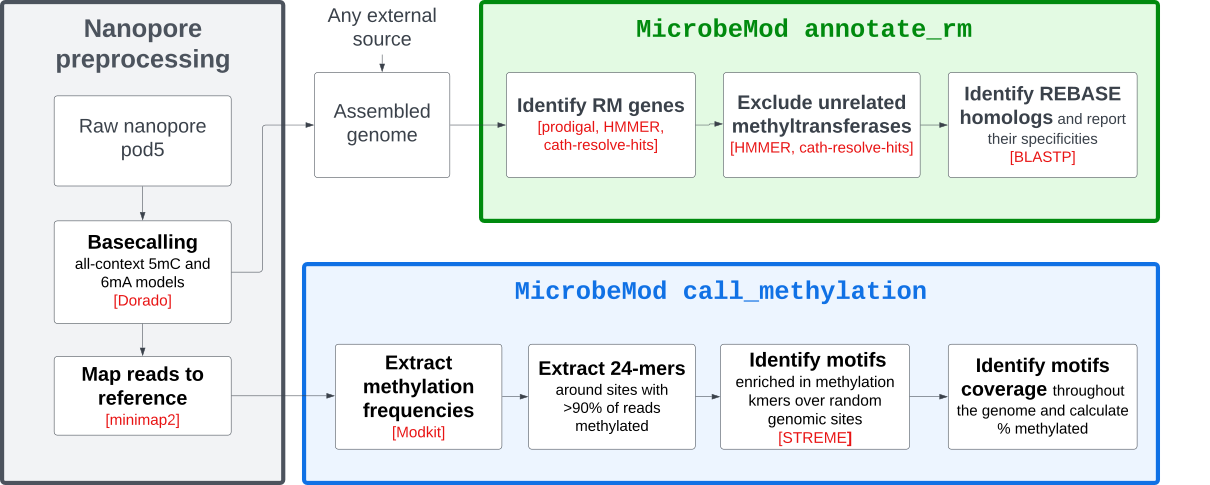
MicrobeMod is a workflow and toolkit for exploring prokaryotic methylation in nanopore sequencing.
December 2023 update: MicrobeMod v1.0.3 is now compatible with the 4mC all-context model available through Rerio!
July 2024 update: MicrobeMod v1.0.4 is now compatible with the 4mC_5mC all-context models available through Dorado 0.7+!
FASTQ data (in the form of BAMs mapped to each reference) and POD5 data for the genome set from the MicrobeMod preprint can be downloaded with the commands below. Note that the raw2 POD5 data is substantial (213 GB total).
aws s3 cp --recursive s3://cultivarium-publication-data/MICROBEMOD-DATA-NOV2023/mapped_bams/ .
aws s3 cp --recursive s3://cultivarium-publication-data/MICROBEMOD-DATA-NOV2023/reference_genomes/ .
aws s3 cp --recursive s3://cultivarium-publication-data/MICROBEMOD-DATA-NOV2023/pod5/ .
Before installation, make sure the following external dependencies are available in your path.
-
Prodigal, BLAST, and HMMER:
-
Cath-resolve-hits: https://github.com/UCLOrengoGroup/cath-tools/releases/tag/v0.16.10
All of the above can easily be installed via conda:
conda install -c bioconda prodigal hmmer blast cath-tools
- Modkit v0.2.2: https://github.com/nanoporetech/modkit
You can also install Modkit via conda:
conda install -c nanoporetech modkit.
July 2024 update: MicrobeMod is also compatible with Modkit 0.3 according to our testing.
- STREME: https://meme-suite.org/meme/doc/download.html
You can also install STREME via conda:
conda install -c bioconda meme.
Both can also be installed via conda, although you may run into errors on some systems:
conda install -c bioconda meme
conda install -c nanoporetech modkit
git clone https://github.com/cultivarium/MicrobeMod.git
cd MicrobeMod/MicrobeMod/
Download the database (required for annotate_rm only - includes HMMs from DefenseFinder and PFAM and REBASE proteins):
python download_db.py
Install:
cd ../
pip install .
To run all tests:
pytest
Optionally, we provide a Docker container which can be built to run MicrobeMod without installing the dependencies on the host system. To build it:
docker build -t microbemod -f Dockerfile .
And to subsequently run it:
docker run -v $PWD:/home/ubuntu/ -w /home/ubuntu/ microbemod -h
The -v option will make the local directory available to the docker instance, and files within this directory can be passed to the container and accessed via their local paths.
If you have a reference mapped, indexed, and sorted BAM output from Dorado, to run MicrobeMod call_methylation with 10 threads:
MicrobeMod call_methylation -b mapped_reads.bam -r genome_reference.fna -t 10
To run MicrobeMod annotate_rm with 10 threads:
MicrobeMod annotate_rm -f genome_reference.fasta -o genome_reference -t 10
Example BAM and FASTA files are available as:
./tests/test_data/test.bam and ./tests/test_data/EcoliCVM05_GCF_000005845.2_ASM584v2_genomic.fna.
FASTQ data (in the form of BAMs mapped to each reference) and POD5 data for the genome set from the MicrobeMod preprint can be downloaded with the commands below. Note that the raw2 POD5 data is substantial (213 GB total).
aws s3 cp --recursive s3://cultivarium-sequencing/MICROBEMOD-DATA-NOV2023/mapped_bams/ .
aws s3 cp --recursive s3://cultivarium-sequencing/MICROBEMOD-DATA-NOV2023/reference_genomes/ .
aws s3 cp --recursive s3://cultivarium-sequencing/MICROBEMOD-DATA-NOV2023/pod5/ .
The first step for methylation motif identification is running Dorado basecalling with modified basecalling models.
You can download models directly through dorado like so:
dorado download --model dna_r10.4.1_e8.2_400bps_sup@v5.0.0
dorado download --model dna_r10.4.1_e8.2_400bps_sup@v5.0.0_6mA@v1
dorado download --model dna_r10.4.1_e8.2_400bps_sup@v5.0.0_4mC_5mC@v1
This downloads the latest (as of July 2024) super high accuracy basecalling model (v5.0.0) and the latest all context 6mA, 5mC, and 4mC modified basecalling models.
You can pass any set of 4mC, 5mC, 6mA, and 5hmC basecalling models to Dorado for MicrobeMod.
The command to run the basecalling should look like the below- the primary input is your directory of pod5 files, here named POD5_LIBRARY_NAME (if you have fast5, you can convert them using pod5 convert fast5: https://pod5-file-format.readthedocs.io/en/latest/docs/tools.html).
This command uses a R10.4.1 basecalling model, and passes two modified basecalling models as well, one for all context 4mC and 5mC and one for all context 6mA.
dorado basecaller dna_r10.4.1_e8.2_400bps_sup@v5.0.0 [LIBRARY NAME] --modified-bases-models dna_r10.4.1_e8.2_400bps_sup@v5.0.0_6mA@v1,dna_r10.4.1_e8.2_400bps_sup@v5.0.0_4mC_5mC@v1 > [LIBRARY NAME].bam
The output is an unmapped BAM file with modified base information for each read.
The next step is to map your basecalled reads, including their methylation metadata, to your reference genome. This can be done with samtools and minimap2:
samtools fastq LIBRARY_NAME.bam -T MM,ML | minimap2 -t 14 --secondary=no -ax map-ont -y reference_genomes.fna -| \
samtools view -b | samtools sort -@ 10 -o LIBRARY_NAME.mapped.bam```
The settings for samtools fastq are crucial: -T MM,ML includings the methylation tags in your fastq to pipe to minimap2. Please note that you'll want samtools version v1.11 or later for this step in order to properly transfer the methylation tags.
The settings for minimap2 here are crucial: this turns off secondary alignments (a strange minimap2 default behavior).
The final two samtools lines generate a sorted bam.
You'll then need to index this BAM file:
samtools index LIBRARY_NAME.mapped.bam
Now, you are ready to call MicrobeMod call_methylation. This can be done with 10 threads like so:
MicrobeMod call_methylation -b LIBRARY_NAME.mapped.bam -r reference_genomes.fna -t 10
Typically, this command will take 10-20 minutes to successfully run. Upon a completed run, you will see the final lines:
Complete!
Saving methylated site table to: LIBRARY_NAME_methylated_sites.tsv
Saving motif output to: LIBRARY_NAME_motifs.tsv
Often, MicrobeMod is robust to the exact parameters used, and the same motifs are returned regardless of these settings. However, there may be tricky motifs or edge cases in which it is valuable to re-run with tweaking these settings:
--min_strand_coverage 10: this is a stranded coverage. So if your genome coverage is 20x, then on average each strand will have 10x coverage. This number should be considerably lower than your actual coverage. If your coverage is as low as 10x, then consider setting this value to--min_strand_coverage 3. I would not recommend much lower than that. You can determine your mean depth of coverage withsamtools coverage LIBRARY_NAME.mapped.bam.--methylation_confidence_threshold 0.66- this is the confidence threshold that Modkit will use to decide if an individual read is methylated.--percent_methylation_cutoff 0.66- this is the percentage of reads mapping to a site that have to be called as methylated to consider that site as methylated. Consider increasing for more stringent motif calling.--percent_cutoff_streme 0.9- this is the percentage of reads mapping to a site that have to be called as methylated to pass that site to motif calling. Consider decreasing for broader motif calling.
Tweaking this parameters, and re-running with slightly different ones, may result in more accurate motifs called, and can be worth playing with.
The two primary processed output files will be two tab-separated tables, one describing information for all methylated sites (large) and one describing output for methylated motifs (small).
If we look at the motifs results LIBRARY_NAME_motifs.tsv, it might look something like:
| Motif | Motif_raw | Methylation_type | Genome_sites | Methylated_sites | Methylation_coverage | Average_Percent_Methylation_per_site | Methylated_position_1 | Methylated_position_1_percent | Methylated_position_2 | Methylated_position_2_percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GATC | 1-YGNYGATCNBNHNVN | a | 38248 | 38216 | 0.999 | 0.93 | 2 | 50.0 | 3 | 50.0 |
| CCWGG | 2-NNSVRCCWGGYBSNN | a | 24100 | 14242 | 0.591 | 0.83 | 3 | 100.0 | NA | 0 |
| GCACNNNNNNGTT | 3-GCACBVNVNNGTTN | a | 595 | 595 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 3 | 48.595 | 12 | 48.099 |
| No Motif Assigned | NA | a | NA | 9163 | NA | 0.77 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| CCWGG | 1-NNNNRCCWGGYNNNN | m | 24100 | 24086 | 0.999 | 0.94 | 2 | 48.87 | 4 | 48.87 |
| No Motif Assigned | NA | m | NA | 542 | NA | 0.72 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
Here is a brief description of the columns:
Motif: A consensus motif sequence called.Motif_raw: The raw motif called by STREME before cleaning up by MicrobeMod. Almost always overly specific.Methylation_type: currently eitherafor 6mA ormfor 5mC.Genome_sites: The number of occurrences of this motif in the genome (total).Methylated_sites: The number of times this motif was actually methylated in the genome.Methylation_coverage: the rato of the two previous columns.Average_Percent_Methylation_per_site: The mean of the percent of mapped reads that were methylated at all sites of this motif. Higher = higher confidence methylation calls.Methylated_position_1: The most frequently methylated position in the motif (1-based indexing). For example, in the first row above, "2" means that A in GATC is methylated.Methylated_position_1_percent: The percent of motif occurrences at whichMethylated_position_1is methylated. 50% for "A" GATC in GATC (because it is palindromic, and 50% of the time it will be the reverse complement).Methylated_position_2: The second most frequently methylated position in the motif.Methylatd_position_2_percent: The percent of motif occurrences at whichMethylated_position_2is methylated.
The LIBRARY_NAME_methylated_sites.tsv is considerable larger, and contains information about every genomic site that was methylated (including their assigned motifs).
The MicrobeMod annotate_rm pipeline is very simple: it just requires any genome assembly, and is not nanopore-specific. You can run it like this:
MicrobeMod annotate_rm -f genome_reference.fasta -o genome_reference -t 10
You can pass either a genome FASTA file with the -f argument, or a genbank file (e.g. downloaded from NCBI) with the -g argument. With -f, prodigal is run to call genes; -g will use gene loci from the GenBank file and skip gene calling.
The following files are then created:
test.blast: Raw BLAST results of RM proteins to REBASE
test.faa: Prodigal .faa file (all proteins)
test.hits: Raw output of HMMER
test.resolved.hits: Resolved best HMMER hits
test.rm.genes.faa: A FASTA file of RM proteins identified in this study
test.rm.genes.tsv: Tabular output describing RM genes
The *.rm.genes.tsv file will look something like this:
| Operon | Gene | System Type | Gene type | HMM | Evalue | REBASE homolog | Homolog identity(%) | Homolog methylation | Homolog motif |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM Operon #1 | NODE_3_length_585136_cov_9.720044_91 | RM_Type_IIG | IIG | Type_IIG_3 | 3.7e-182 | Bfr4856TORF10500P | 100.0 | m6A | GANGGAG |
| RM Operon #2 | NODE_3_length_585136_cov_9.720044_276 | RM_Type_I | RE | Type_I_REases_FAM_2.einsi_trimmed | 7.2e-27 | Bfr14ORF3855P | 100.0 | ||
| RM Operon #2 | NODE_3_length_585136_cov_9.720044_277 | RM_Type_I | MT | Type_I_MTases_FAM_1 | 1.1e-164 | M.Bsp2737ORF11960P | 100.0 | m6A | |
| RM Operon #2 | NODE_3_length_585136_cov_9.720044_280 | RM_Type_I | SP | Type_I_S_52 | 8.9e-32 | S.Bfr1512ORF18655P | 100.0 | ||
| RM Operon #3 | NODE_4_length_554179_cov_10.591782_322 | RM_Type_II | RE | Type_II_REase09 | 7.1e-17 | Bfr4856TORF22075P | 100.0 | ATGCAT | |
| RM Operon #3 | NODE_4_length_554179_cov_10.591782_323 | RM_Type_II | MT | Type_II_MTases_FAM_1 | 7.3e-89 | M.Bfr4856TORF22075P | 100.0 | ATGCAT | |
| RM Operon #4 | NODE_5_length_489011_cov_9.441508_131 | RM_Type_IV | RE | Type_IV_21-RM_Type_IV__Type_IV_REases | 3.8e-113 | ||||
| RM Operon #5 | NODE_6_length_416426_cov_9.438798_313 | RM_Type_I | RE | Type_I_REases_FAM_0.einsi_trimmed | 5.5e-199 | Bfr4856TORF13485P | 100.0 | ||
| RM Operon #5 | NODE_6_length_416426_cov_9.438798_311 | RM_Type_I | MT | Type_I_MTases_FAM_0 | 1.5e-172 | M.Bfr4856TORF13485P | 100.0 | m6A | |
| RM Operon #5 | NODE_6_length_416426_cov_9.438798_310 | RM_Type_I | SP | Type_I_S_51 | 9.9e-53 | S1.Bfr1512ORF16830P | 100.0 | GACNNNNNGRTY | |
| RM Operon #5 | NODE_6_length_416426_cov_9.438798_307 | RM_Type_I | SP | Type_I_S_01 | 1.3e-35 | S4.Bfr1512ORF16830P | 100.0 | ||
| Singleton #1 | NODE_17_length_27965_cov_10.731518_5 | RM_Type_II | RE | Type_II_REase06 | 4.2e-09 | ||||
| Singleton #2 | NODE_1_length_700861_cov_9.167701_172 | RM_Type_II | MT | Type_II_MTases_FAM_33 | 1e-12 | ||||
| Singleton #3 | NODE_3_length_585136_cov_9.720044_324 | RM_Type_II | MT | Type_II_MTases_FAM_5 | 5.7e-05 | M.Hgu7ORFBP | 100.0 |
Each line describes an individual gene: Genes are grouped by whether they are in an "operon" (complete RM system - for Type IV and Type IIG this is just one gene) or are a "singleton" (methyltransferase or RE without a pair).
Description of columns:
- Operon: The operon number for a given gene
- Gene: The gene name (designated by prodigal).
- System Type: The predicted RM system type of that gene.
- Gene type: The number of gene (either MT, SP, RE, or IIG)
- HMM: The exact HMM that hit that gene.
- Evalue: The Evalue of the HMM hit.
- REBASE homolog: closest homolog in the REBASE dataset.
- Homology identity: Amino acid percent identity of closest hit.
- Homolog methylation: The methylation type of the closest homolog, if known.
- Homolog motif: The motif specificity of the closest homolog, if known.
usage: MicrobeMod call_methylation [-h] -b BAM_FILE -r REFERENCE_FASTA [-m METHYLATION_TYPES] [-o OUTPUT_PREFIX] [-s STREME_PATH] [--min_strand_coverage MIN_STRAND_COVERAGE]
[--methylation_confidence_threshold METHYLATION_CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD] [--percent_methylation_cutoff PERCENT_METHYLATION_CUTOFF]
[--percent_cutoff_streme PERCENT_CUTOFF_STREME] [-t THREADS]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-b BAM_FILE, --bam_file BAM_FILE
BAM file of nanopore reads mapped to reference genome with the MM and ML tags preserved.
-r REFERENCE_FASTA, --reference_fasta REFERENCE_FASTA
Reference genome FASTA file.
-m METHYLATION_TYPES, --methylation_types METHYLATION_TYPES
Methylation types to profile
-o OUTPUT_PREFIX, --output_prefix OUTPUT_PREFIX
Output prefix. Default is based on the BAM filename.
-s STREME_PATH, --streme_path STREME_PATH
Path to streme executable.
--min_strand_coverage MIN_STRAND_COVERAGE
Minimum coverage required to call a site as methylated. Note this is per strand (so half of total coverage). Default: 10x
--methylation_confidence_threshold METHYLATION_CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD
The minimum confidence score to call a base on a read as methylated. Passed to modkit. Default: 0.66
--percent_methylation_cutoff PERCENT_METHYLATION_CUTOFF
The fraction of methylated reads mapping to a site to count that site as methylated. Default: 0.66
--percent_cutoff_streme PERCENT_CUTOFF_STREME
The fraction of methylated reads mapping to a site to pass that site to motif calling. Default: 0.9
-t THREADS, --threads THREADS
Number of threads to use. Only the first step (modkit) is multithreaded.
usage: MicrobeMod annotate_rm [-h] [-f FASTA] [-g GENBANK] [-o OUTPUT_PREFIX] [-t THREADS]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f FASTA, --fasta FASTA
FASTA file for a genome. This option runs gene calling with prodigal. Either --fasta or --genbank is required.
-g GENBANK, --genbank GENBANK
GenBank (gbk or gbff) file with coding regions annotated as CDS features. No gene calling is run. Either --fasta or --genbank is required.
-o OUTPUT_PREFIX, --output_prefix OUTPUT_PREFIX
Output prefix.
-t THREADS, --threads THREADS
Number of threads to use.
More questions? Open an issue and I will respond!