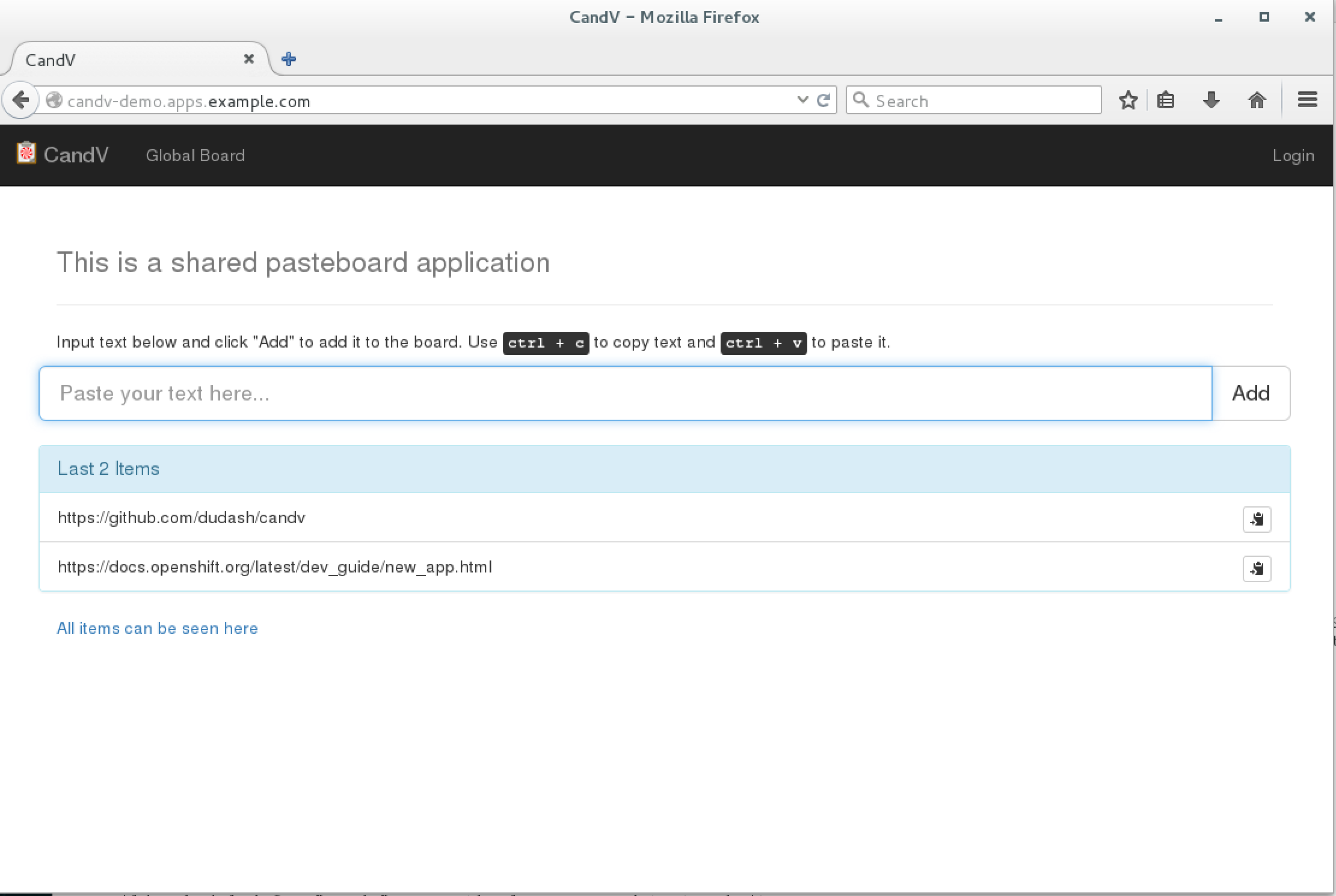
A simple copy and paste (ctrl+c, ctrl+v) application and database that is configured for Red Hat's OpenShift.
This app is configured to be deployed and managed via OpenShift. Which means all you'll need to do is: point Open Shift to the source code, tell it you want a mongo database, and then set any variables you want to customize for your environment.
Here's how from the Open Shift command line tool:
oc new-project candvdemo
oc new-app https://github.com/dudash/candv
oc process openshift//mongodb-ephemeral | oc create -f -
oc expose service candv
(Note that using this method you will also have to create ENV vars in the app to allow for the MongoDB connection - see the deployment config of mongodb for the variables)
There is also template for this to be an Instant app for OpenShift. It contains the definitions of resources and configuration parameters that OpenShift can use to create everything you need to run. This makes things even more automated. Try this by typing this into the command line (after logging into an OpenShift server):
oc new-app -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dudash/candv/master/oc_templates/candv-instantapp-template.json
Or if you are an Open Shift administrator you can install the template for users to create with the web console.
Click here if you want to read about making your own instant apps for OpenShift.
What is now running and being managed by OpenShift looks like the diagram below.
- TBD Conceptual Arch - webapp node.js serverside, webapp client side java script, database
- TBD Deployment Arch - openshift containers, pods, services, routes
oc new-app is creating a bunch of configuration metadata for the app. Then the app is getting built into a container image with a tool called Source 2 Image (s2i). You can read about S2I here. And even more here. The container then gets pushed to a container registry so that it's accessible to all nodes in the cluster. And then an instance of the container is getting deployed (pulled and run) in the cluster. Kubernetes does the orchestrating of container placement in the best fit of your cluster and then keeps watching it to keep it running. A route configuration is allowing external traffic into the container and a service layer is acting as an internal load balancer to get traffic to the correct container.
- Learning OpenShift, try it out here
- OpenShift Container Platform, documentation here
The webapp is mostly obvious in terms of user interaction. Click in the box and paste your data, then press enter or click the 'Add' button to insert into the global clipboard list. You can retrieve previously entered data from the list by clicking the copy icon located to the right of the data. Currently delete is not supported.
The REST interface and corresponding OpenAPI spec is in-progress, so the write-up is TBD.
Currently there are no common problems - if you have some please submit issues. Here are some tips on debugging openshift origin.
Everything is tracked in the github issue tracker.
Please write up bugs with as much detail as possible and include:
- Details on what happened
- How to reproduce it
- Anything unqiue about your deployment environment
Under the terms of the MIT.