Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed machine learning service. With SageMaker, data scientists and developers can quickly and easily build and train machine learning models, and then directly deploy them into a production-ready hosted environment.
In this demo, we will showcase how you can leverage SageMaker for managing your training jobs and experiments on AWS, using Amazon SageMaker Python SDK with your local IDE such as Pycharm.
In order to run training jobs on AWS, you will need:
- An AWS account and configured with AWS CLI to have sufficient permission to run SageMaker training jobs
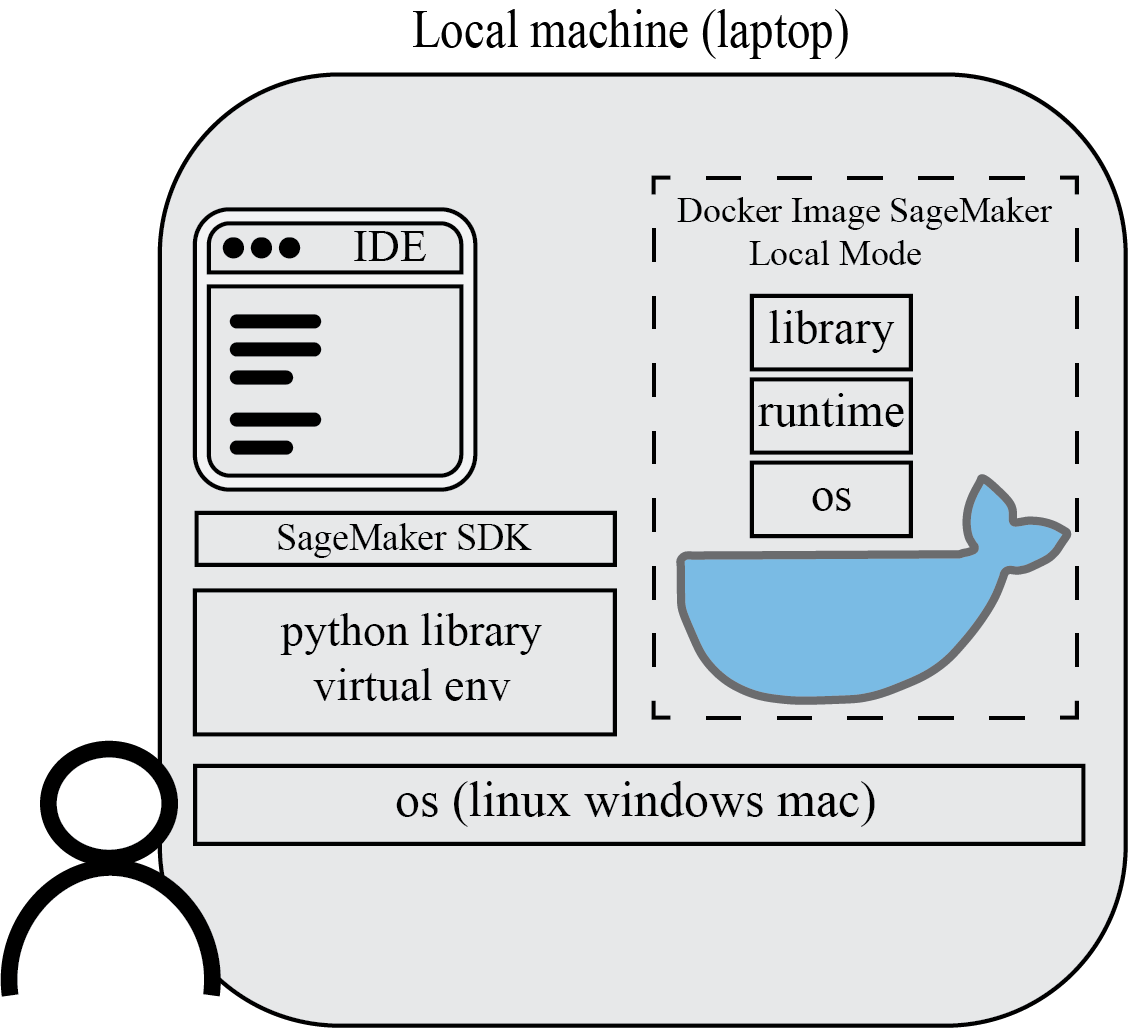
- Docker configured (SageMaker local mode) and Amazon SageMaker Python SDK installed on local computer
- (Optional) SageMaker Studio for experiment tracking and Amazon SageMaker Experiments Python SDK
Setup:
-
Create a new user with programmatic access that enables an access key ID and secret access key for the AWS CLI, attach permissions AmazonSageMakerFullAccess and AmazonS3FullAccess (limit the permissions to specific buckets if possible). You also need an execution role for SageMaker AmazonSageMakerFullAccess and AmazonS3FullAccess. SageMaker uses this execution role to perform operations on your behalf on the AWS hardware that is managed by SageMaker
-
Install AWS CLI on local computer and quick configuration with aws configure, see Configuring the AWS CLI
$ aws configure AWS Access Key ID [None]: AKIAI*********EXAMPLE AWS Secret Access Key [None]: wJal********EXAMPLEKEY Default region name [None]: eu-west-1 Default output format [None]: json -
Install Docker and your favorite local Python IDE. Here we use Pycharm. Make sure that you have all required python libraries to run your code locally. Add SageMaker Python SDK to your local library. You can use pip install sagemaker (or create a virtual environment with venv for your project then install sagemaker within virtual environment). See the documentation
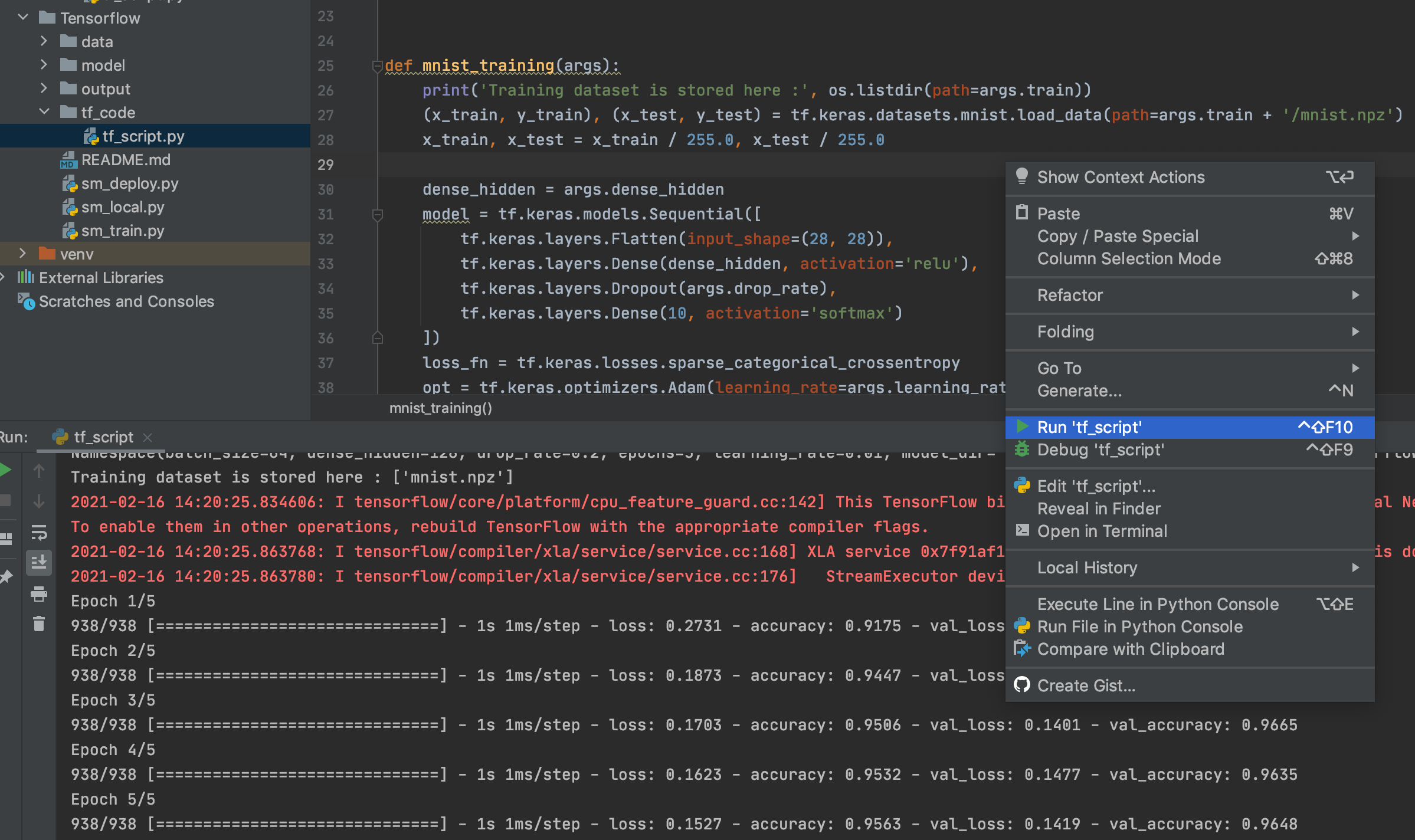
./tf_code/tf_script.py
Many data scientists use local IDE for machine learning algorithm development, such as Pycharm. In this demo, the algorithm python script tf_code/tf_script.py is a simple file that uses TensorFlow keras to create a feedforward neural network. You can run the python script locally as you do usually.
./tf_code/tf_script.py
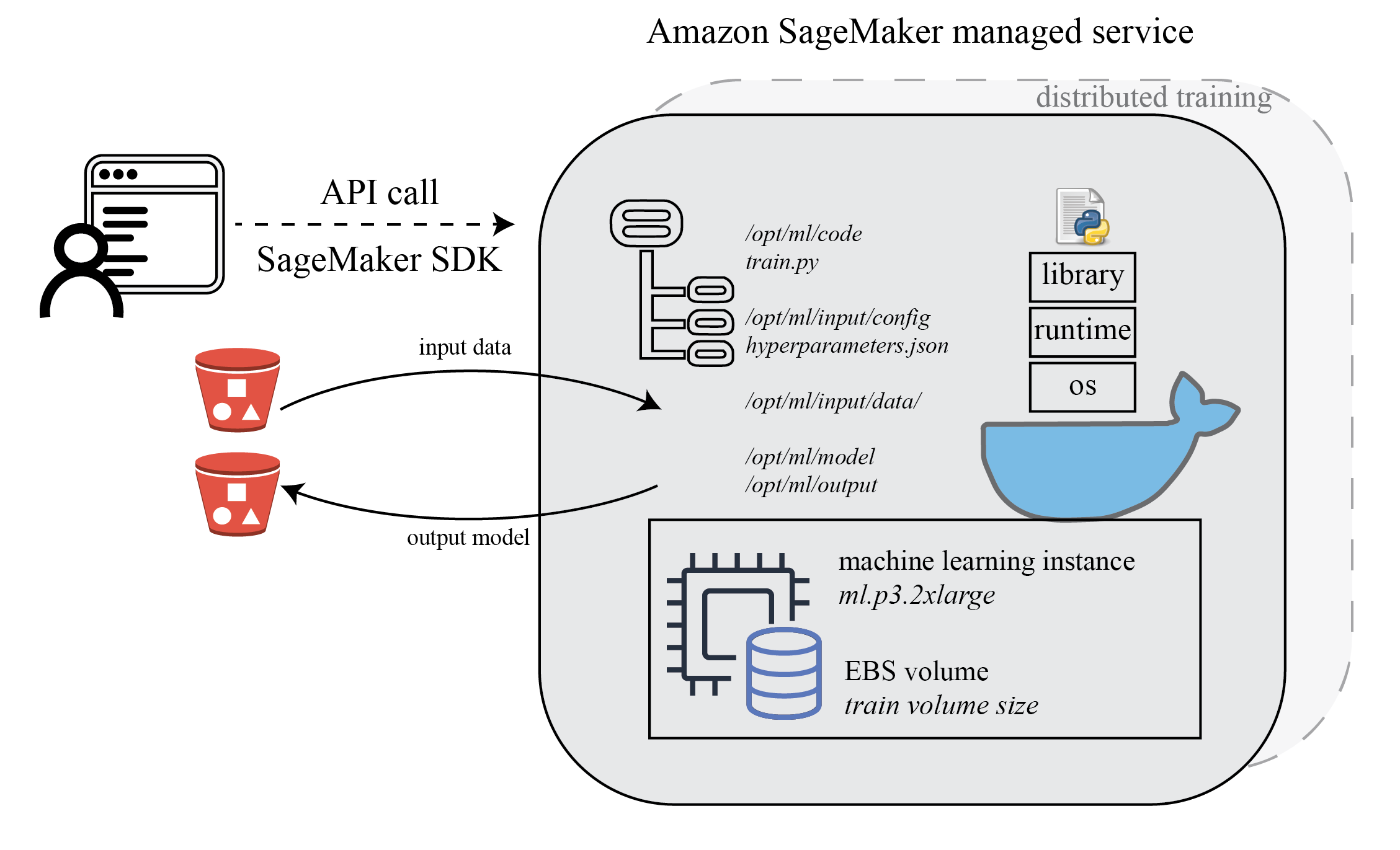
To make your code compatible for SageMaker, you need to follow certain rules for reading input data and writing output model and other artifacts. The training script is very similar to a training script you might run outside of SageMaker, but you can access useful properties about the training environment through various environment variables. See SageMaker Toolkits Containers Structure
Here are some important environment variables used by SageMaker for managing the infrastructure:
Input data location SM_CHANNEL_{channel_name}
SM_CHANNEL_TRAINING=/opt/ml/input/data/training
SM_CHANNEL_VALIDATION=/opt/ml/input/data/validation
SM_CHANNEL_TESTING=/opt/ml/input/data/testing
Model output location to save model artifact
SM_MODEL_DIR=/opt/ml/model
Output artifact location to write non-model training artifacts (e.g. evaluation results)
SM_OUTPUT_DATA_DIR=/opt/ml/output
You can pass these SageMaker environment variable as argument, so that you can still run the training script outside of SageMaker
# SageMaker default SM_MODEL_DIR=/opt/ml/model
if os.getenv("SM_MODEL_DIR") is None:
os.environ["SM_MODEL_DIR"] = os.getcwd() + '/model'
# SageMaker default SM_OUTPUT_DATA_DIR=/opt/ml/output
if os.getenv("SM_OUTPUT_DATA_DIR") is None:
os.environ["SM_OUTPUT_DATA_DIR"] = os.getcwd() + '/output'
# SageMaker default SM_CHANNEL_TRAINING=/opt/ml/input/data/training
if os.getenv("SM_CHANNEL_TRAINING") is None:
os.environ["SM_CHANNEL_TRAINING"] = os.getcwd() + '/data'
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--train', type=str, default=os.environ.get('SM_CHANNEL_TRAINING'))
parser.add_argument('--model_dir', type=str, default=os.environ.get('SM_MODEL_DIR'))
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', type=str, default=os.environ.get('SM_OUTPUT_DATA_DIR'))
./sm_local.py
The SageMaker Python SDK supports local mode, which allows you to create estimators and deploy them to your local environment. This is a great way to test your deep learning scripts before running them in SageMaker’s managed training or hosting environments. Local Mode is supported for frameworks images (TensorFlow, MXNet, Chainer, PyTorch, and Scikit-Learn) and images you supply yourself.
sagemaker_role = 'arn:aws:iam::707684582322:role/RandomRoleNameHere'
sagemaker_session = LocalSession()
sagemaker_session.config = {'local': {'local_code': True}}
def sagemaker_estimator(sagemaker_role, code_entry, code_dir, hyperparameters):
sm_estimator = TensorFlow(entry_point=code_entry,
source_dir=code_dir,
role=sagemaker_role,
instance_type='local',
instance_count=1,
model_dir='/opt/ml/model',
hyperparameters=hyperparameters,
output_path='file://{}/model/'.format(os.getcwd()),
framework_version='2.2',
py_version='py37',
script_mode=True)
return sm_estimator
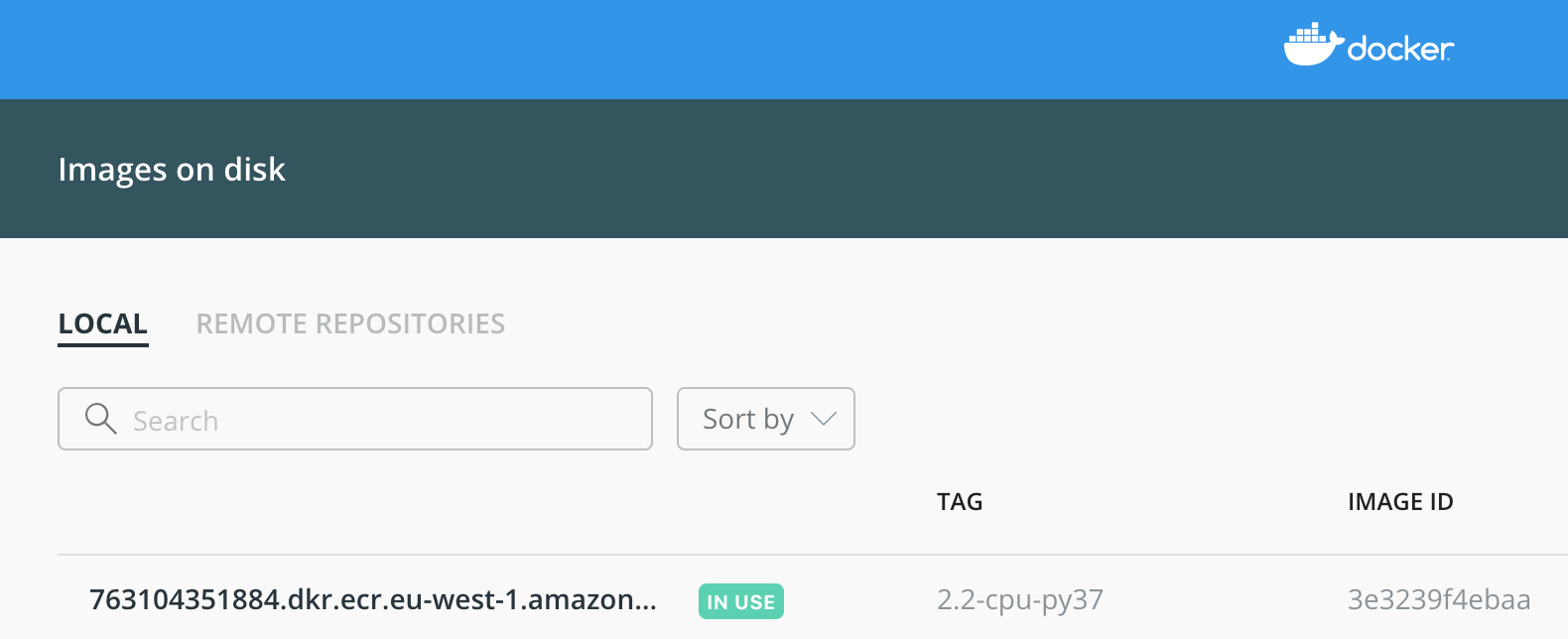
With SageMaker local mode, you will have the managed TensorFlow Image from service account donwloaded into your local compute and show up in Docker. This docker image is the same as in SageMaker’s managed training or hosting environments, so that you can debug your code locally and faster.
You can see the service account tensorflow docker image is now running in your local computer.
./sm_train.py
After you create the training job, SageMaker launches the ML compute instances and uses the training code and the training dataset to train the model. It saves the resulting model artifacts and other output in the S3 bucket you specified for that purpose.
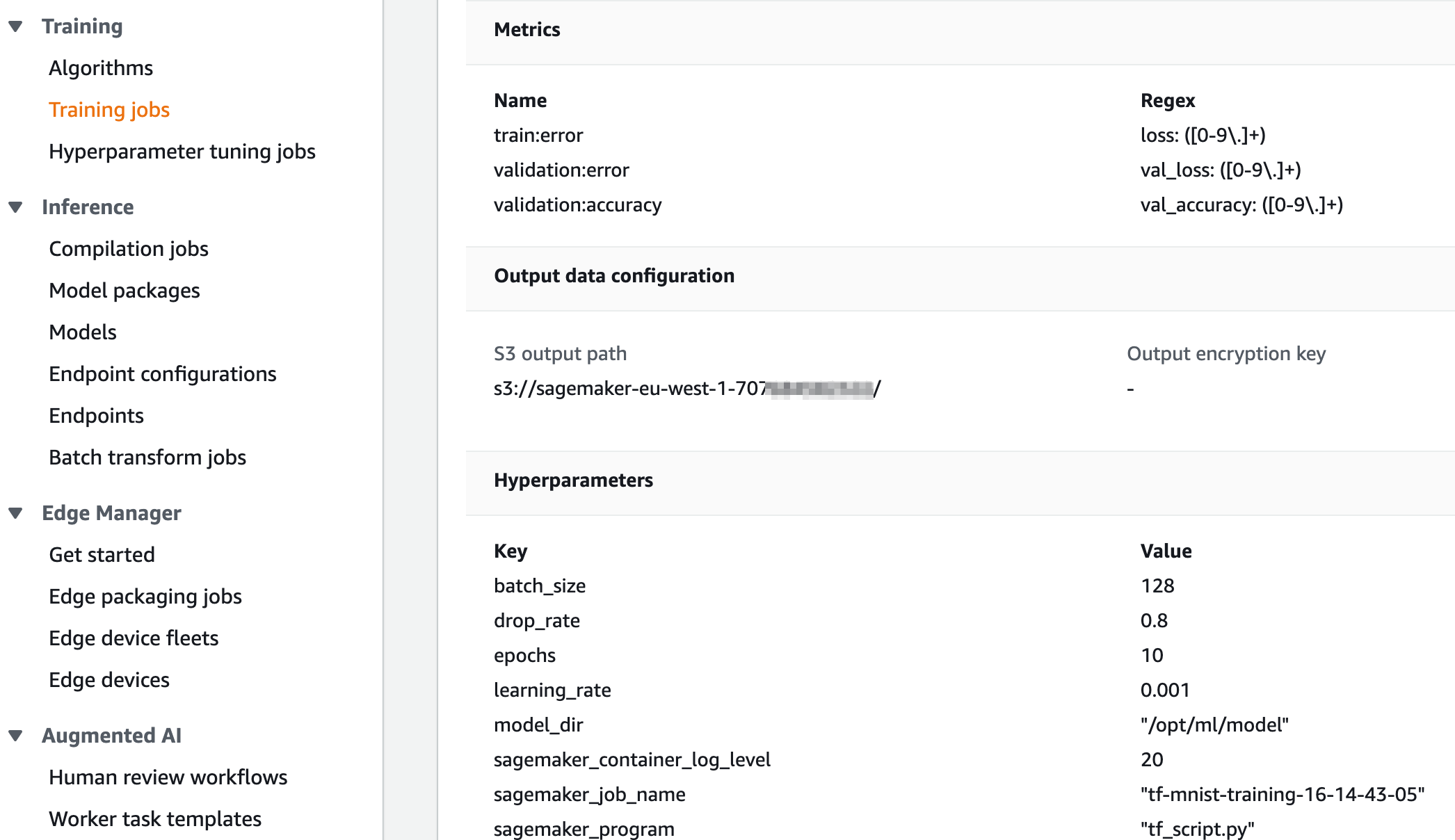
In AWS SageMaker console, you will see your training job launched, together with all training job related meta data, including metrics for model accuracy, input data location, output data configuration, hyperparameters etc. This helps you to manage and track all your SageMaker training jobs.
./sm_deploy.py
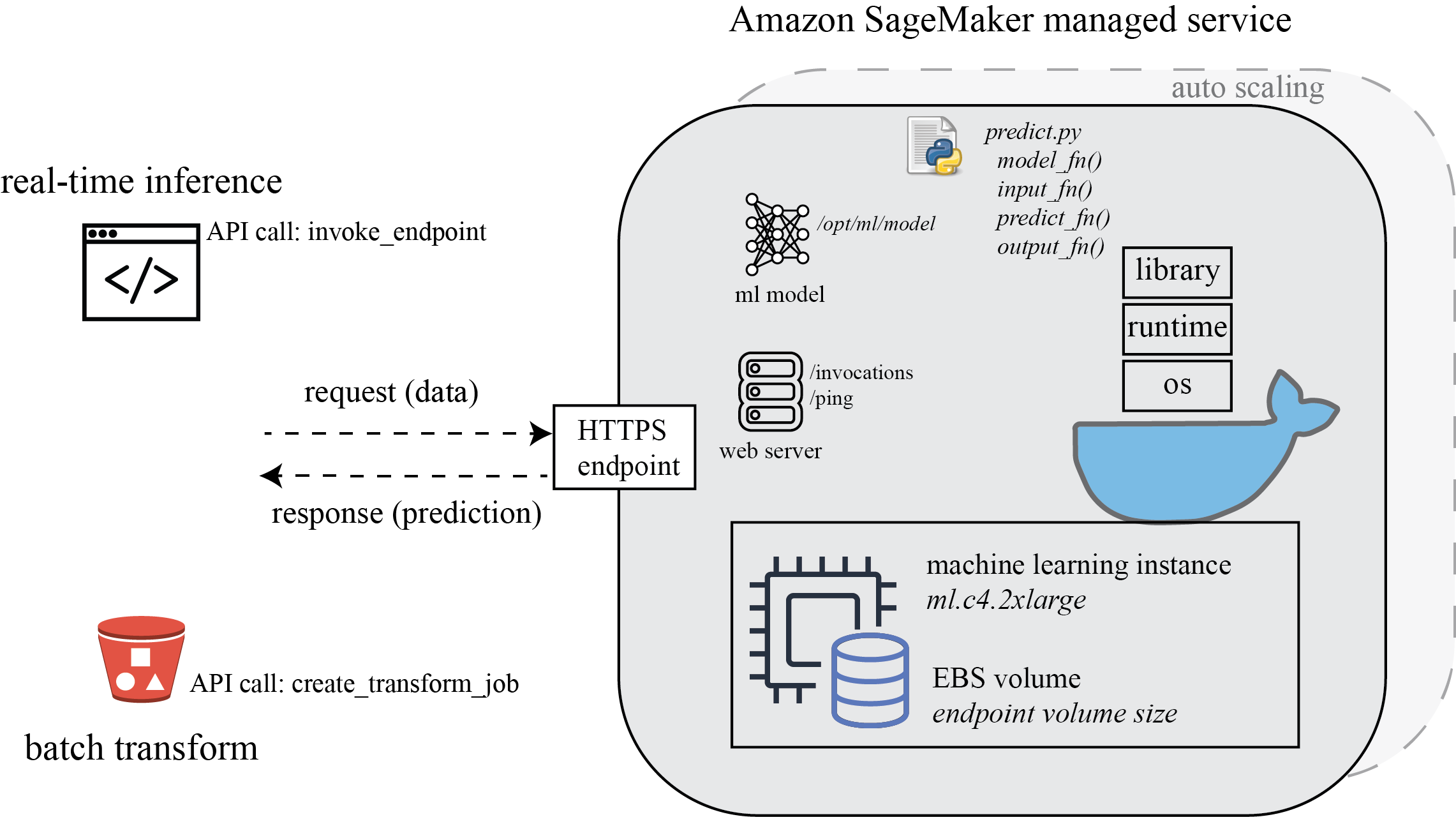
Once your trained model seems satisfactory, you might want to test the real-time inference against an HTTPS endpoint, or with batch prediction. With SageMaker SDK, you can easily setup the inference environment to test your inference code, model performance i.e. accuracy, latency and throughput.
SageMaker provides model hosting services for model deployment, as shown in the following diagram. It provides an HTTPS endpoint where your machine learning model is available to perform inference.
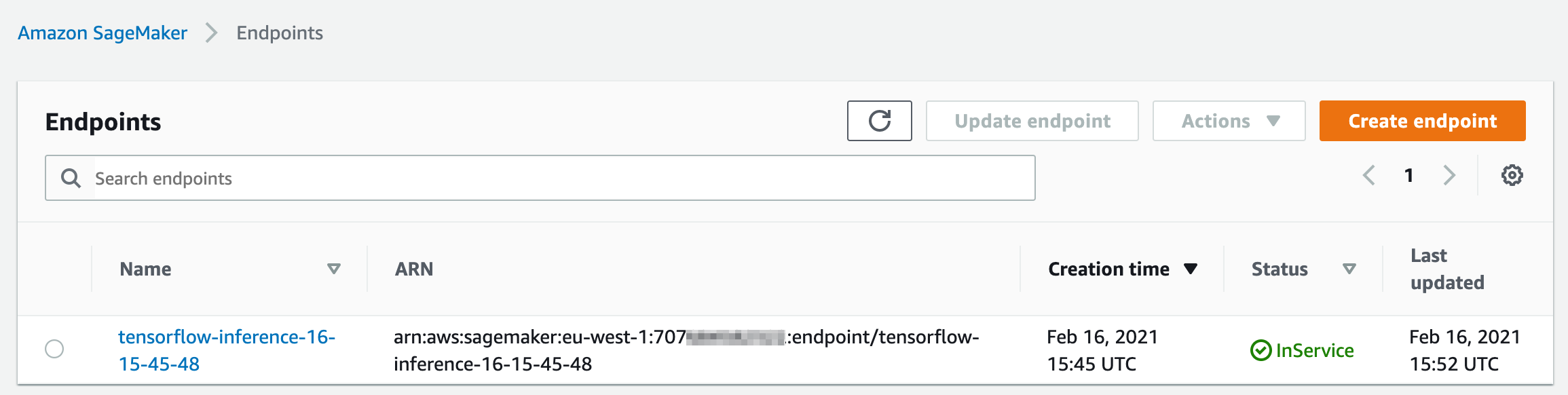
The persistent endpoint deployed with SageMaker hosting services will show up in your AWS SageMaker console.
Finally, if you have lots of experiments with different preprocessing configurations, different hyperparameters or even with different machine learning algorithms to test, I sugguest you to check SageMaker Experiments to help you group and organize their machine learning iterations.
SageMaker Experiments automatically tracks the inputs, parameters, configurations, and results of your iterations as trials. You can assign, group, and organize these trials into experiments. SageMaker Experiments is integrated with Amazon SageMaker Studio providing a visual interface to browse your active and past experiments, compare trials on key performance metrics, and identify the best performing models. See documentation for setting up SageMaker Experiments