- Translate the breadth first search procedure into code.
In this section we will translate our breadth first search algorithm into code. We will work towards a function called bfs that returns a list of vertices in the order they are first visited. We'll provide some guidance along the way.
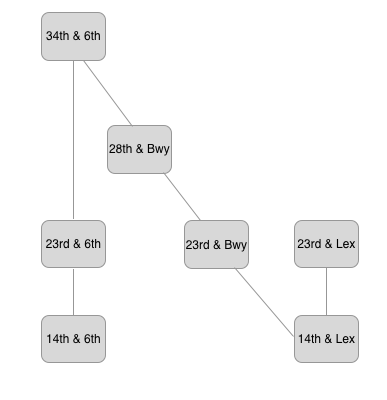
So let's take another look at our graph.
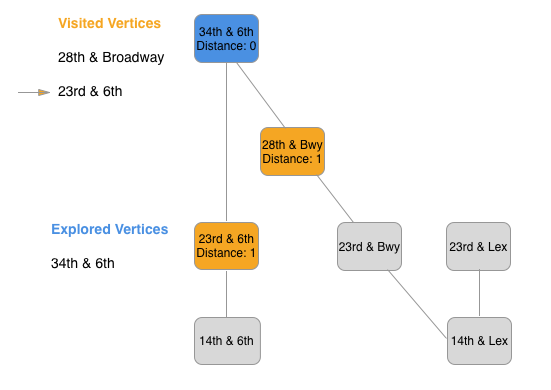
In breadth first search, we explore the first vertex, and visit the adjacent vertices adding each one to a queue in turn. Then we remove the first vertex added to the queue and explore it.
Let's go back to our representation of our graph and see if we can make more progress translating this into code.
let edges = [
['14th&6th', '23rd&6th'],
['23rd&6th', '34th&6th'],
['34th&6th', '28th&Bwy'],
['28th&Bwy', '23rd&Bwy'],
['23rd&Bwy', '14th&Lex'],
['14th&Lex', '23rd&Lex']
]
let vertices = [
{name: '34th&6th', distance: null, predecessor: null},
{name: '23rd&6th', distance: null, predecessor: null},
{name: '14th&6th', distance: null, predecessor: null},
{name: '28th&Bwy', distance: null, predecessor: null},
{name: '23rd&Bwy', distance: null, predecessor: null},
{name: '14th&Lex', distance: null, predecessor: null},
{name: '23rd&Lex', distance: null, predecessor: null},
]What's a good summary of our procedure? Add a vertex to the queue. Then we remove the first vertex added and visit the adjacent vertices. As each is visited, add each vertex to the queue. Then continue the process exploring each vertex explored in turn.
Let's translate this summary into pseudocode.
Note: Pseudocode is code that may not actually work, but reflects our thought process.
Give the pseudocode a shot, it shouldn't take that long.
You may get to something like the following:
rootNode = vertices[0]
queue = []
addVertexToQueue(rootNode)
// queue = [rootNode]
while(!queue.length == 0) {
let firstNode = queue.shift()
adjacentVertices = findAdjacent(firstNode)
for vertex in adjacentVertices {
markDistanceAndPredecessor(vertex)
addToQueue(vertex)
}
}
So we can start to see some methods forming. So now we write the following methods:
findAdjacent
markDistanceAndPredecessor
addToQueue
You can write these methods, and then complete our breadth first search algorithm which returns a list of vertices in the order they are visited. Use the tests in the lab to guide you through.