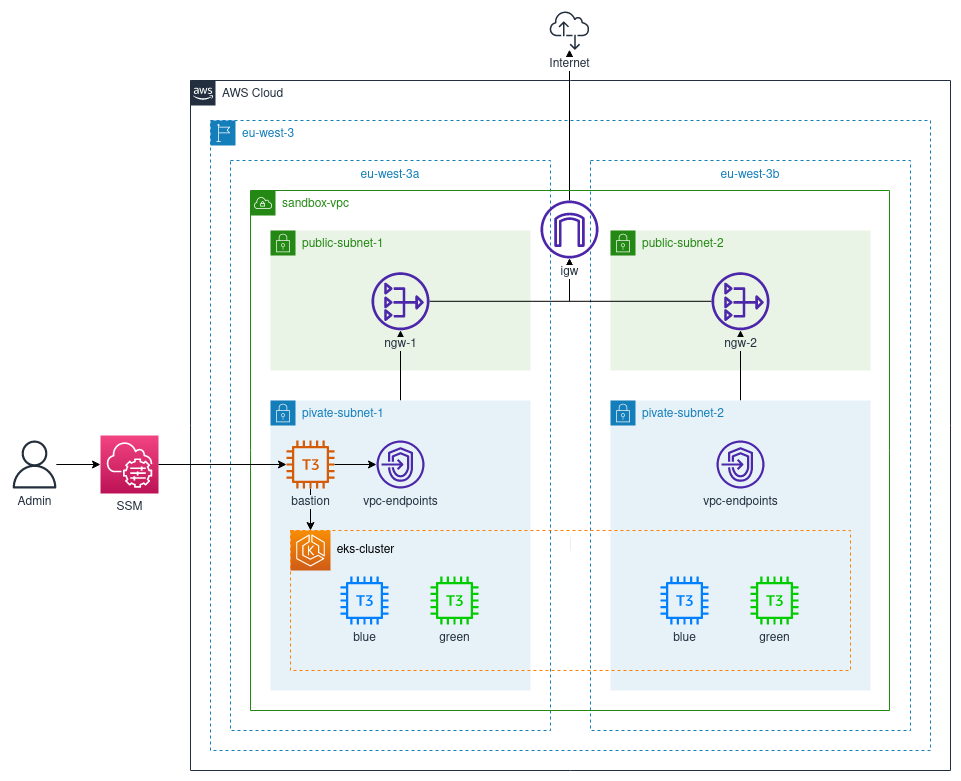
Crossplane configuration files and tools to deploy a private EKS cluster accessible through a SSM bastion instance.
- Region : eu-west-3
- VPC with a public/private subnet per AZ (a & b)
- Internet/NAT gateways and route tables giving internet access to the private subnet
- VPC endpoints in the private subnets for SSM
- Compute : an EC2 bastion instance and an EKS cluster with blue/green node groups
- IAM and security groups
- Root access on an AWS account
- Access to a Kubernetes cluster and a crossplane deployment configured with AWS on the master branch
- AWS CLI with the Session Manager plugin,
jq,helm,kubectland sshuttle installed on your machine
Crossplane
Deploy the Crossplane Helm chart :
helm repo add crossplane-stable https://charts.crossplane.io/stable
helm install crossplane crossplane-stable/crossplane -n crossplane-system --create-namespace=true --set 'provider.packages[0]=crossplane/provider-aws:master'
AWS
With the root account in the console :
-
Create an IAM user with console access and access keys with the AdministratorAccess policy attached
- Add this to your
~/.aws/credentialsfile :
[default] aws_access_key_id = <your_access_keys> aws_secret_access_key = <your_secret_keys> role_arn = arn:aws:iam::<your_account_id>:role/administrator source_profile = default - Add this to your
-
Create a
crossplaneIAM user with no attached policy and access keys -
Create an
administratorIAM role with the AdministratorAccess policy attached and a trust relationship allowing the two user above to assume the role
Why do we do this?
When creating an EKS cluster, AWS creates a Configmap named aws-auth which maps IAM identities to Kubernetes users and groups. If Crossplane creates the cluster only using its user credentials, it will be the only one able to access it.
The trick is if you set the provider's credentials to assume an IAM role that your personal user and Crossplane's user can assume, it will be the one added to the aws-auth Configmap, thus granting you access to the cluster from the get go.
Resources to create manually
Create these resources manually (no crossplane support yet) :
- SSH key pair (create, save and set secure permissions) :
aws ec2 create-key-pair --key-name bastion | jq -r .KeyMaterial > ~/.ssh/bastion.pem
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/bastion.pem- IAM instance profile
aws iam create-instance-profile --instance-profile-name ec2-ssm-ip- Fill the manifests in the config directory with the needed infos
- Apply the config manifests
- Apply the whole resources directory
- Link the created
ec2-ssm-roleIAM role to theec2-ssm-ipIAM instance profileaws iam add-role-to-instance-profile --instance-profile-name ec2-ssm-ip --role-name ec2-ssm-role
Add the cluster's credentials to your kubeconfig :
aws eks update-kubeconfig --cluster eks-clusterUse the tunnel script to connect to the bastion (will need sudo for sshuttle) :
# You can specify the bastion name and cluster name as args 1 and 2 of this script if you changed them
./tools/tunnel_eks.sh
Open a new terminal and you should be able to kubectl into the created EKS cluster !
If something goes wrong, check the events visible in the description of the resources, the error messages are understandable.
To destroy all the resources, just delete everything from the management cluster.
Delete the resources created with the CLI (the instance profile in particular will block you from destroying everything)
# SSH key
aws ec2 delete-key-pair --key-name bastion
# Instance profile
aws iam remove-role-from-instance-profile --instance-profile-name ec2-ssm-ip --role-name ec2-ssm-role
aws iam delete-instance-profile --instance-profile-name ec2-ssm-ip