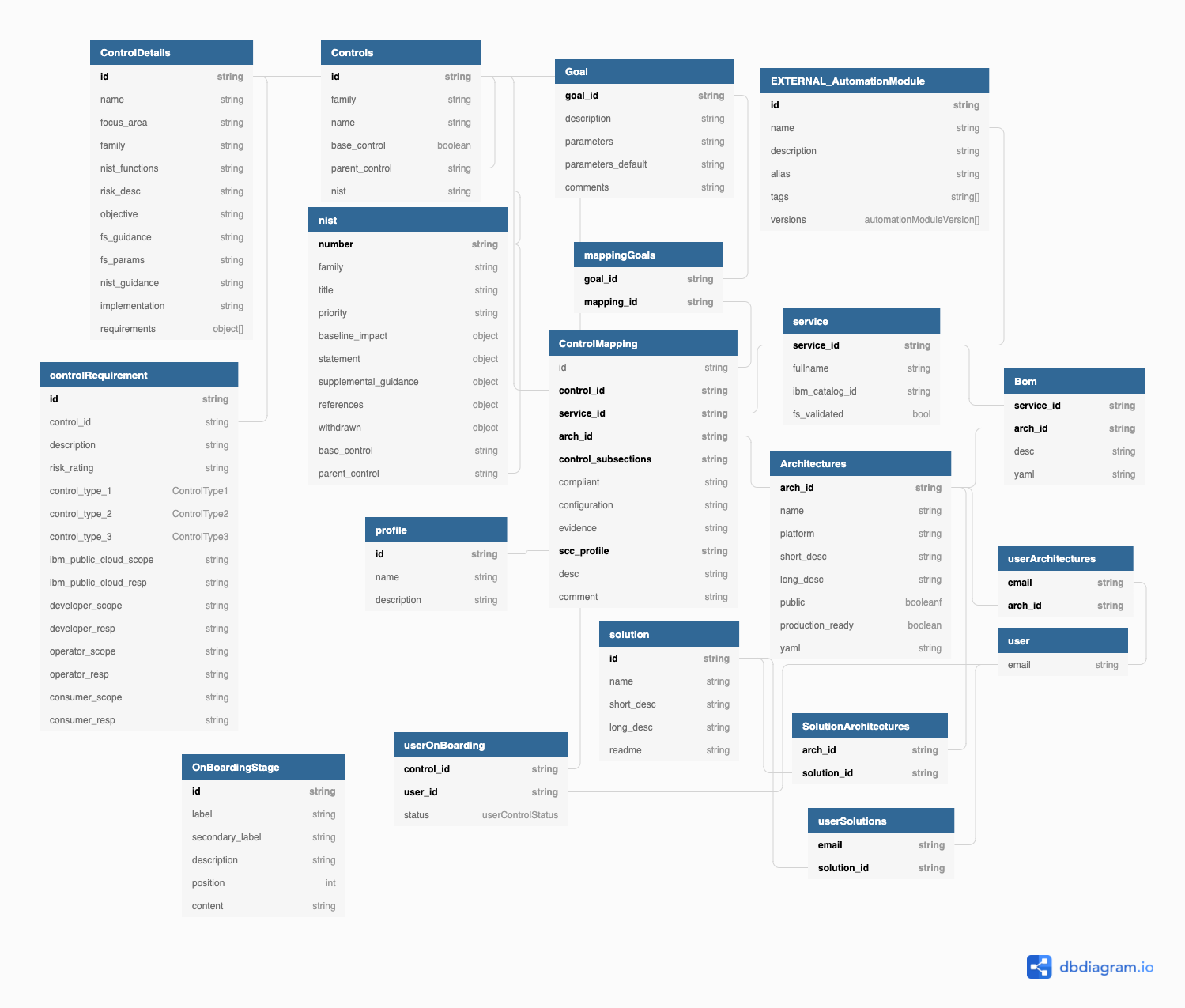
The following diagram describes our database model in details:
To help speed up the data loading a simple ingestion model has been created. The core
data entities are created in Excel spreadsheets. The first row of the entity holds
the column name or JSON attribute name. To ingest data save the entity in csv file
format. into the data/source folder. To then convert the into JSON format
install the following package`
Install the csvtojson tool npm install csvtojson -g
Then run the script ./convert.sh this will export the csv files into json files
From the data folder download the MongoDB certificate into export DBCERT=~/projects/certs/cloud-mongodb.pem
From the MongoDB services instance screen in IBM Cloud take the composed value and configure
the URI environment variable export URI="mongodb://ibm_cloud_4...
For the test database you want to do the same thing with the URI_TEST environment variable export URI_TEST="mongodb://ibm_cloud_4...
You can then run ./mload-cloud { $URI | $URI_TEST } to configure the MongoDB collection with the initial data to
feed the API.
Setup the following environment variables before you can run the application.
To run this locally you need to take the mongo binding value that is registered as a secret in the OpenShift environment or from the Service Credentials section of a managed MongoDB instance. Take the binding value and configure it as a environment value.
A script has been provided to simplify this process. The steps to run the script are as follows:
- Log into the IBM Cloud account using the ibmcloud cli, for example running:
❯ ibmcloud login --apikey <APIKEY>
- Find the names of the MongoDB and Object Storage instances:
❯ ibmcloud resource service-instances
- Source the setup-environment script to create the environment variables, passing the names of the services:
❯ export MONGO_NAME="MONGO_NAME" # e.g. builder-mongodb ❯ export COS_NAME="COS_NAME" # e.g. dev-mapper-storage ❯ export APPID_NAME="APPID_NAME" # e.g. dev-mapper ❯ export INSTANCE_ID="INSTANCE_ID" ❯ source ./scripts/setup-environment.sh $MONGO_NAME $COS_NAME $APPID_NAME
- Verify the environment variables have been created by running the following:
❯ echo $DATABASE_DEV ❯ echo $STORAGE ❯ echo $APPID_OAUTH_SERVER_URL
- Once these values are set it is now possible to run the application:
❯ yarn install ❯ yarn start:dev
- Install Cloud-Native Toolkit.
- Create projects on your cluster
❯ oc login ... ❯ oc new-project ascent-dev ❯ oc new-project ascent-test ❯ oc new-project ascent-staging ❯ oc project ascent-dev
- Bind your IBM Cloud Object Storage service to your namespaces:
❯ icc <your-cluster> # Log in to cluster using "icc" or "oc login" command ❯ export CLUSTER_NAME="dev-mapper-ocp" # Name of your IBM Cloud MongoDB service ❯ export COS_SERVICE_NAME="dev-mapper-storage" # Name of your IBM Cloud MongoDB service ❯ ic oc cluster service bind --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME --service $COS_SERVICE_NAME -n ascent-dev # COS ❯ kubectl get secret binding-$COS_SERVICE_NAME -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed "s/binding-${COS_SERVICE_NAME}/ascent-cos-config/g" | oc create -f - # Rename COS secret ❯ oc get secret ascent-cos-config -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed 's/ascent-dev/ascent-test/g' | oc create -f - # Copy COS secret to ascent-test namespace ❯ oc get secret ascent-cos-config -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed 's/ascent-dev/ascent-staging/g' | oc create -f - # Copy COS secret to ascent-staging namespace
Follow either of the steps below depending on the type of MongoDB service you are going to use.
- Bind your Databases for MongoDB services to your namespaces:
❯ icc <your-cluster> # Log in to cluster using "icc" or "oc login" command ❯ export CLUSTER_NAME="dev-mapper-ocp" # Name of your IBM Cloud MongoDB service ❯ export MONGO_SERVICE_NAME="builder-mongodb" # Name of your IBM Cloud MongoDB service ❯ ic oc cluster service bind --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME --service $MONGO_SERVICE_NAME -n ascent-dev # MongoDB ❯ oc get secret binding-$MONGO_SERVICE_NAME -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed "s/binding-${MONGO_SERVICE_NAME}/ascent-mongo-config/g" | oc create -f - # Rename Mongo secret ❯ oc get secret ascent-mongo-config -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed 's/ascent-dev/ascent-test/g' | oc create -f - # Copy Mongo secret to ascent-test namespace ❯ oc get secret ascent-mongo-config -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed 's/ascent-dev/ascent-staging/g' | oc create -f - # Copy Mongo secret to ascent-staging namespace
- Provision a self-managed DB using Helm Chart (Note: Repeat for
ascent-dev,ascent-testandascent-stagingnamespaces):- Get the chart values:
❯ helm show values stable/mongodb > mongo.values.yaml - Update the following values in
mongo.values.yaml:... ommited ... mongodbUsername: ascent-admin mongodbPassword: <YOUR_PASSWORD> mongodbDatabase: ascent-db ... ommited ... securityContext: enabled: false ... ommited ...
- Install the chart:
❯ helm install ascent-mongodb stable/mongodb --values mongo.values.yaml
- Create the
ascent-mongo-configconnection secret:❯ export MONGODB_PASSWORD=<YOUR_PASSWORD> ❯ oc create secret generic ascent-mongo-config --from-literal=binding="{\"connection\":{\"mongodb\":{\"composed\":[\"mongodb://ascent-admin:${MONGODB_PASSWORD}@ascent-mongodb:27017/ascent-db\"],\"authentication\":{\"username\":\"ascent-admin\",\"password\":\"${MONGODB_PASSWORD}\"},\"database\":\"ascent-db\",\"hosts\":[{\"hostname\":\"localhost\",\"port\":27017}]}}}"
- Get the chart values:
Follow either of the steps below depending on the authentication provider you want to use.
- Bind your IBM Cloud services (MongoDB, AppId, and COS) to your namespaces:
❯ icc <your-cluster> # Log in to cluster using ICC ❯ export APPID_SERVICE_NAME="dev-mapper" # Name of your IBM Cloud App ID service ❯ ic oc cluster service bind --cluster $CLUSTER_NAME --service $APPID_SERVICE_NAME -n ascent-dev # AppID ❯ oc get secret binding-$APPID_SERVICE_NAME -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed "s/binding-${APPID_SERVICE_NAME}/ascent-appid-config/g" | oc create -f - # Rename AppID secret
- Update the AppID secret to add a new
binding-applicationkey for UI to use and retrieve user roles.- Copy the application credentials of your AppId service on IBM Cloud
- Go to your resource list.
- Select your AppId service.
- In the Applications section, copy your app credentials. If none:
- Create one with following scopes:
edit,super_edit. - Create Roles
adminwith scopes:read,edit,super_edit
- Assign Roles
- Create one with following scopes:
- In the
ascent-devproject, update the AppId secrets to add the newbinding-applicationkey with the value you just copied:- In the Workloads > Secrets section, select the
ascent-appid-configsecret. - On the top right, click Edit Secret.
- Scroll down to the bottom and add the new
binding-applicationkey. - Copy the value you copied earlier, replace
oAuthServerUrlwithoauthServerUrl, then click Save. - Copy the secret in the
ascent-testandascent-stagingprojects:
❯ oc get secret ascent-appid-config -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed 's/ascent-dev/ascent-test/g' | oc create -f - # Copy AppID secret to ascent-test namespace ❯ oc get secret ascent-appid-config-n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed 's/ascent-dev/ascent-staging/g' | oc create -f - # Copy AppID secret to ascent-test namespace
- In the Workloads > Secrets section, select the
- Copy the application credentials of your AppId service on IBM Cloud
- Create OpenShift
OAuthClientfor Ascent:Note: You'll have to add valid> cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: oauth.openshift.io/v1 grantMethod: auto kind: OAuthClient metadata: name: ascent selfLink: /apis/oauth.openshift.io/v1/oauthclients/ascent redirectURIs: - http://localhost:3000/login/callback secret: <YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET> EOF
redirectURIsin the later steps. - Create the
ascent-oauth-configsecret with the config of the client you've just created:❯ export OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET="<YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>" ❯ oc create secret generic ascent-oauth-config --from-literal=api-url=$(oc whoami --show-server) --from-literal=oauth-config="{\"clientID\": \"ascent\", \"clientSecret\": \"${OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET}\", \"api_endpoint\": \"$(oc whoami --show-server)\"}" -n ascent-dev ❯ oc get secret ascent-oauth-config -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed 's/ascent-dev/ascent-test/g' | oc create -f - # Copy OAuth secret to ascent-test namespace ❯ oc get secret ascent-oauth-config -n ascent-dev -o yaml | sed 's/ascent-dev/ascent-staging/g' | oc create -f - # Copy OAuth secret to ascent-staging namespace
- Create a configmap in each project for the ui:
❯ oc create configmap ascent --from-literal=route=https://ascent-dev.openfn.co --from-literal=api-host=todo --from-literal=instance-id=$(date +%s | sha256sum | head -c 16 ; echo) -n ascent-dev ❯ oc create configmap ascent --from-literal=route=https://ascent-test.openfn.co --from-literal=api-host=todo --from-literal=instance-id=$(date +%s | sha256sum | head -c 16 ; echo) -n ascent-test ❯ oc create configmap ascent --from-literal=route=https://ascent.openfn.co --from-literal=api-host=todo --from-literal=instance-id=$(date +%s | sha256sum | head -c 16 ; echo) -n ascent-staging
- Note: We'll update the
api-hostvalue once we've deployed the BFF APIs.
- Note: We'll update the
- Create the pipeline for the BFF
- Update the
ascent-mongo-configsecret inascent-devnamespace to add a newbinding-testkey with the same content as thebindingkey, in which you replace everyibmclouddbto your test database (mine isibmcloudtestdb). - In OpenShift console, update the
teststep of theibm-nodejs-test-v2-6-13tekton task intoolsproject, to add the variables BFF needs to run testing:... omitted ... - env: - name: DATABASE_TEST valueFrom: secretKeyRef: key: binding-test name: ascent-mongo-config - name: STORAGE valueFrom: secretKeyRef: key: binding name: ascent-cos-config image: $(params.js-image) name: test resources: {} script: | CI=true npm test workingDir: $(params.source-dir) ... omitted ...
- Create the
docker-iosecret to pullredisimage without encountering docker limit
❯ docker login ❯ kubectl create secret generic docker-io --from-file=.dockerconfigjson=$HOME/.docker/config.json --type=kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson -n ascent-dev- Create the BFF pipeline:
❯ oc sync ascent-dev --dev ❯ oc pipeline --tekton -u ${GIT_USERNAME} -P ${GIT_ACCESS_TOKEN} -g -n ascent-dev ❯ oc secret link pipeline docker-io --for=pull
- Once the pipeline is successful, create the UI pipeline:
❯ oc create configmap ascent \ --from-literal=route=https://ascent-dev.openfn.co \ --from-literal=api-host=https://$(oc get routes/architecture-builder-bff -n ascent-dev -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}') \ --from-literal=instance-id=$(date +%s | sha256sum | head -c 16 ; echo) -n ascent-dev ❯ cd path/to/architecture-builder-ui ❯ oc pipeline --tekton -n ascent-dev
- Set up ArgoCD:
- Create a new blank gitops repo, refered here as
https://github.ibm.com/gsi-labs/architecture-builder-gitops) - Set up gitops:
❯ git clone https://github.com/IBM/template-argocd-gitops architecture-builder-gitops ❯ cd architecture-builder-gitops ❯ git remote remove origin ❯ git remote add origin https://github.ibm.com/gsi-labs/architecture-builder-gitops ❯ git push -u origin main ❯ git checkout -b test ❯ cp -r templates/project-config-helm architecture-builder-bff ❯ cp -r templates/project-config-helm architecture-builder-ui ❯ git add . ❯ git commit -m "Added helm template" ❯ git push -u origin test ❯ igc namespace ascent-test ❯ oc policy add-role-to-group system:image-puller system:serviceaccounts:ascent-test -n ascent-dev ❯ git checkout -b staging ❯ git push -u origin staging ❯ igc namespace ascent-staging ❯ oc policy add-role-to-group system:image-puller system:serviceaccounts:ascent-staging -n ascent-dev ❯ oc project ascent-dev ❯ git checkout test ❯ igc gitops
- On ArgoCD:
- Connect gitops repository
- Create a new project
architecture-builder:- With gitops repo as source repo
- With 2 destinations
ascent-testandascent-stagingin current cluster
- Create 4 applications under
architecture-builderproject:test-architecture-builder-bff:- Sync policy: Automatic
- Source: gitops repo,
testrevision,architecture-builder-bffpath - Destination: local cluster,
ascent-testproject - Click Create
staging-architecture-builder-bff:- Sync policy: Automatic
- Source: gitops repo,
stagingrevision,architecture-builder-bffpath - Destination: local cluster,
ascent-stagingproject - Click Create
test-architecture-builder-ui:- Sync policy: Automatic
- Source: gitops repo,
testrevision,architecture-builder-uipath - Destination: local cluster,
ascent-testproject - Click Create
staging-architecture-builder-ui:- Sync policy: Automatic
- Source: gitops repo,
stagingrevision,architecture-builder-uipath - Destination: local cluster,
ascent-stagingproject - Click Create
- Run the BFF and UI pipelines.
- Create a new blank gitops repo, refered here as
- In AppId service dashboard (or in
ascentOAuthClient if you're using OpenShift auth), add theuiroute as valid callback uri. To get it you can copy the output from:❯ echo "https://$(oc get route architecture-builder-ui -n ascent-test -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}')/login/callback"
- Update the
ascentconfig map inascent-testproject:❯ export API_HOST=https://$(oc get route architecture-builder-bff -n ascent-test -o jsonpath="{.spec.host}") \ && export APP_URI=https://$(oc get route architecture-builder-ui -n ascent-test -o jsonpath="{.spec.host}") \ && oc patch cm ascent -n ascent-test --type='json' -p="[{'op' : 'replace' ,'path' : '/data/api-host' ,'value' : $API_HOST}]" \ && oc patch cm ascent -n ascent-test --type='json' -p="[{'op' : 'replace' ,'path' : '/data/route' ,'value' : $APP_URI}]"
- Once you've tested the app works on test env, submit a PR to
stagingbranch of gitops repo fromtest. - In AppId service dashboard (or in
ascentOAuthClient if you're using OpenShift auth), add theuiroute to appid valid callback uri. To get it you can copy the output from:
❯ echo "https://$(oc get route architecture-builder-ui -n ascent-staging -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}')/login/callback"
- Update the
ascentconfig map inascent-stagingproject:
❯ export API_HOST=https://$(oc get route architecture-builder-bff -n ascent-staging -o jsonpath="{.spec.host}") \ && export APP_URI=https://$(oc get route architecture-builder-ui -n ascent-staging -o jsonpath="{.spec.host}") \ && oc patch cm ascent -n ascent-staging --type='json' -p="[{'op' : 'replace' ,'path' : '/data/api-host' ,'value' : $API_HOST}]" \ && oc patch cm ascent -n ascent-staging --type='json' -p="[{'op' : 'replace' ,'path' : '/data/route' ,'value' : $APP_URI}]"
- Update the
There you go, you should have your delivery pipeline up and running!
Known issues:
- ArgoCD application controller might not be able to create resource in
ascent-testandascent-stagingprojects. If so the following should fix the issue:❯ oc policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccounts:tools:argocd-argocd-application-controller -n ascent-test ❯ oc policy add-role-to-user edit system:serviceaccounts:tools:argocd-argocd-application-controller -n ascent-staging
- Access to IBM Cloud image registry from
ascent-testandascent-staging:❯ oc get secret all-icr-io -n default -o yaml | sed 's/default/ascent-test/g' | oc create -n ascent-test -f - ❯ oc get secret all-icr-io -n default -o yaml | sed 's/default/ascent-staging/g' | oc create -n ascent-staging -f - ❯ oc secret link default all-icr-io --for=pull -n ascent-test ❯ oc secret link default all-icr-io --for=pull -n ascent-staging
To incrementally build the project:
yarn run buildTo force a full build by cleaning up cached artifacts:
yarn run rebuildyarn run lintTo automatically fix such issues:
yarn run lint:fixexport DATABASE_TEST="{connection....}"
yarn testbrew install redis
brew services start redis
redis-cli
SET "Key" "value"
GET Key
brew services stop redisPlease check out LoopBack 4 documentation to understand how you can continue to add features to this application.
-@2x.png?raw=true)