- What is Easegress
- Features
- Getting Started
- Use Cases
- Documentation
- Easegress Portal
- Community
- Contributing
- License
Easegress is a Cloud Native traffic orchestration system designed for:
- High Availability: Built-in Raft consensus & leader election provides 99.99% availability.
- Traffic Orchestration: Simple orchestration of various filters for each traffic pipeline.
- High Performance: Lightweight and essential features speed up the performance.
- Observability: There are many meaningful statistics periodically in a readable way.
- Extensibility: It's easy to develop your own filter or controller with high-level programming language.
- Integration: The simple interfaces make it easy to integrate with other systems, such as Kubernetes Ingress, EaseMesh sidecar, Workflow, etc.
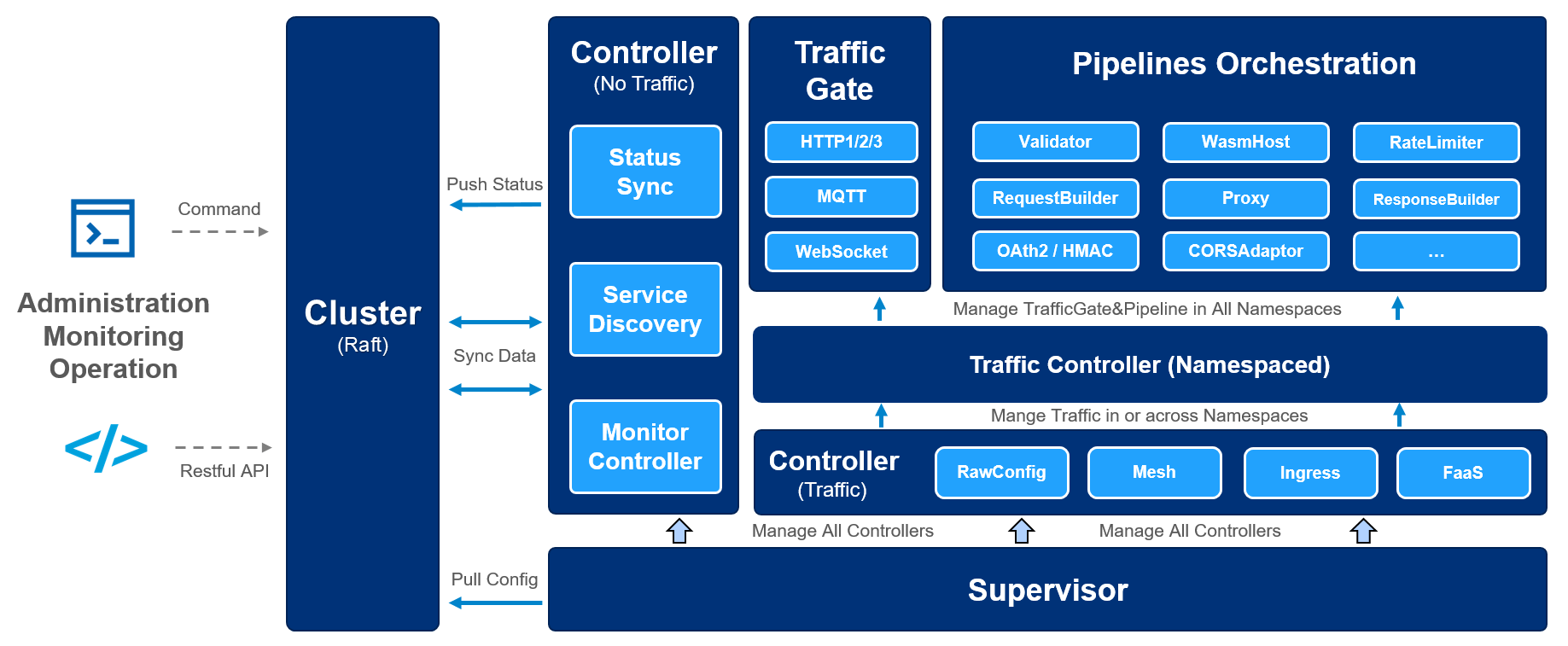
The architecture of Easegress:
- Service Management
- Multiple protocols:
- HTTP/1.1
- HTTP/2
- HTTP/3(QUIC)
- MQTT
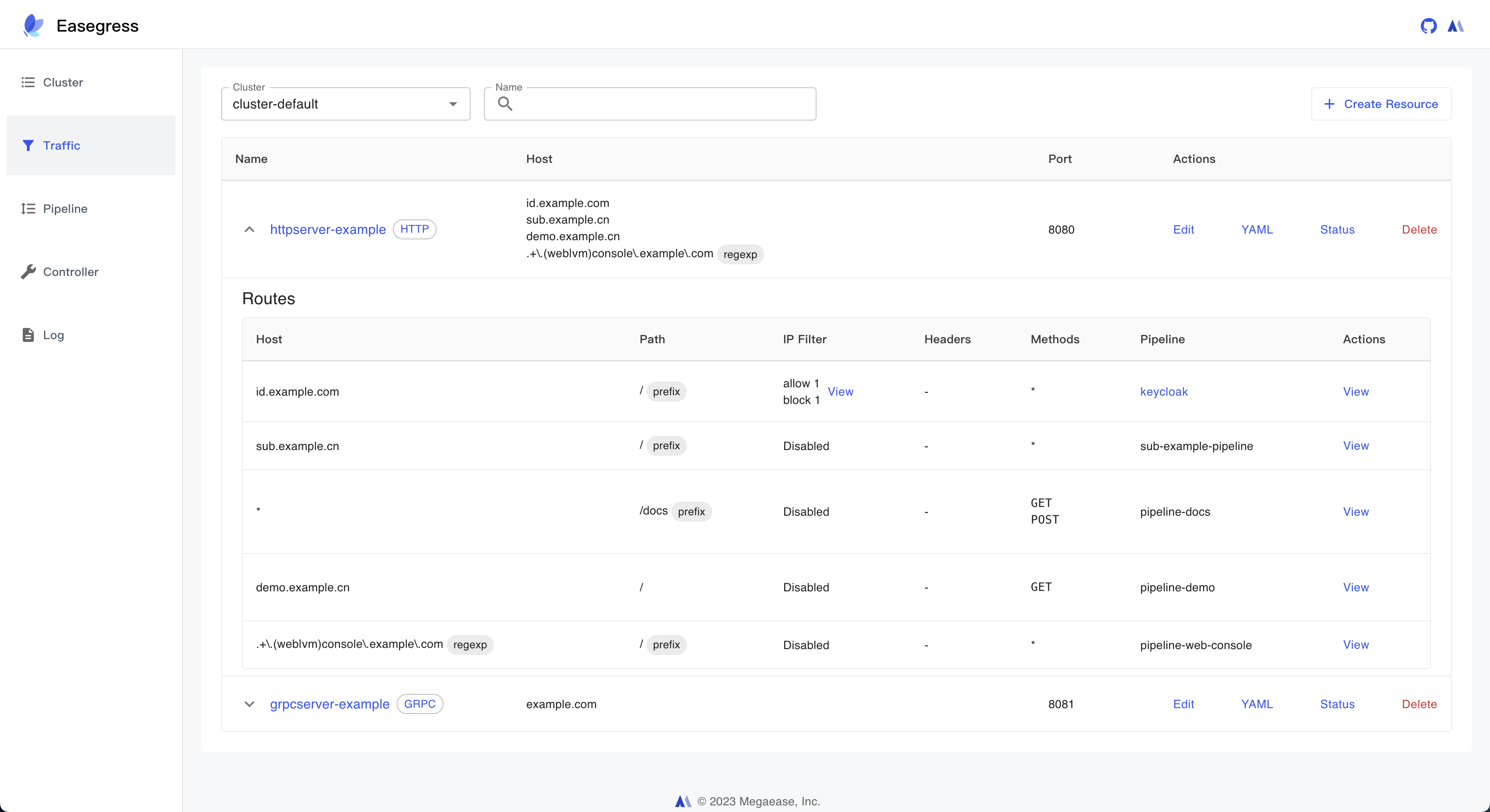
- Rich Routing Rules: exact path, path prefix, regular expression of the path, method, headers, clientIPs.
- Resilience&Fault Tolerance
- CircuitBreaker: temporarily blocks possible failures.
- RateLimiter: limits the rate of incoming requests.
- Retry: repeats failed executions.
- TimeLimiter: limits the duration of execution.
- Deployment Management
- Blue-green Strategy: switches traffic at one time.
- Canary Strategy: schedules traffic slightly.
- API Management
- API Aggregation: aggregates results of multiple APIs.
- API Orchestration: orchestrates the flow of APIs.
- Security
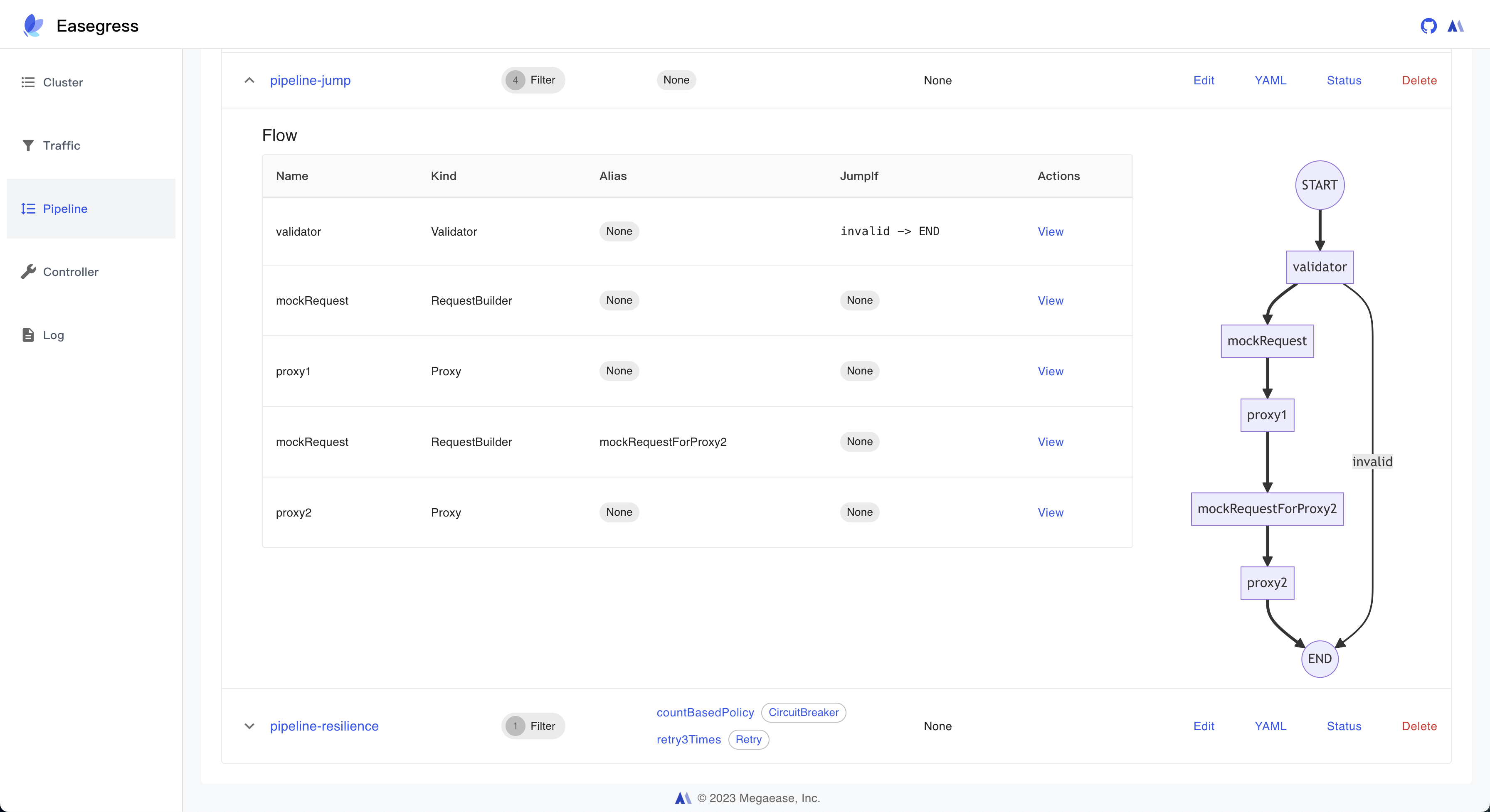
- Pipeline-Filter Mechanism
- Filter Management: makes it easy to develop new filters.
- Service Mesh
- Mesh Master: is the control plane to manage the lifecycle of mesh services.
- Mesh Sidecar: is the data plane as the endpoint to do traffic interception and routing.
- Mesh Ingress Controller: is the mesh-specific ingress controller to route external traffic to mesh services.
Notes: This feature is leveraged by EaseMesh
- Third-Part Integration
- FaaS integrates with the serverless platform Knative.
- Service Discovery integrates with Eureka, Consul, Etcd, and Zookeeper.
- Ingress Controller integrates with Kubernetes as an ingress controller.
- Multiple protocols:
- Extensibility
- WebAssembly executes user developed WebAssembly code.
- High Performance and Availability
- Adaption: adapts request, response in the handling chain.
- Validation: headers validation, OAuth2, JWT, and HMAC verification.
- Load Balance: round-robin, random, weighted random, IP hash, header hash and support sticky sessions.
- Cache: for the backend servers.
- Compression: compresses body for the response.
- Hot-Update: updates both config and binary of Easegress in place without losing connections.
- Operation
- Easy to Integrate: command line(egctl), MegaEase Portal, HTTP clients such as curl, postman, etc.
- Distributed Tracing
- Built-in OpenTelemetry, which provides a vendor-neutral API.
- Observability
- Node: role(primary, secondary), raft leader status, healthy or not, last heartbeat time, and so on
- Traffic: in multi-dimension: server and backend.
- Throughput: total and error statistics of request count, TPS/m1, m5, m15, and error percent, etc.
- Latency: p25, p50, p75, p95, p98, p99, p999.
- Data Size: request and response size.
- Status Codes: HTTP status codes.
- TopN: sorted by aggregated APIs(only in server dimension).
The basic usage of Easegress is to quickly set up a proxy for the backend servers.
Easegress can be installed from pre-built binaries or from source. For details, see Install.
Then we can execute the server:
$ easegress-server
2023-09-06T15:12:49.256+08:00 INFO cluster/config.go:110 config: advertise-client-urls: ...
...By default, Easegress opens ports 2379, 2380, and 2381; however, you can modify these settings along with other arguments either in the configuration file or via command-line arguments. For a complete list of arguments, please refer to the easegress-server --help command.
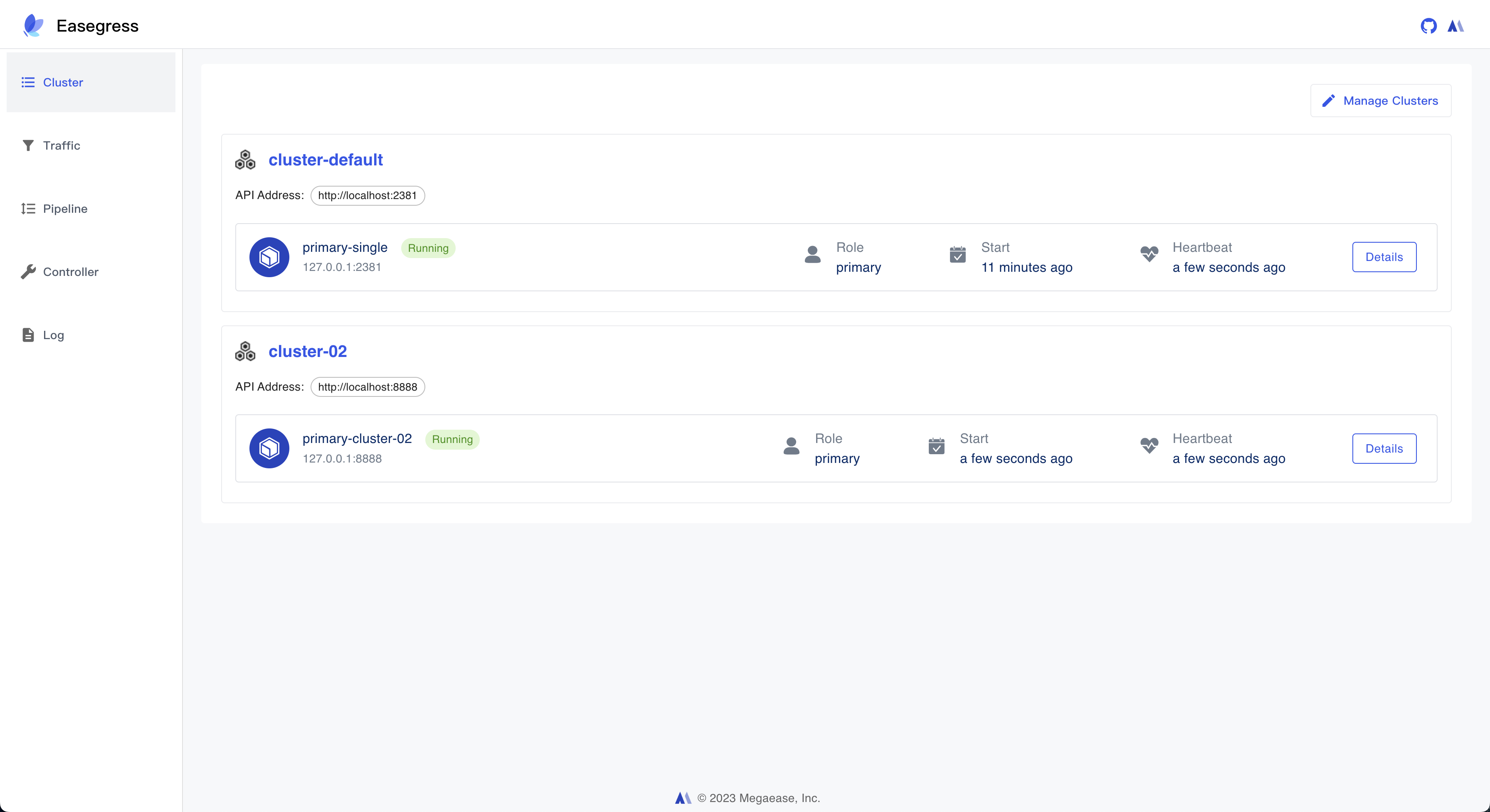
After launching successfully, we could check the status of the one-node cluster.
$ egctl get member
...
$ egctl describe member
...Assuming you have two backend HTTP services running at 127.0.0.1:9095 and 127.0.0.1:9096, you can initiate an HTTP proxy from port 10080 to these backends using the following command:
$ egctl create httpproxy demo --port 10080 \
--rule="/pipeline=http://127.0.0.1:9095,http://127.0.0.1:9096"Then try it:
$ curl -v 127.0.0.1:10080/pipelineThe request will be forwarded to either 127.0.0.1:9095/pipeline or 127.0.0.1:9096/pipeline, utilizing a round-robin load-balancing policy.
More about getting started with Easegress:
The following examples show how to use Easegress for different scenarios.
- API Aggregation - Aggregating many APIs into a single API.
- Cluster Deployment - How to deploy multiple Easegress cluster nodes.
- Canary Release - How to do canary release with Easegress.
- Distributed Tracing - How to do APM tracing - Zipkin.
- FaaS - Supporting Knative FaaS integration
- Flash Sale - How to do high concurrent promotion sales with Easegress
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller - How to integrate with Kubernetes as ingress controller
- LoadBalancer - A number of the strategies of load balancing
- MQTTProxy - An Example to MQTT proxy with Kafka backend.
- Multiple API Orchestration - An Telegram translation bot.
- Performance - Performance optimization - compression, caching etc.
- Pipeline - How to orchestrate HTTP filters for requests/responses handling
- Resilience and Fault Tolerance - CircuitBreaker, RateLimiter, Retry, TimeLimiter, etc. (Porting from Java resilience4j)
- Security - How to do authentication by Header, JWT, HMAC, OAuth2, etc.
- Service Registry - Supporting the Microservice registries - Zookeeper, Eureka, Consul, Nacos, etc.
- WebAssembly - Using AssemblyScript to extend the Easegress
- WebSocket - WebSocket proxy for Easegress
- Workflow - An Example to make a workflow for a number of APIs.
For full list, see Tutorials and Cookbook.
Easegress Portal is an intuitive, open-source user interface for the Easegress traffic orchestration system. Developed with React.js, this portal provides config management, metrics, and visualizations, enhancing the overall Easegress experience.
1. Cluster Management
2. Traffic Management
3. Pipeline Management
- Join Slack Workspace for requirement, issue and development.
- MegaEase on Twitter
See Contributing guide. The project welcomes contributions and suggestions that abide by the CNCF Code of Conduct.
Easegress is under the Apache 2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details.