cronitor-airflow
Cronitor integration for Airflow
Setting up the Cronitor Airflow provider
Installation
Install the package using pip:
pip install apache-airflow-providers-cronitorCreate a connection
Then, you need to create an Airflow "Connection" to store your Cronitor API key. There are a number of ways you can do this, including storing the connection information using a Secrets Backend.
The simplest way to quickly create the connection is to use the Airflow UI:
Once you've selected "Connections", click "add a new record":
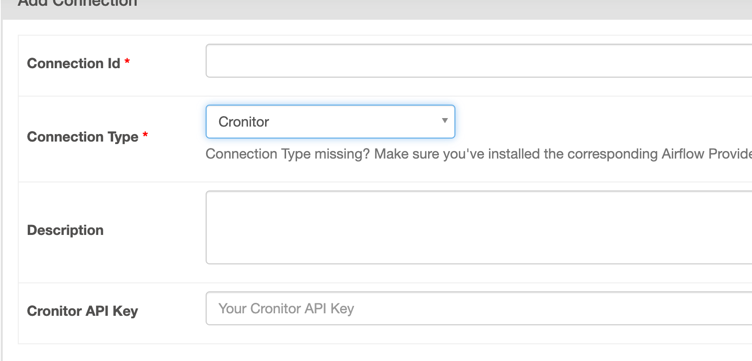
You will then see the "Add Connection" form. Select "Cronitor" as the connection type. It should be available as long as you have properly installed apache-airflow-providers-cronitor in your Airflow environment.
The best name for the connection is cronitor_default, following the default connection names for Airflow. This is the default Cronitor connection name used by the hook and operator. Finally, add your API key, and save.
Usage
Use the Operator directly
With that, you are ready to use the operator. Using the operator directly is simple. To import the operator:
from cronitor_airflow.operators.cronitor_operator import CronitorOperatorFor a full example of how to use the operator, take a look at this sample DAG provided.
Usage Notes
- When using the operator,
monitor_keymust be the key of your Cronitor monitor. You cannot use the monitor's display name.
Autoprovision monitors
The Cronitor Airflow integration can automatically watch your Airflow instances for active DAGs and create monitors in Cronitor that correspond to those DAGs. This is done via a specialized DAG that we've pre-written for you.
To use it, all you have to do is import and initialize the DAG in any Python file in the folder you are using to store your Airflow DAGs. (This is set by the dags_folder setting in airflow.cfg.)
from cronitor_airflow.example_dags.cronitor_autodiscover import autoprovision_monitors
# Defaults to the connection `cronitor_default`.
dag_1 = autoprovision_monitors()
# To specify a custom connection name:
dag_2 = autoprovision_monitors(cronitor_conn_id='cronitor_connection_2')Airflow will load the DAG on the next DagBag refresh. Make sure you turn on the DAG in the Airflow UI once it is loaded so that it can start running.
Usage Notes
- Currently, autodiscover will only provision and update monitors for DAGs that are in the DagBag and turned on.
- Autodiscover does not currently support complex timetables. Any timetable that cannot be generalized to a cron schedule will be ignored, and noted as such in the logs.