Test automation project for service Bookmate
Bookmate is a subscription based e-book service providing access to books, comics, audiobooks,
related social activity - reviews, comments, ratings, private and public bookshelfs.
Consists of website and mobile applications for Android and iOS.
- Description
- Tools and technologies
- How to run
- Telegram Notifications
- Test results report in Allure Report
- Allure TestOps integration
- GitHub webhooks
- Jira integration
- Video of running tests
The test project consists of Web, API and mobile(android) tests.
A brief list of interesting facts about the project:
-
Page Objectwith steps usingChain of Invocations - Fake data generating with
Fakerlibrary - Parametrized tests
- Parametrized build
- Different configuration files for test running depending on build parameters
- Config with
Ownerlibrary - Using
Lombokfor models for API tests - Objects serialization/deserialization for API requests/responses using
Jackson - Using request/response specifications for API tests
- Custom Allure listener for beautiful API requests/responses logging
-
Allure TestOpsintegration - Autotests as test documentation
-
Github webhookson each push to triggerJenkinsbuild -
Jiraintegration - Parallel execution
The autotests in this project are written in Java using Selenide framework.
Gradle - is used as a build automation tool.
JUnit5 - to execute tests.
REST Assured - for easy API testing of REST services.
Jenkins - CI/CD for running tests remotely.
Selenoid - to remote launching browsers in Docker containers.
Browserstack - to run mobile tests.
Android Studio tools, Appium - to tun mobile tests locally in a mobile device emulator.
Allure Report - for test results visualisation.
Telegram Bot - for test results notifications.
Allure TestOps - as Test Management System.
Back to the table of contents ⬆
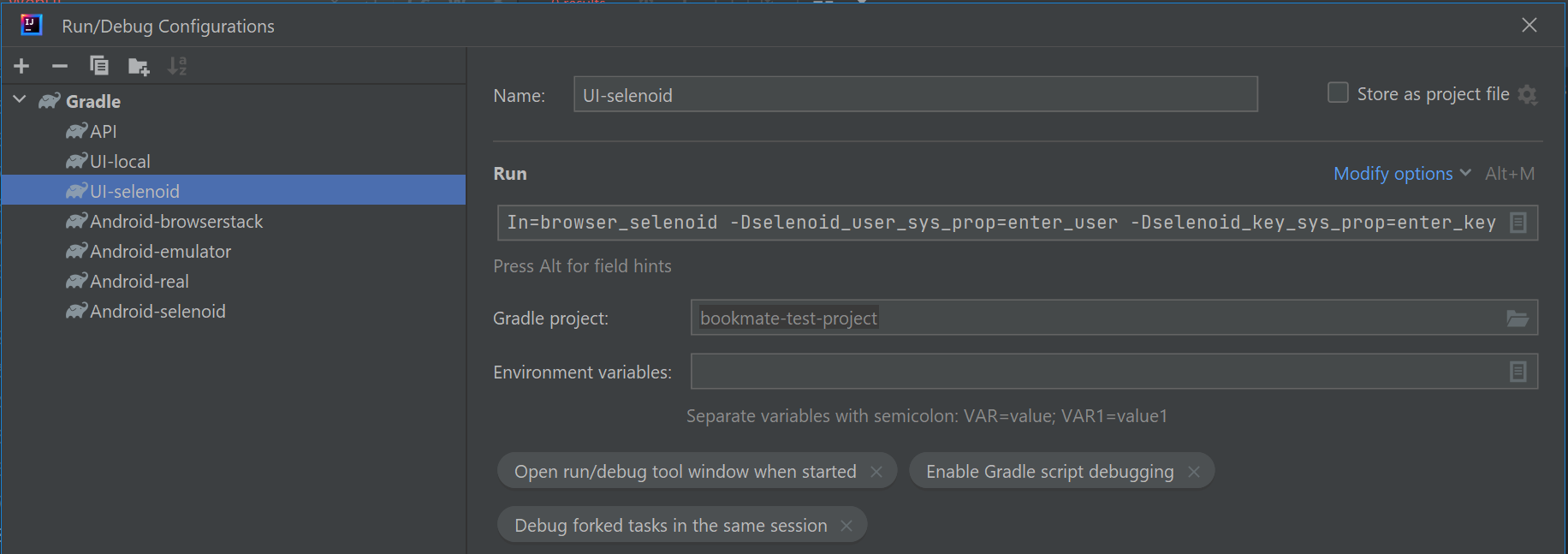
To run locally and in Jenkins the following command is used:
gradle clean test -Dtag=<tag> -DrunIn=<runIn>Additional parameters:
-Dselenoid_user_sys_prop=enter_user-Dselenoid_key_sys_prop=enter_key- credentials for selenoid
-Dbrowserstack_user_sys_prop=enter_user-Dbrowserstack_key_sys_prop=enter_key- credentials for browserstack
-Dthreads=number_of_threadscan be added for parallel tests execution
-DapiBaseUrl=urlcan be added to set a base url for API tests
tag - tests with this tag will be executed:
- API
- Web
- Android
runIn - defines an environment for running these tests:
- <not defined>(for API tests)
- browser_selenoid
- browser_local
- android_browserstack
- android_emulator
- android_real
- android_selenoid
Additional properties are retrieved from the corresponding properties file(depending on runIn value):
./resources/config/project-${runIn}.propertiesValid combinations:
graph LR
A[tag] --> B[API]
A --> C[Web]
A --> D[Android]
C --> E[browser_selenoid]
C --> F[browser_local]
D --> G[android_browserstack]
D --> H[android_emulator]
D --> I[android_real]
D --> J[android_selenoid]
Back to the table of contents ⬆
Possible properties in a project-${runIn}.properties file:
remoteDriver=
baseUrl=
browser=
browserSize=
user=
key=
deviceName=
platformVersion=
- remoteDriver - URL for remote WebDriver
- baseUrl - base URL for Web tests
- browser - browser for Web tests
- browserSize - size of browser for Web tests
- user - login for authorization. By default, it's
${browserstack_user_sys_prop}or${selenide_user_sys_prop}, that is it comes from system properties- key - key/password for authorization. By default, it's
${browserstack_key_sys_prop}or${selenide_key_sys_prop}, that is it comes from system properties- deviceName - android device name or serial number
- platformVersion - android version
Back to the table of contents ⬆
The section below is automatically updated from content of src/test/resources/config/ directory.
Back to the table of contents ⬆
For convenience of running tests, IDEA run configurations are committed to this project
Back to the table of contents ⬆
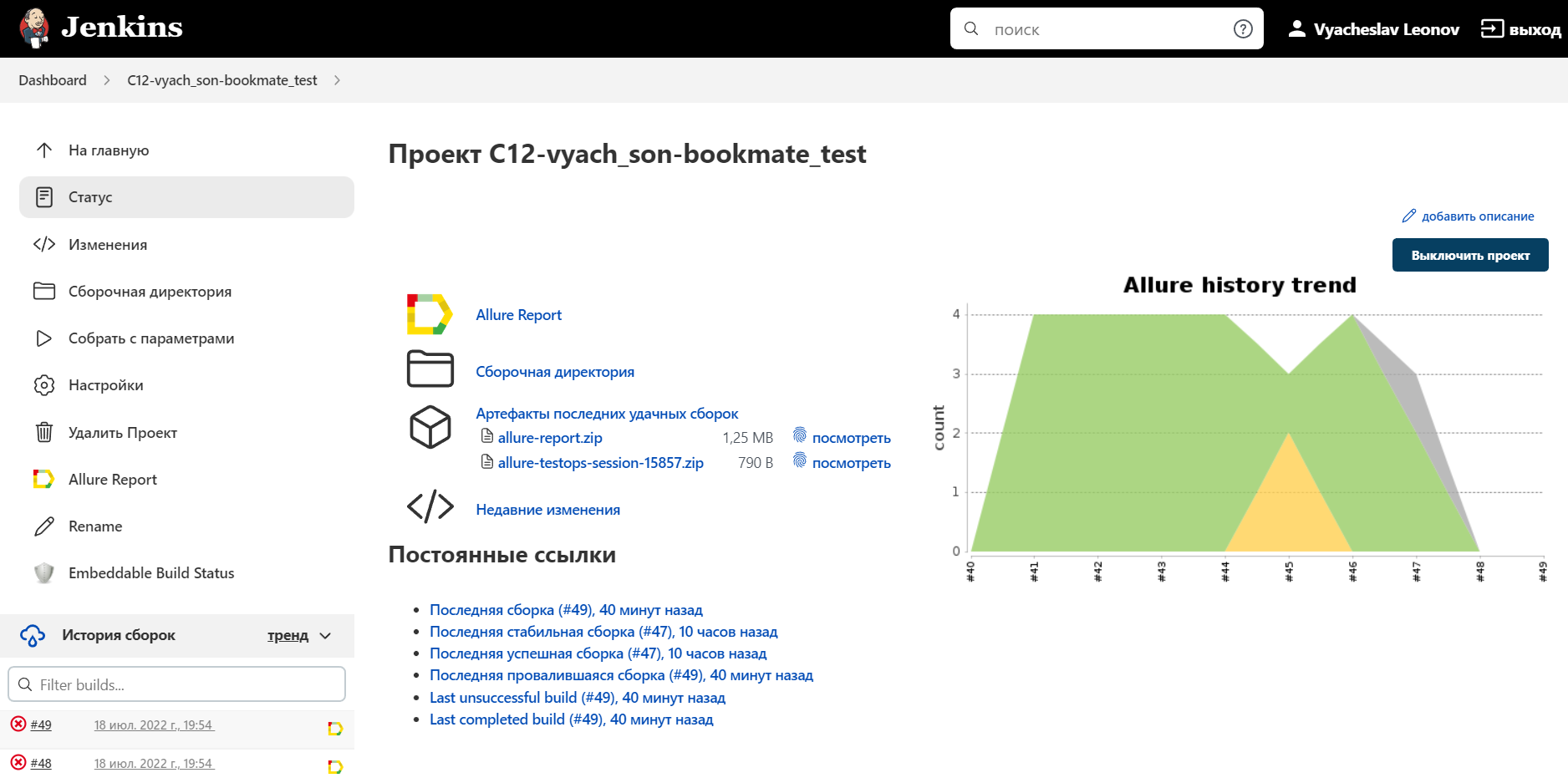
Main page of the build:
A parametrized Jenkins job can be launched with needed tag and runIn:
project-{runIn}.properties config files are created in the build workspace on start build.
Sensitive information(login names and passwords) is stored in an encrypted form in Jenkins credential storage.
And relatively safe transferred to the build by gradle arguments(see Gradle command section, 'Additional parameters') and it's values masked in the logs.
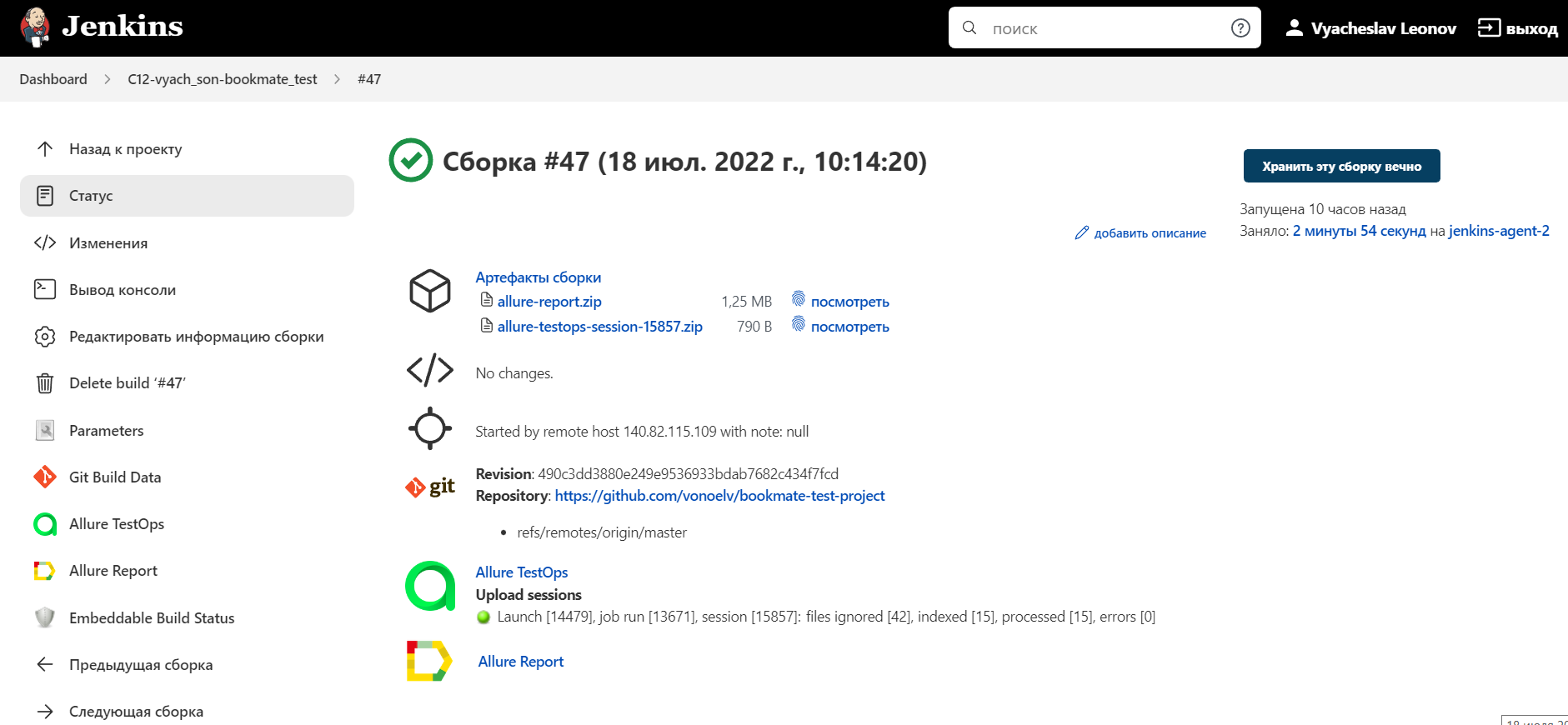
After the build is done the test results are available in:
Allure ReportAllure TestOps- results are uploaded there and the automated test-cases can be automatically updated accordingly to the recent changes in the code.
Back to the table of contents ⬆
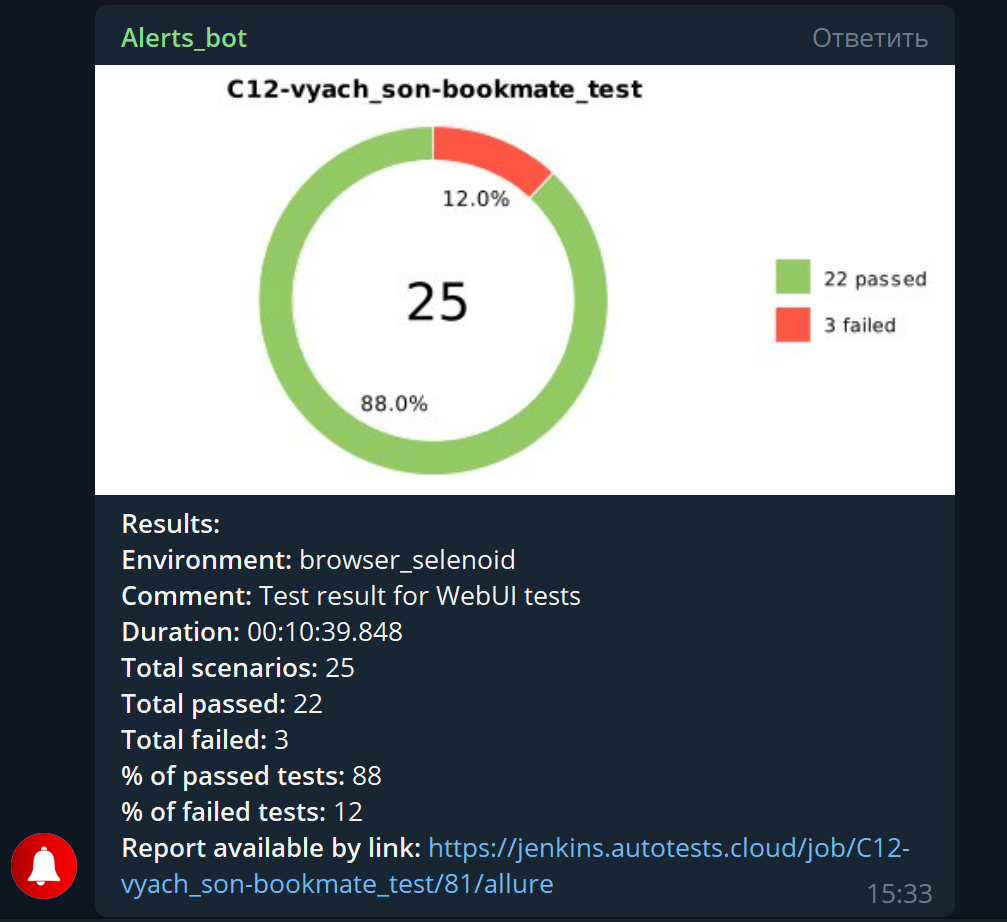
Telegram bot sends a brief report to a specified telegram chat by results of each build.
Back to the table of contents ⬆
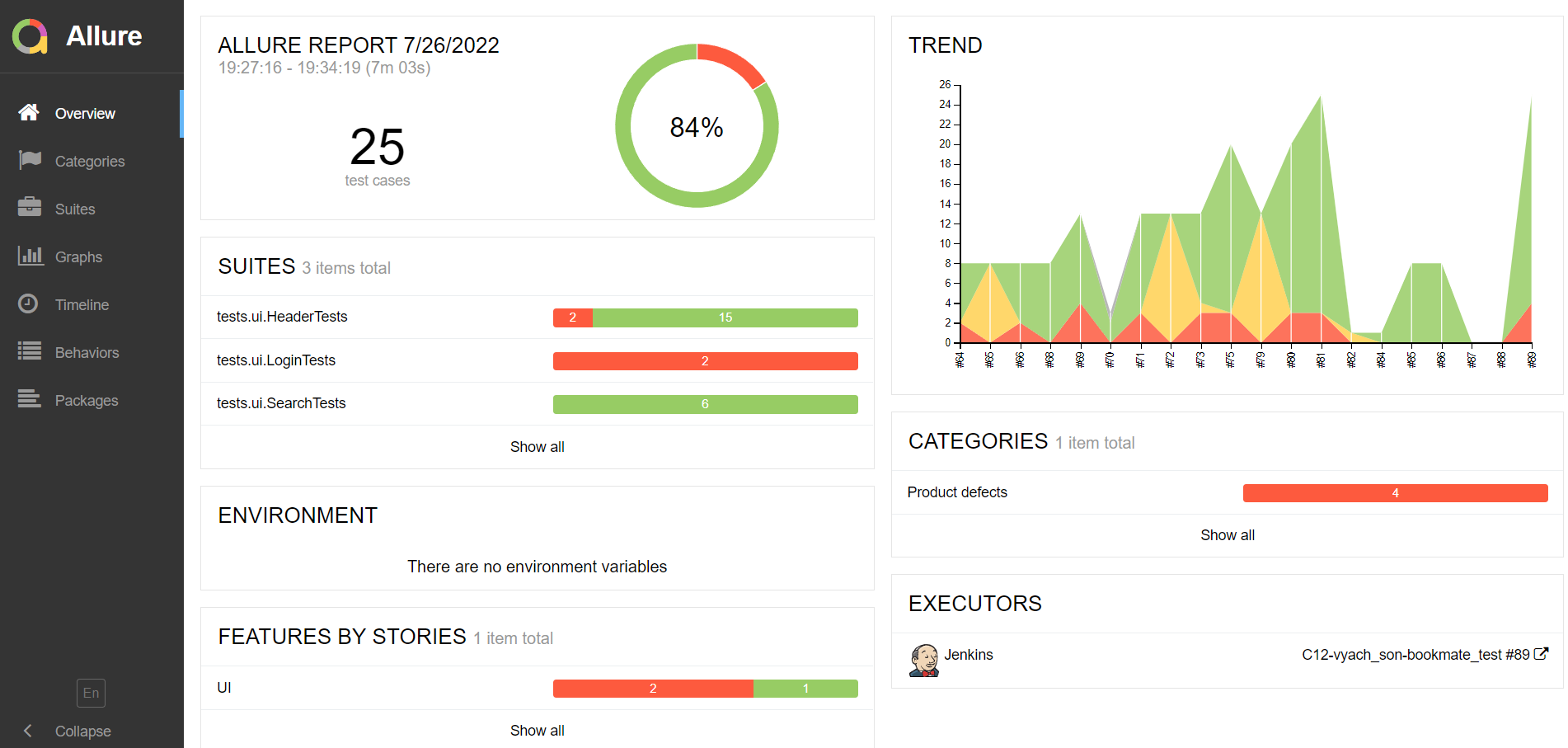
Main page of Allure report contains the following blocks:
ALLURE REPORT- displays date and time of the test, overall number of launched tests, а также диаграмму с указанием процента и количества успешных, упавших и сломавшихся в процессе выполнения тестовTREND- displays trend of running tests for all runsSUITES- displays distribution of tests by suitesCATEGORIES- displays distribution of unsuccessful tests by defect types
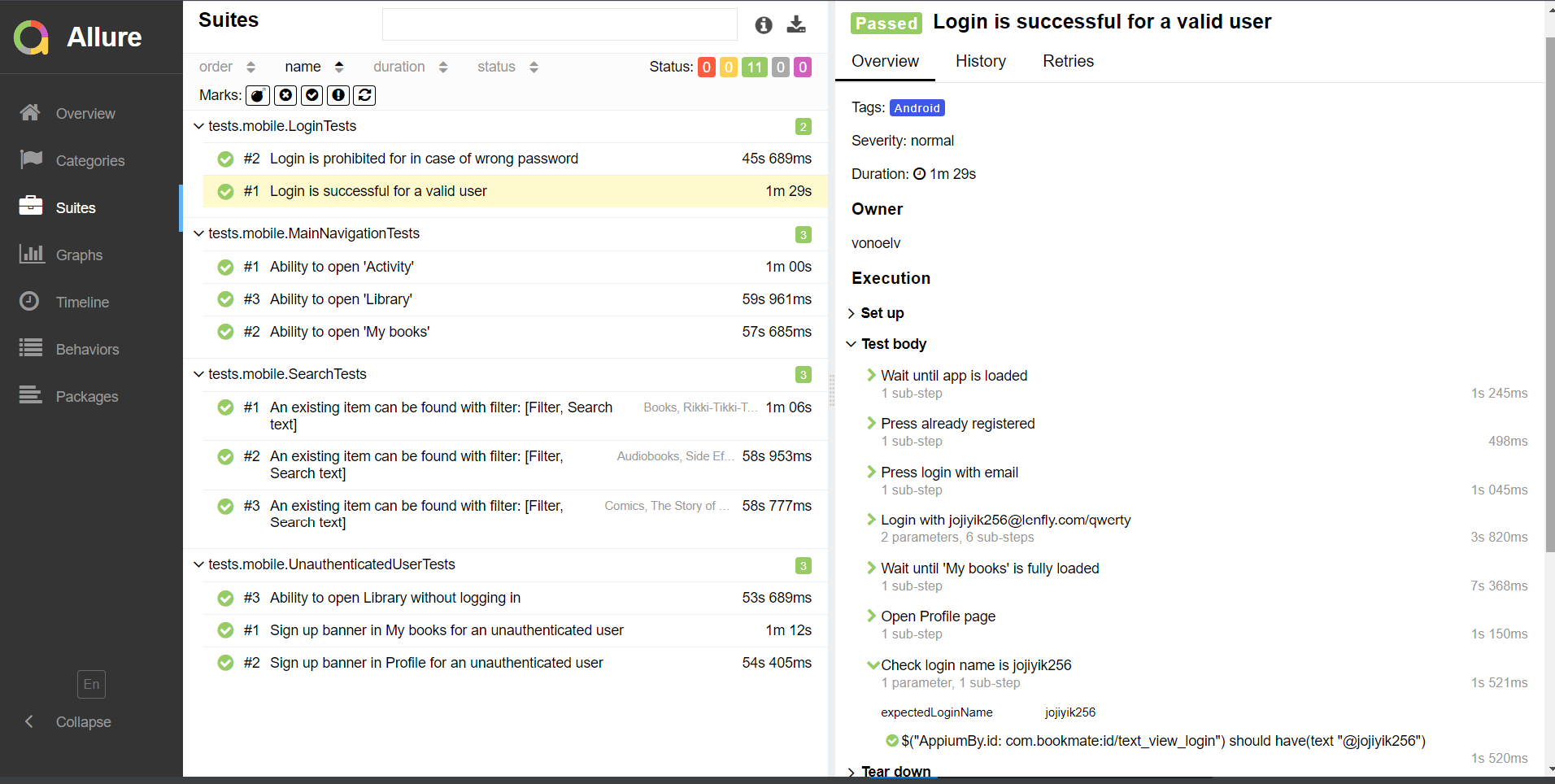
On the page the list of the tests grouped by suites with status shown for each test.
Full info about each test can be shown: tags, severity, duration, detailed steps.
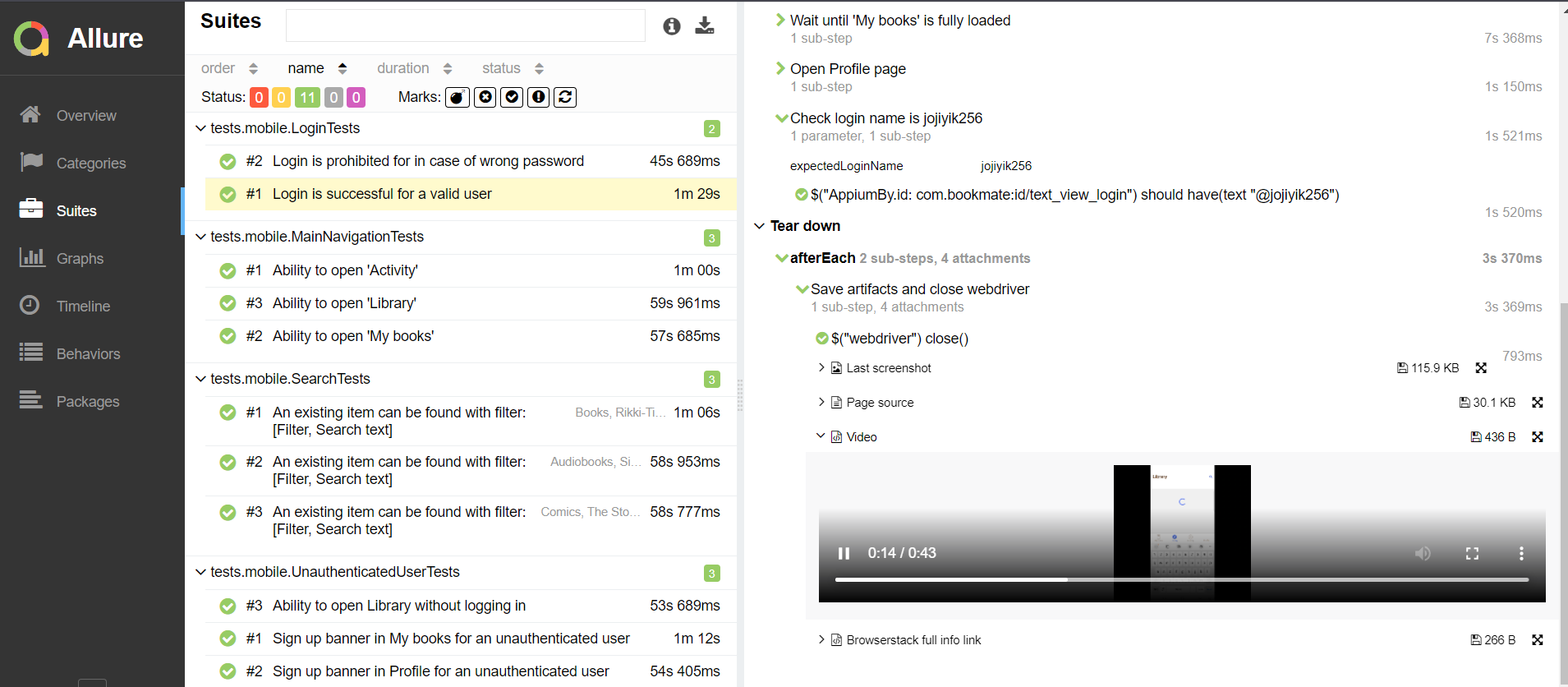
Also additional test artifacts are available:
- Screenshot
- Page Source
- Video
- Browserstack full info link
Back to the table of contents ⬆
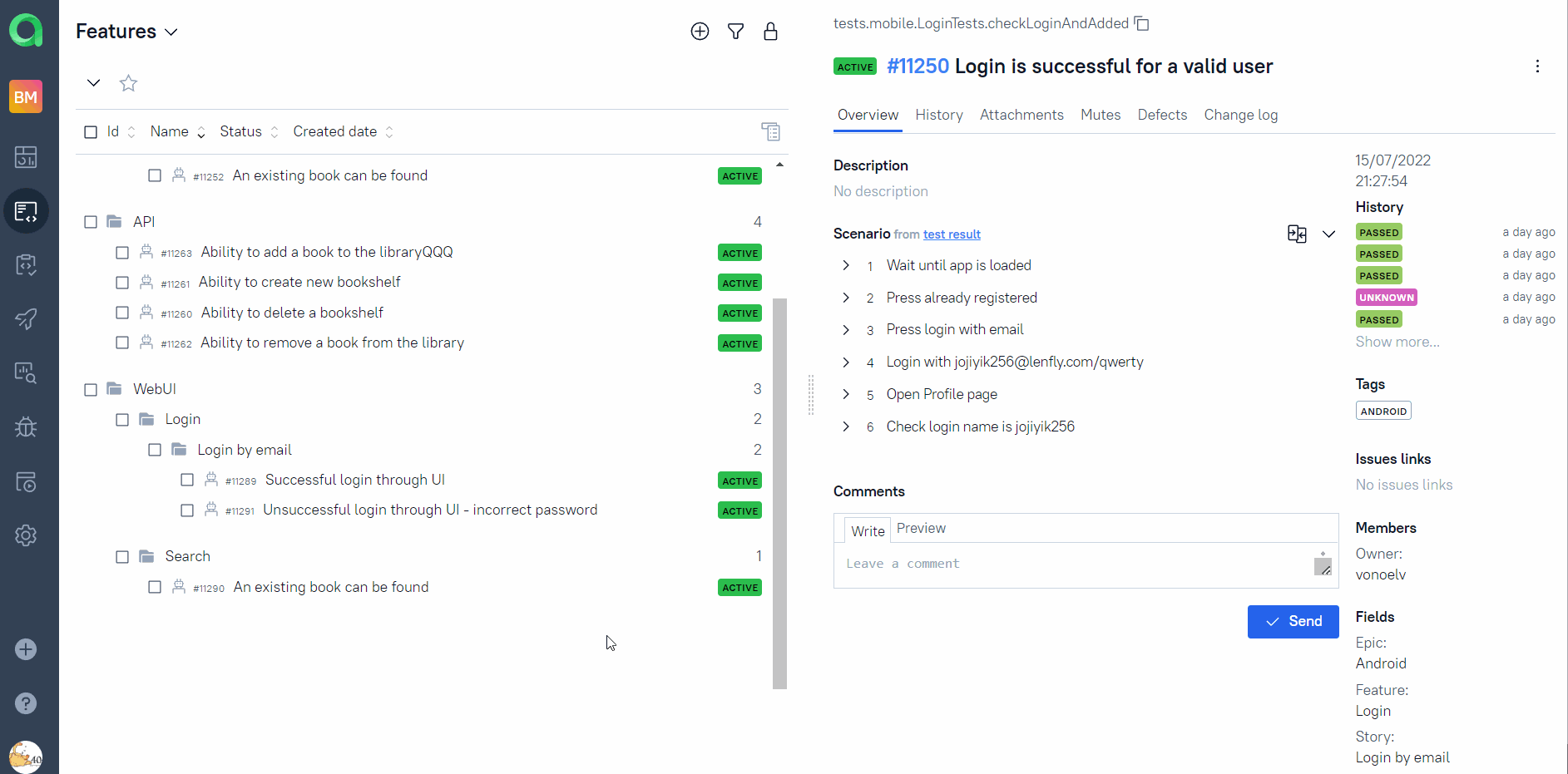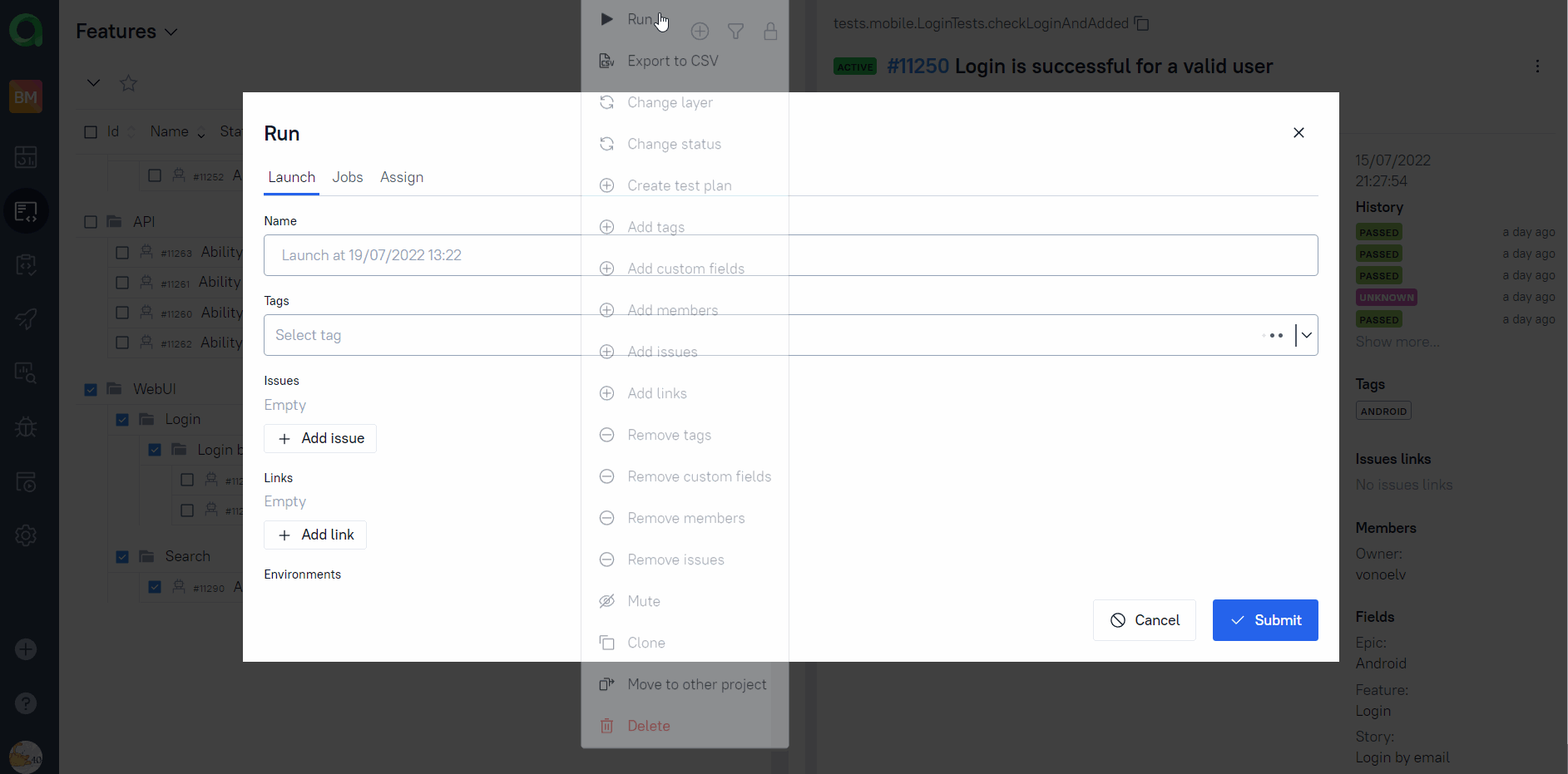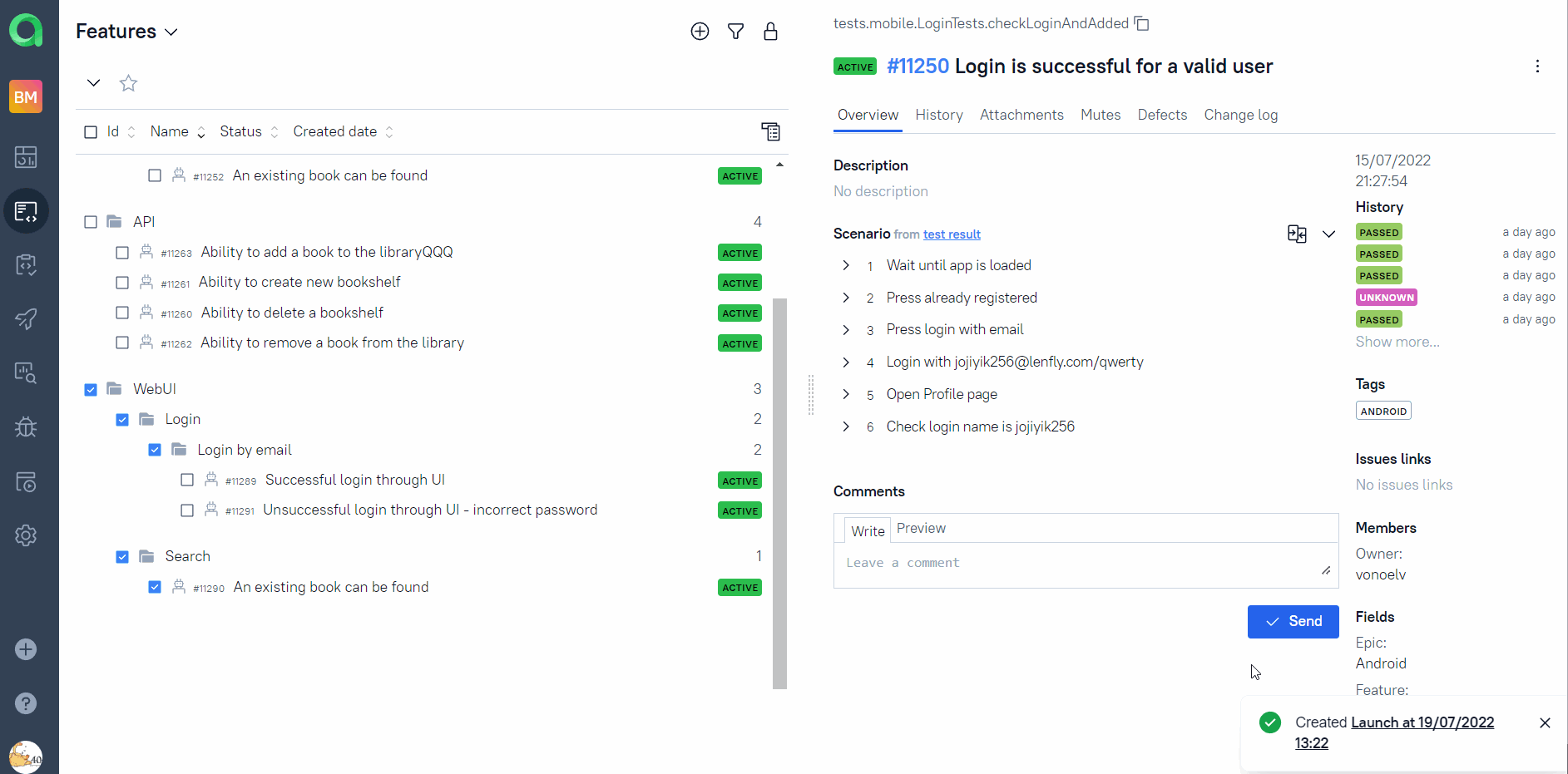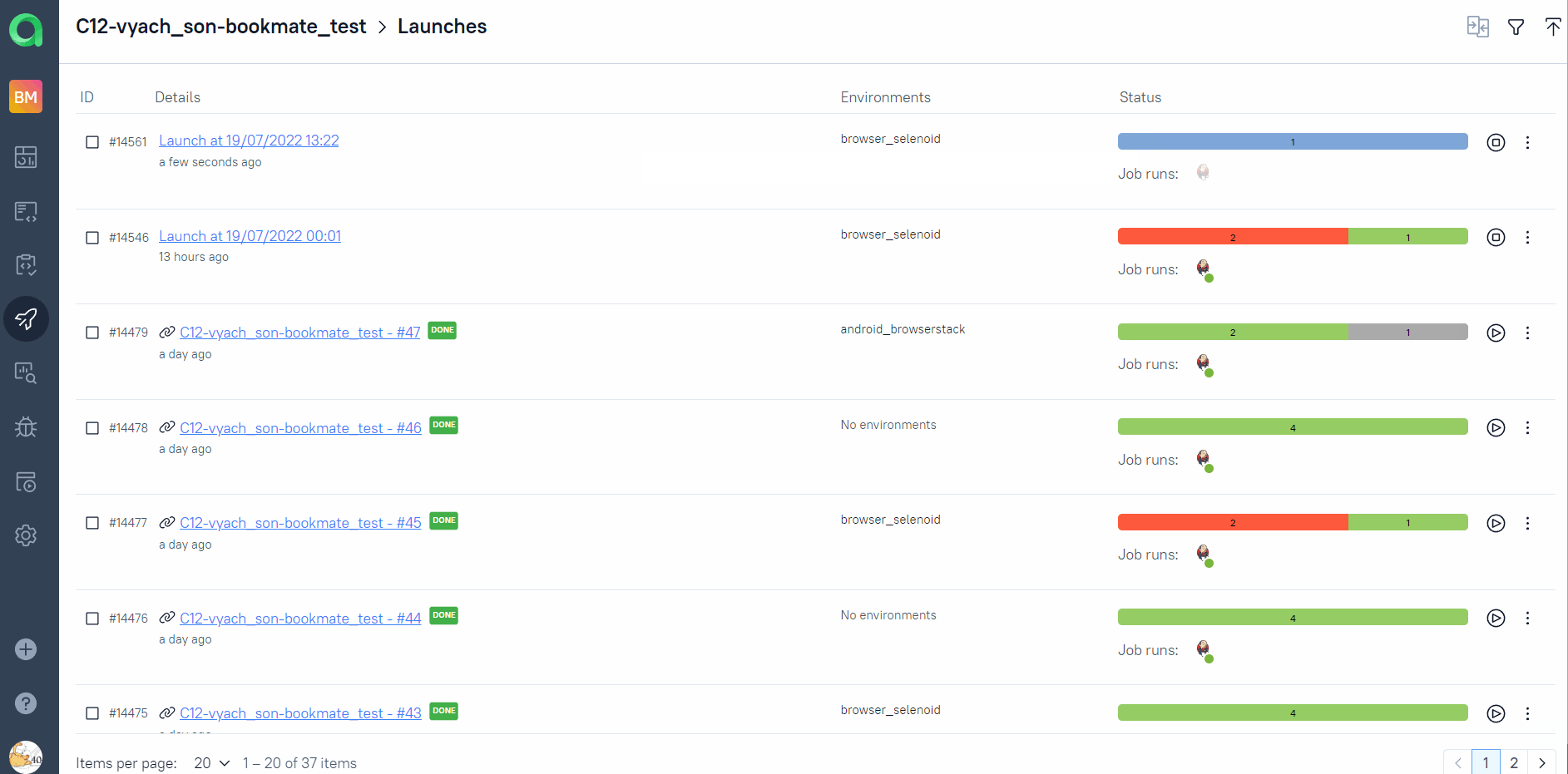
Allure TestOps integration
The link can be accessed only by authorized users.
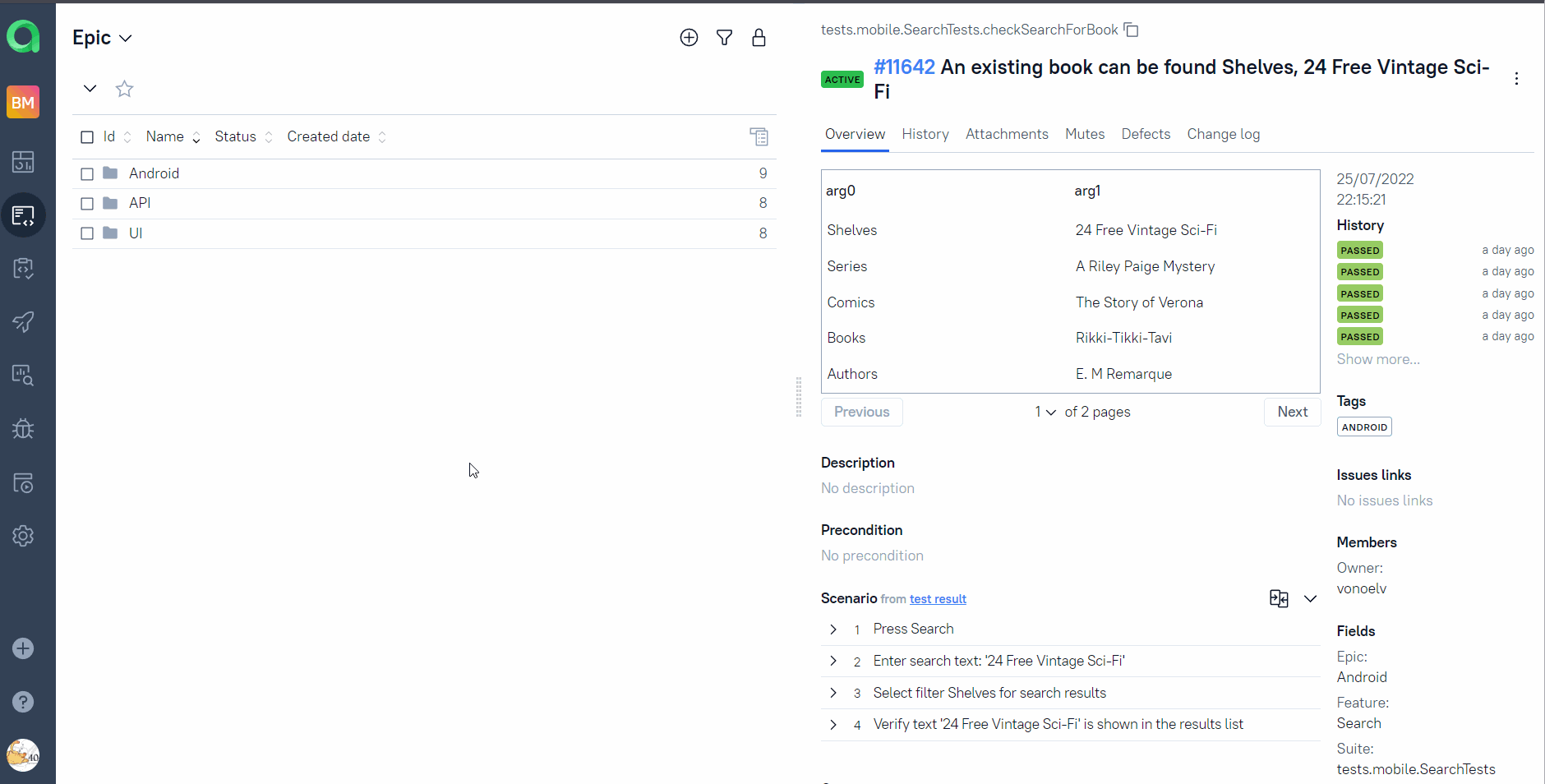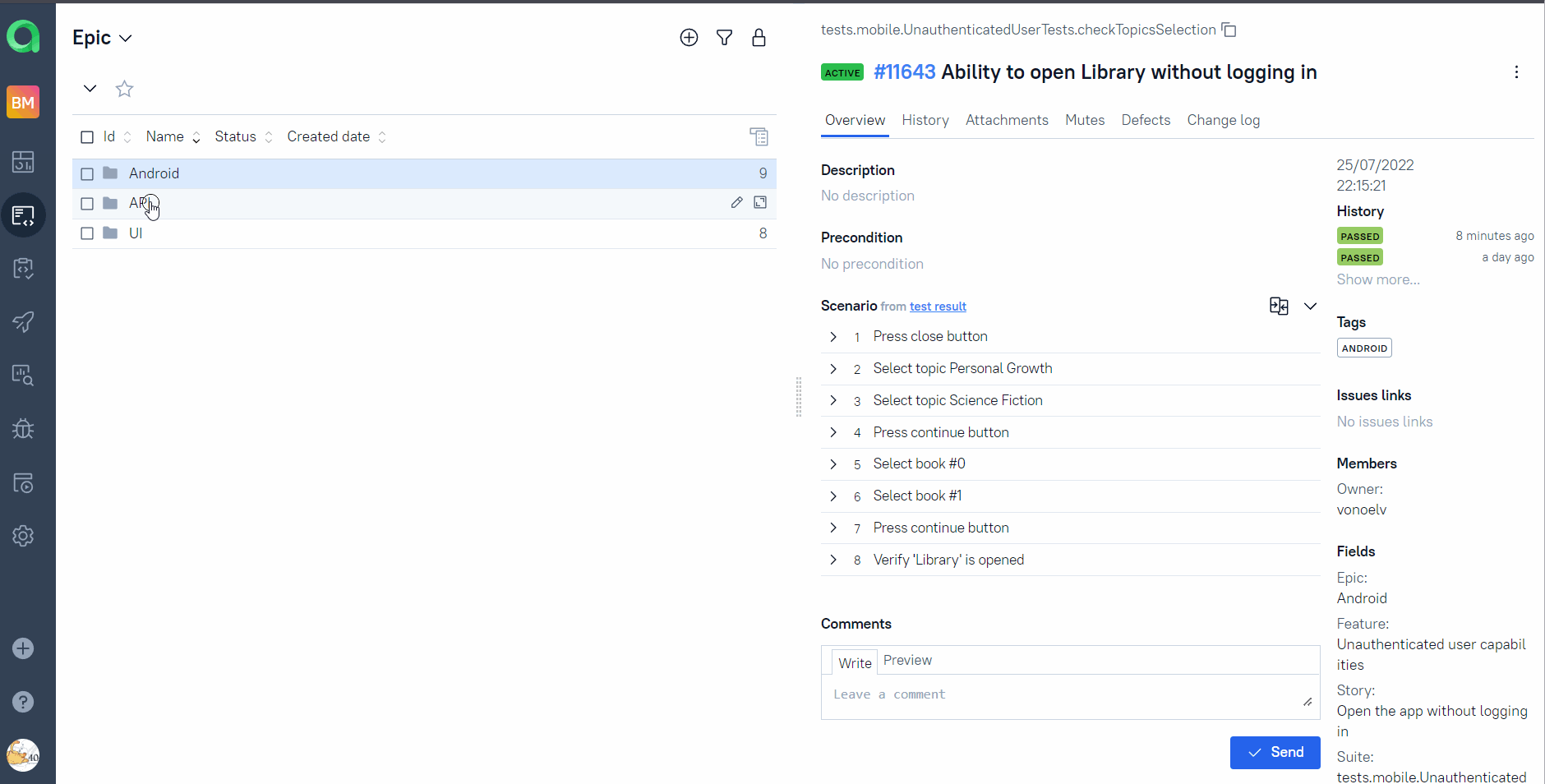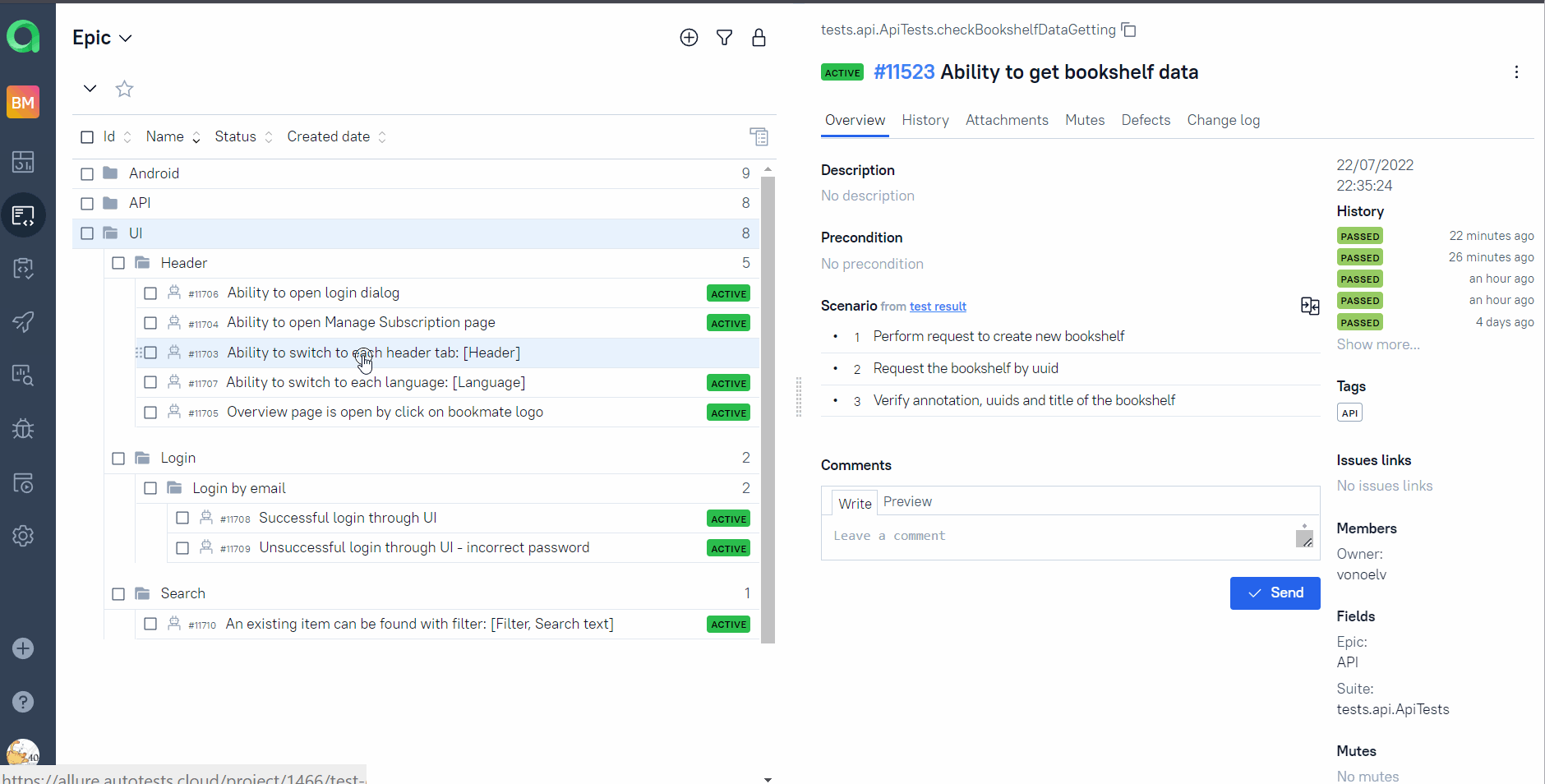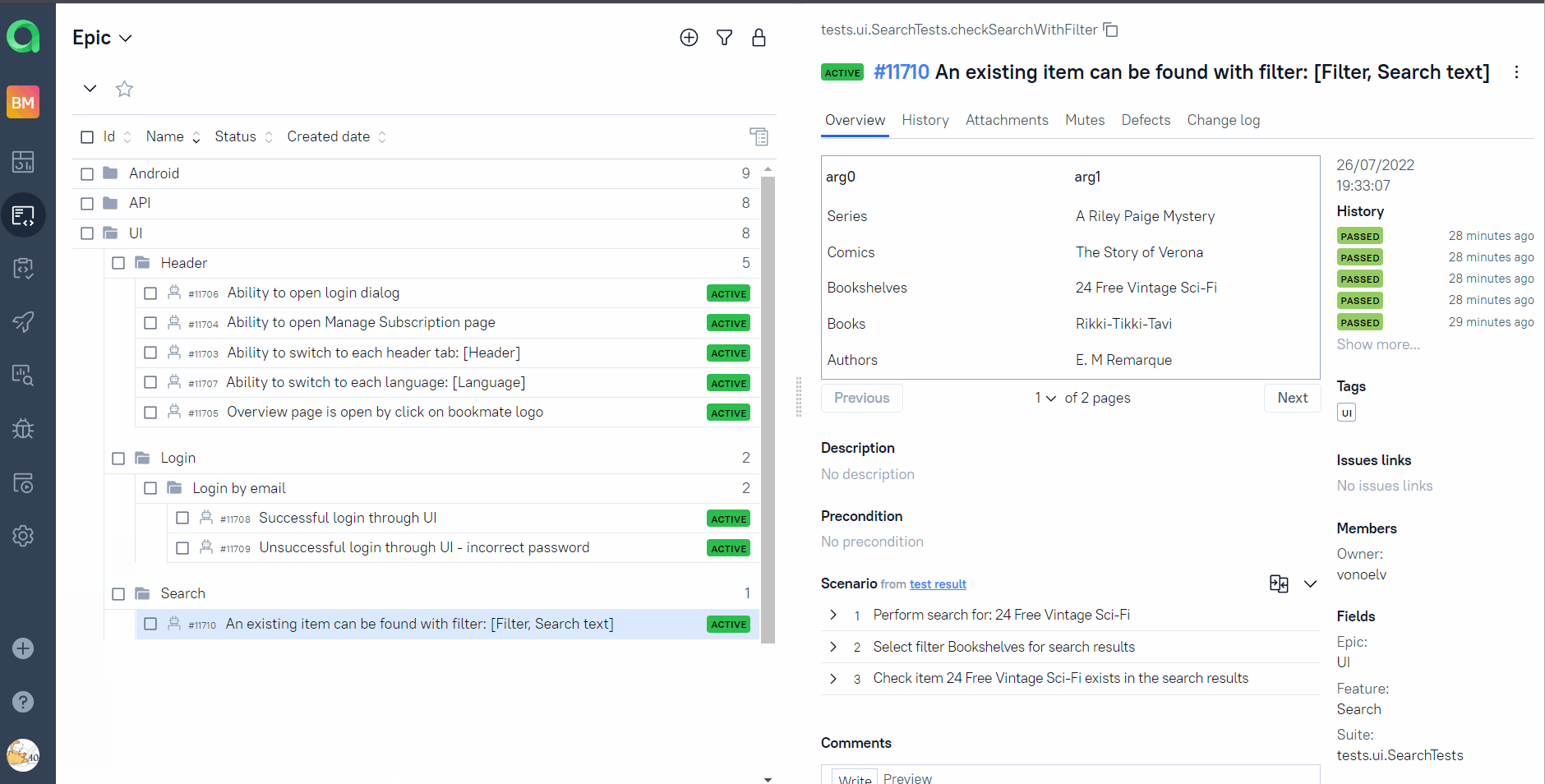
Test-cases in the project are imported and constantly updated from the code,
so there is no need in complex process of synchronization manual test-cases and autotests.
It is enough to create and update an autotest in the code and the test-case in TMS always will be in actual state.
Manual test-cases also can be added in TMS in case of need(via web interface or via code).
stateDiagram-v2
state "Test created/updated in the code" as A
state "Build in Jenkins is triggered on push or started manually" as B
state "Jenkins build is done" as C
state "Allure TestOps launch related to the build marked as closed" as D
state "All executed test-cases are automatically created/updated according to the code" as E
[*] --> A
A --> B
B --> C
C --> D
D --> E
E --> A
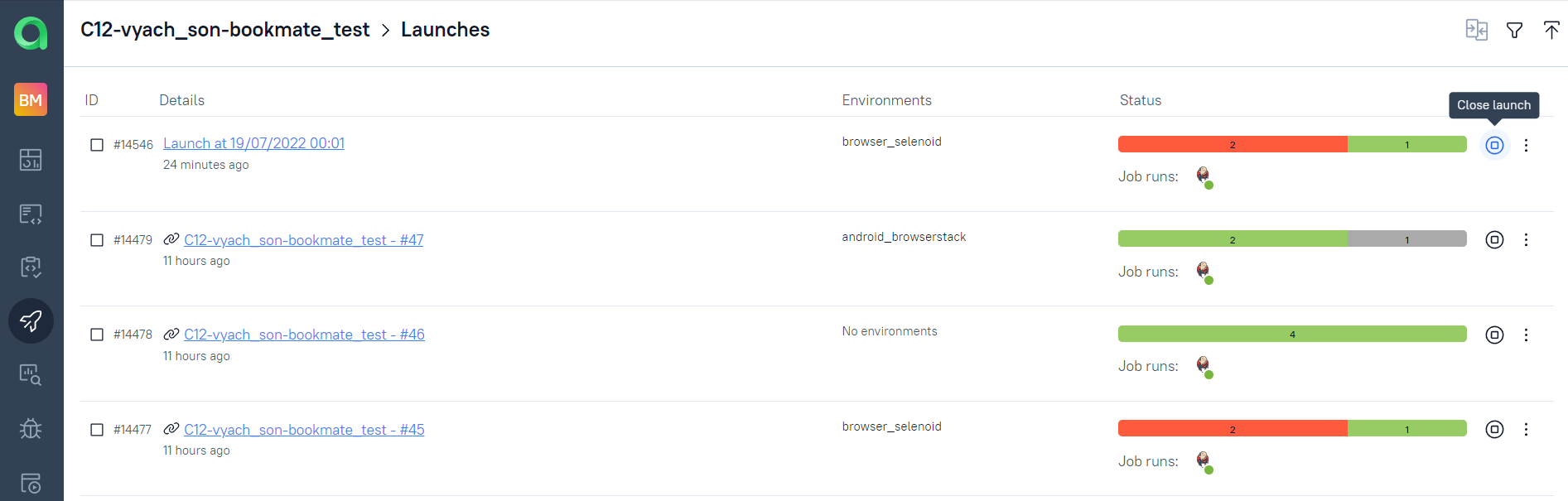
Any person not related to autotest creation can select a set of tests, environment parameter(RunIn) and start a run.
Allure TestOps run will be created, Jenkins job triggered with correct parameters. And results of the job will be seamlessly integrated into Allure TestOps.
As soon as the Jenkins job is done, corresponding tests get their statuses. A tester can finish manual tests(if any) and click "Close launch".
After that all these test-cases(names, steps, tags etc.) will be updated according to the recent code changes.
Back to the table of contents ⬆
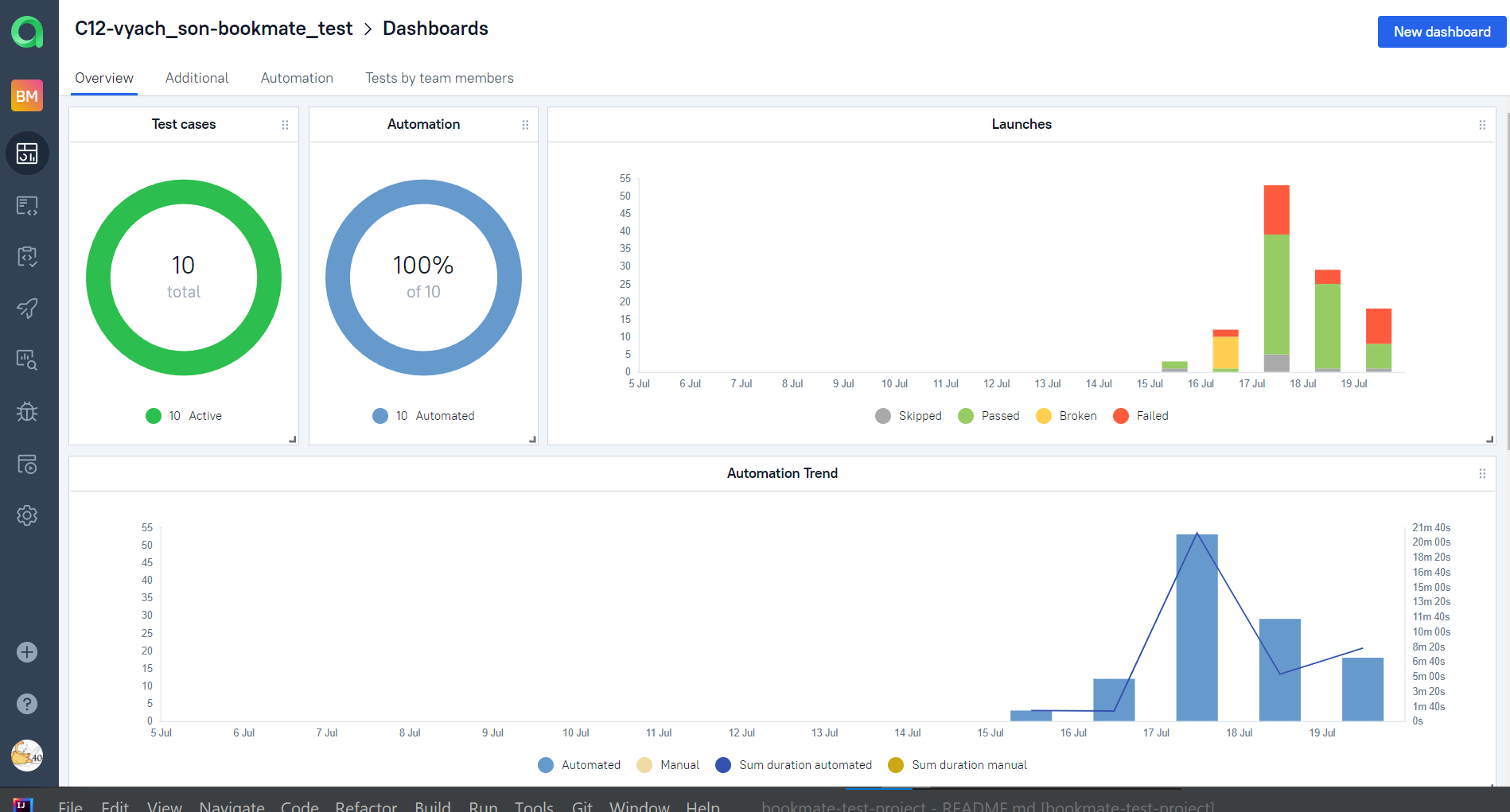
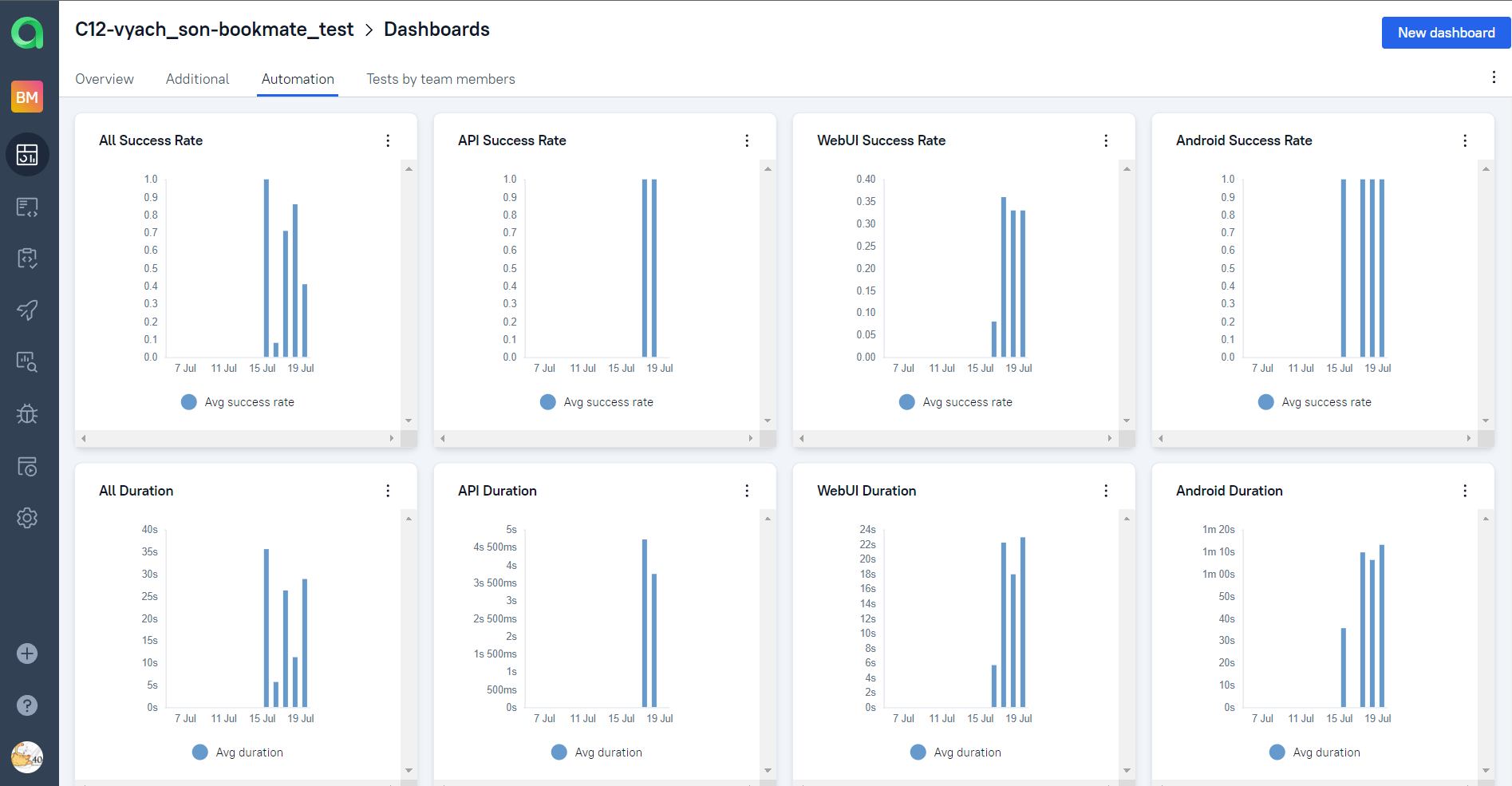
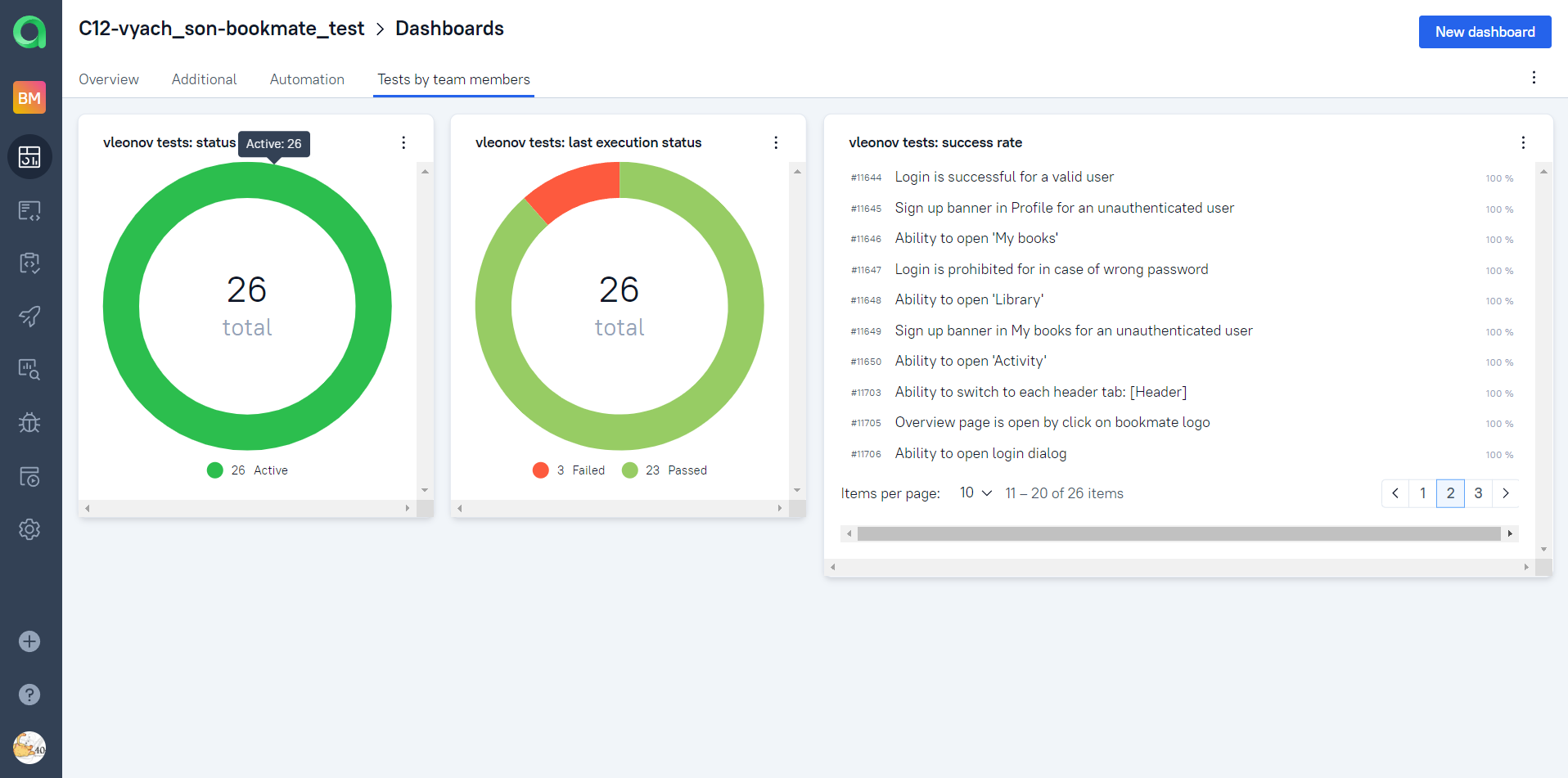
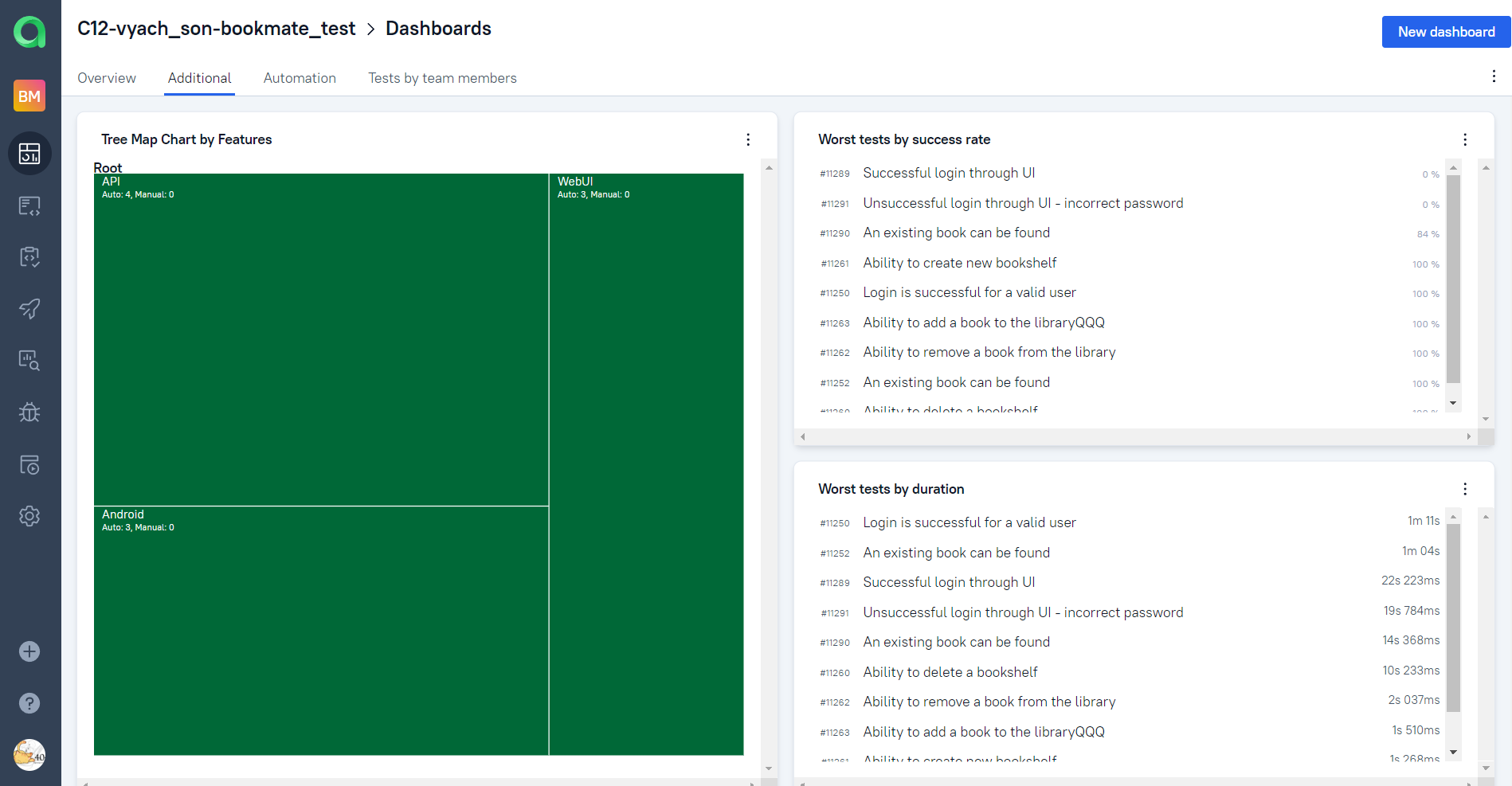
Automation trends charts, distribution tests by some different parameters etc.:
Back to the table of contents ⬆
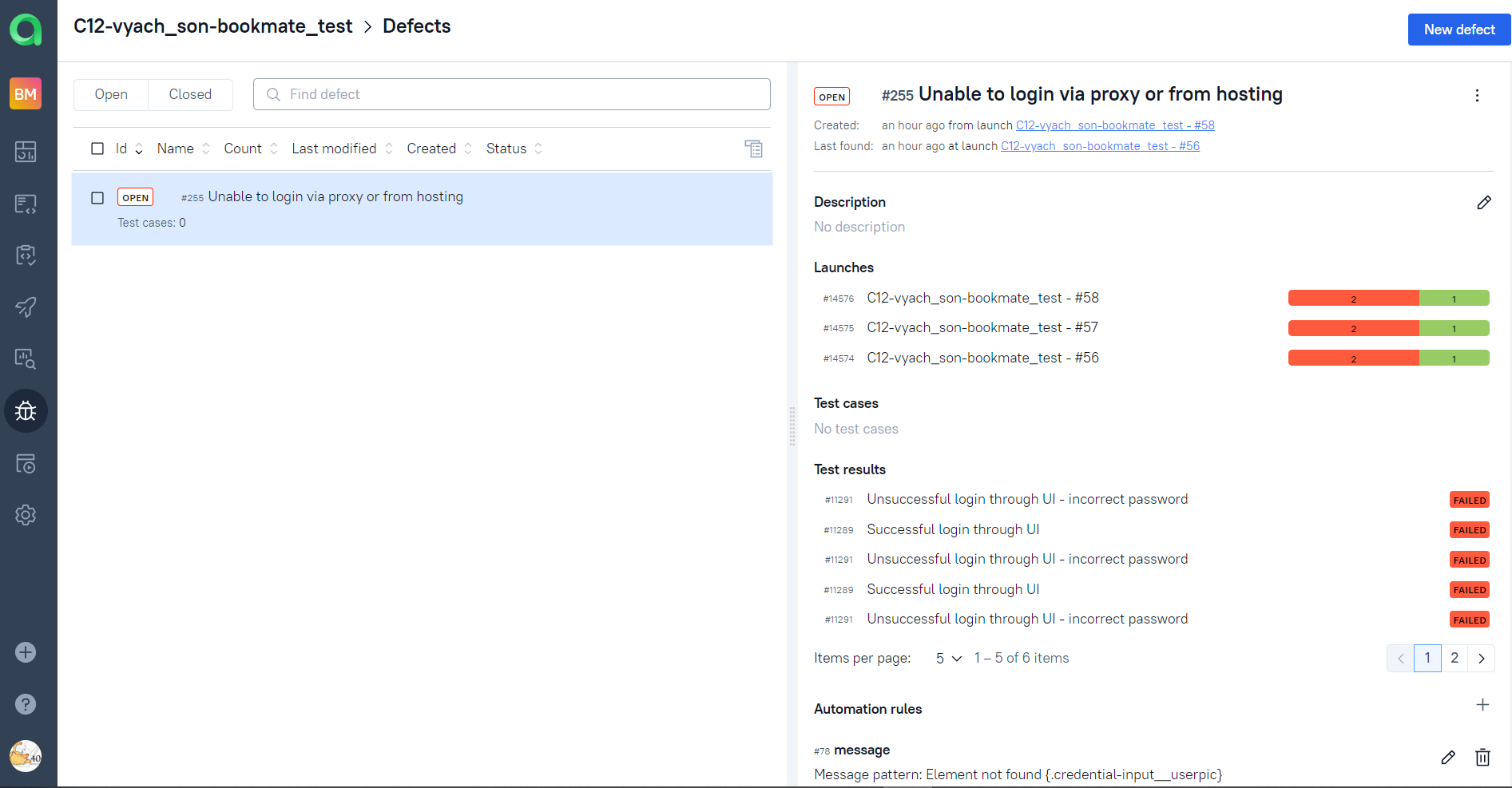
Knows defects are automatically recognized by defined patterns for test fails in further launches.
Back to the table of contents ⬆
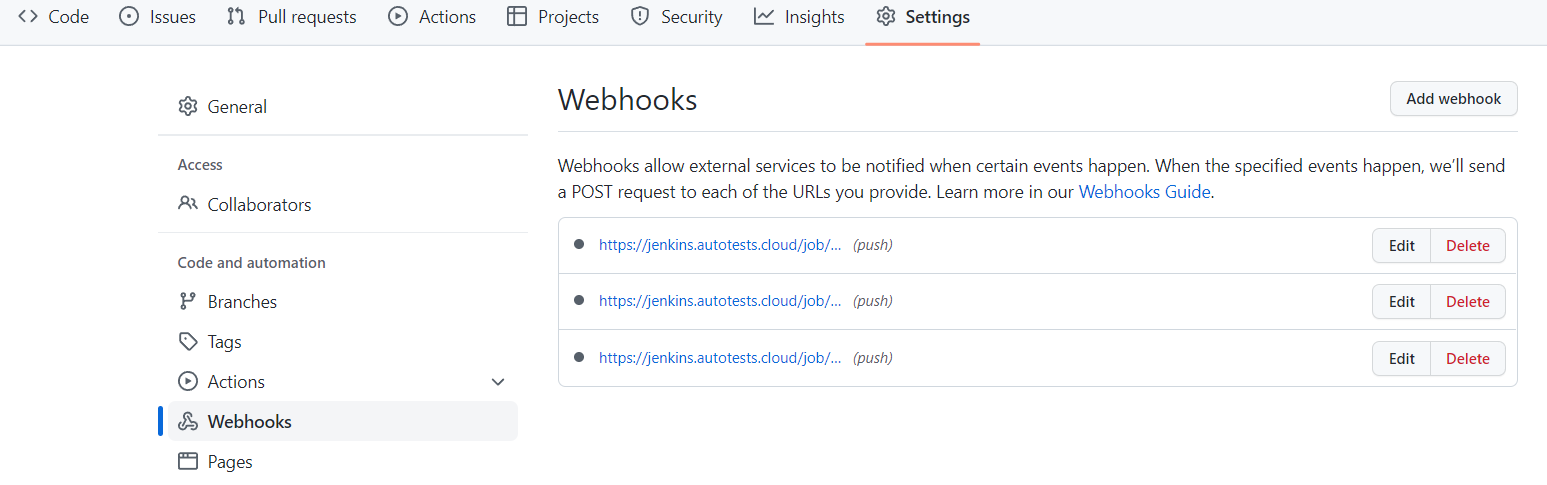
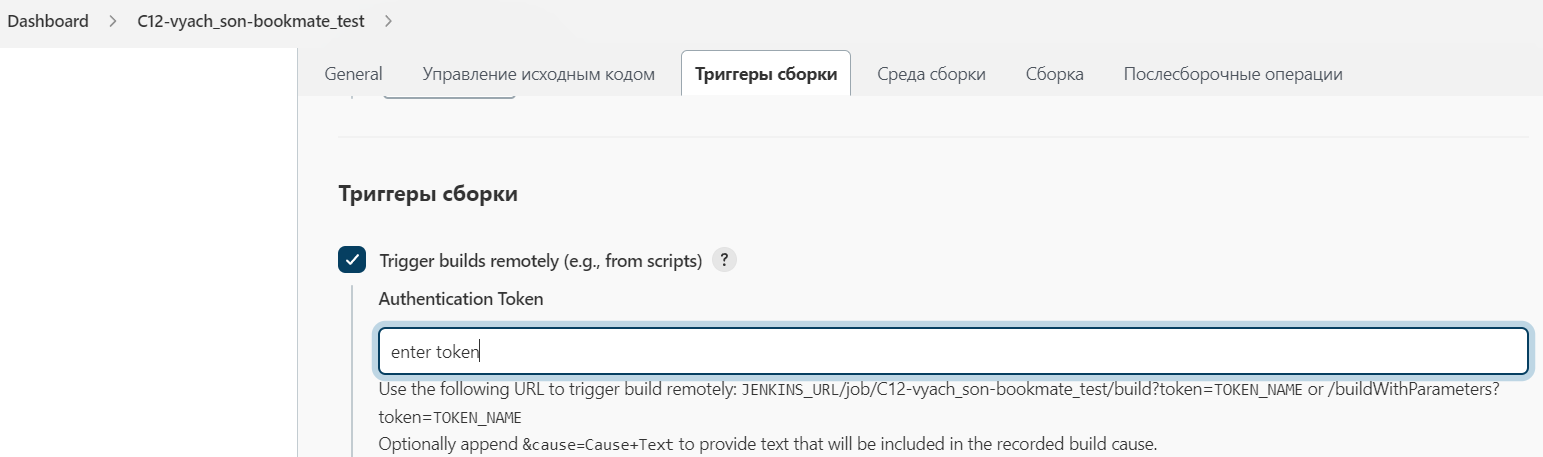
Each push to the repository triggers 3 builds in Jenkins:
gradle clean test -Dtag=APIgradle clean test -Dtag=Web -DrunIn=browser_selenoidgradle clean test -Dtag=Android -DrunIn=android_browserstackThis way we can find problems earlier and always have actual state of test-cases in Allure TestOps.
Back to the table of contents ⬆
Back to the table of contents ⬆