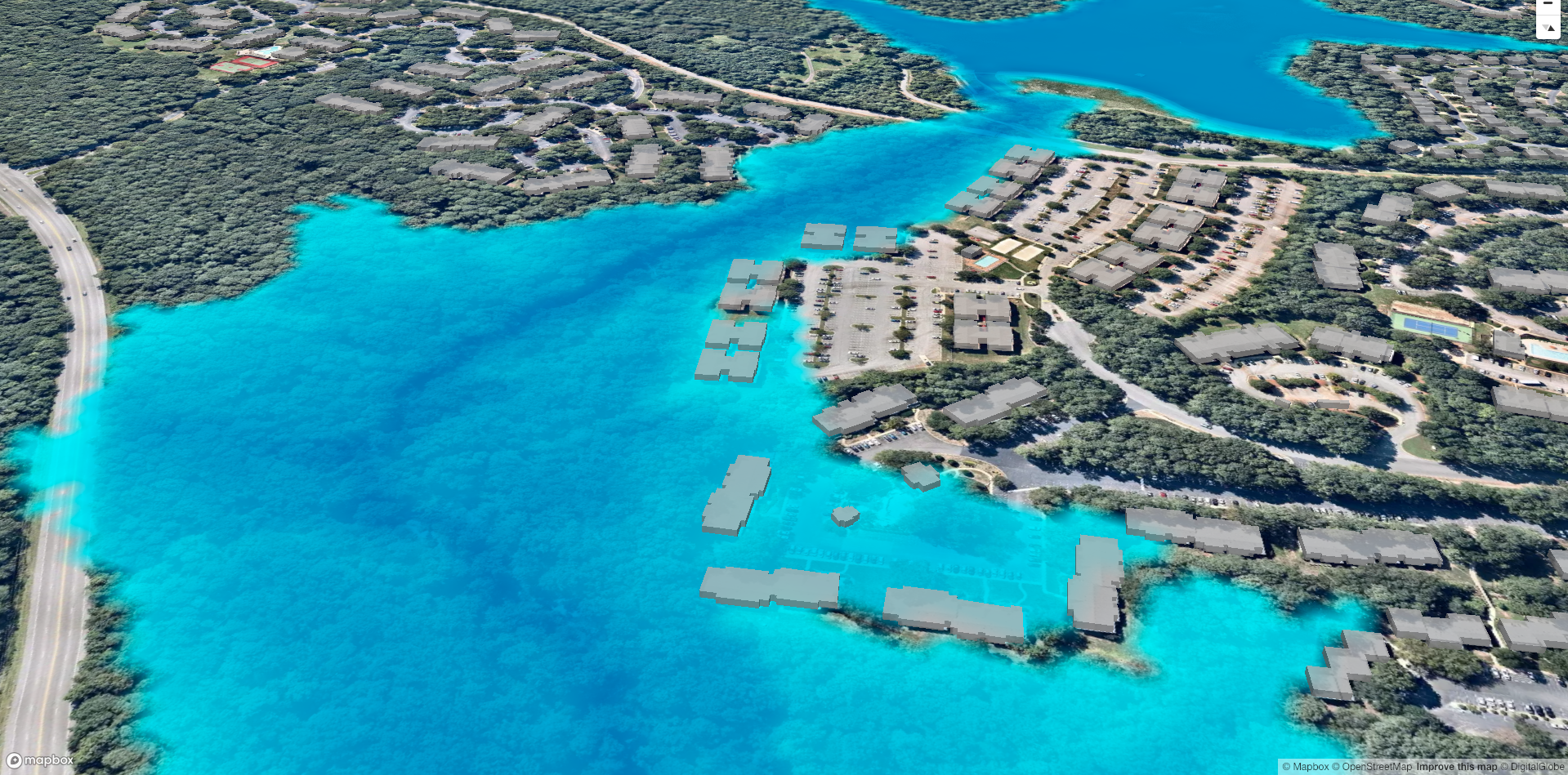
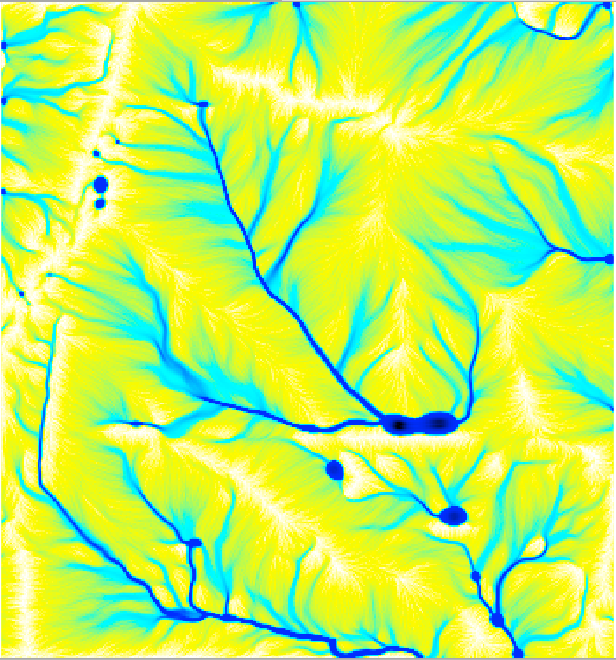
Visualizes SIMWE and the HAND methodolgy using sample datasets from GRASS GIS North Carolina sample data set
The HAND methodology is used to estimate inundation over a given landscape using a combination of GRASS GIS hydrologic modules. To run the HAND methodology first two extensions must be installed (r.stream.distance and r.lake.series) using the g.extension command. After the extensions are installed the computational region must be set to the desired extent. Once the computational region is set the r.watershed module is used to calculate flow accumulation, drainage, and streams with a user-defined threshold. With these newly created layers r.stream.distance can now run to calculate the distance to, and elevation above streams and outlet (GRASS GIS manual: r.stream.distance). Now either r.lake or r.lake.series can be run to create inundation maps. Use r.lake to calculate a single inundation map and r.lake.series to generate inundation maps at various steps intervals from a given start and end depth. Once the inundation maps are generated t.rast.univar can be used to calculate the volume and extent of flooding (From GRASS GIS novice to power user (workshop at FOSS4G Boston 2017)).
Condensed script from From GRASS GIS novice to power user (workshop at FOSS4G Boston 2017).
https://grasswiki.osgeo.org/wiki/From_GRASS_GIS_novice_to_power_user_(workshop_at_FOSS4G_Boston_2017
# GRASS Location: nc_spm_08_grass7
g.extension r.stream.distance
g.extension r.lake.series
r.watershed elevation=elevation accumulation=flowacc drainage=drainage stream=streams threshold=100000
r.to.vect input=streams output=streams type=line
r.stream.distance stream_rast=streams direction=drainage elevation=elevation method=downstream difference=above_stream
r.lake.series elevation=above_stream start_water_level=0 end_water_level=5 water_level_step=0.5 output=inundation seed_raster=streams
| Static Raster Output | Animated |
|---|---|
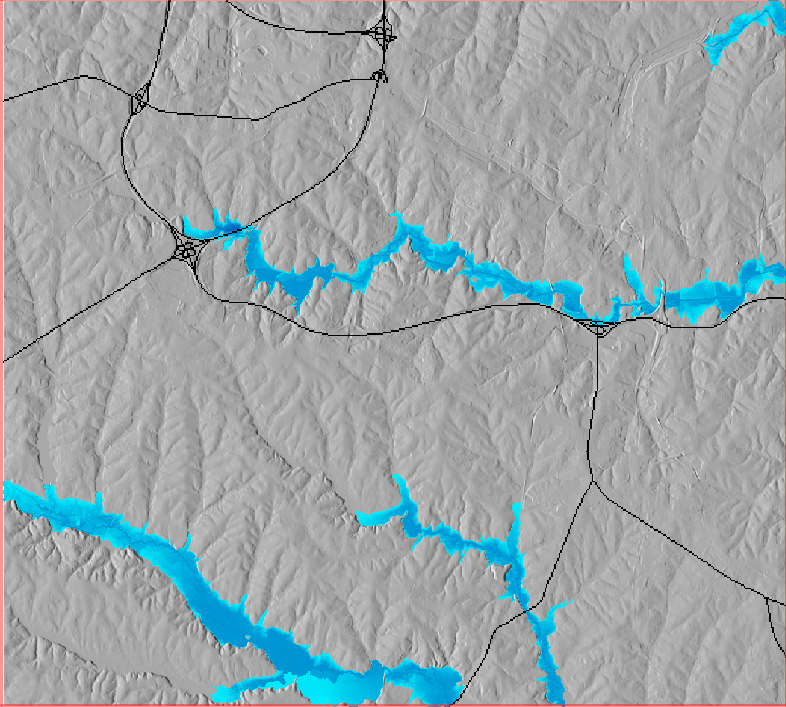 |
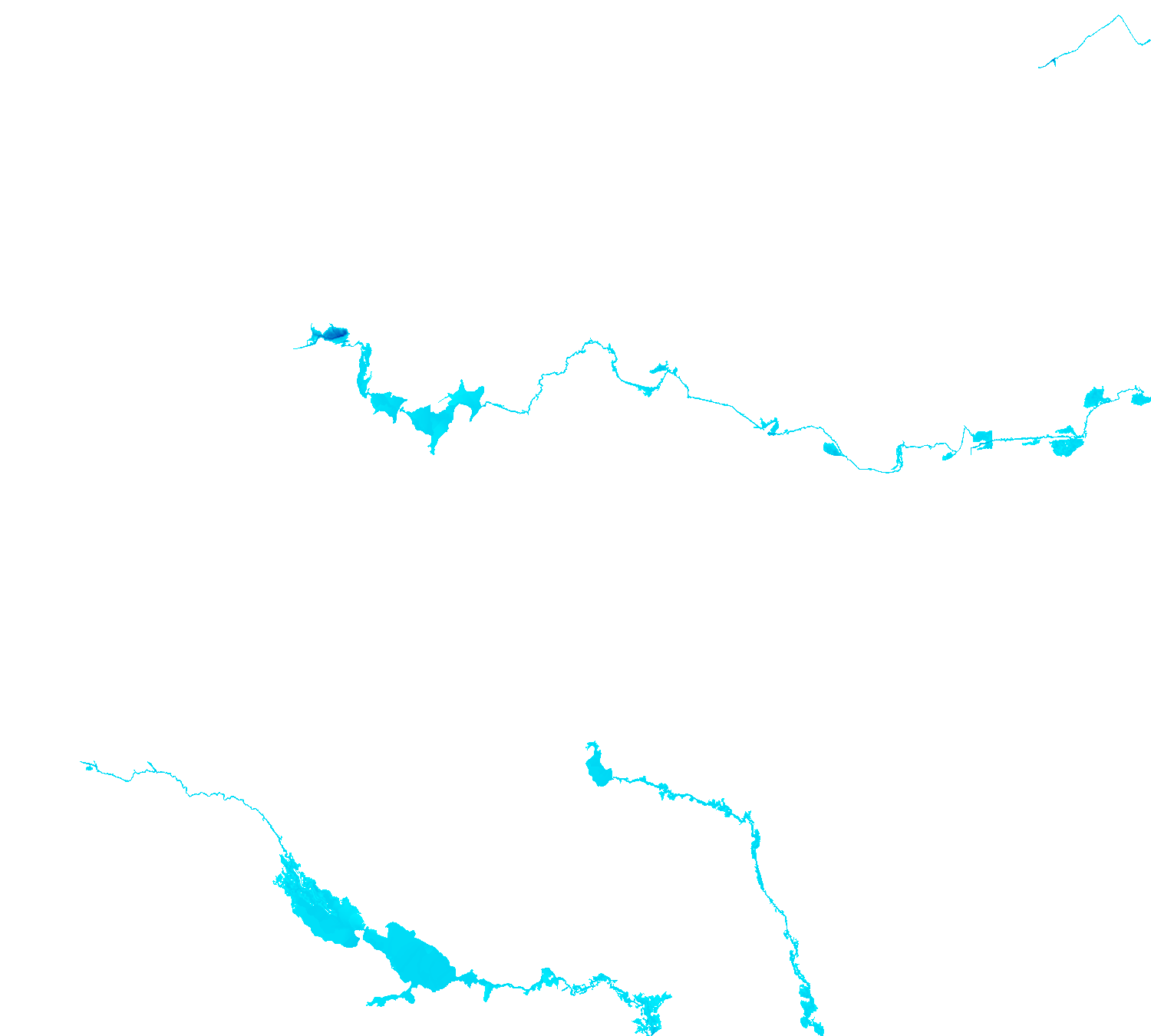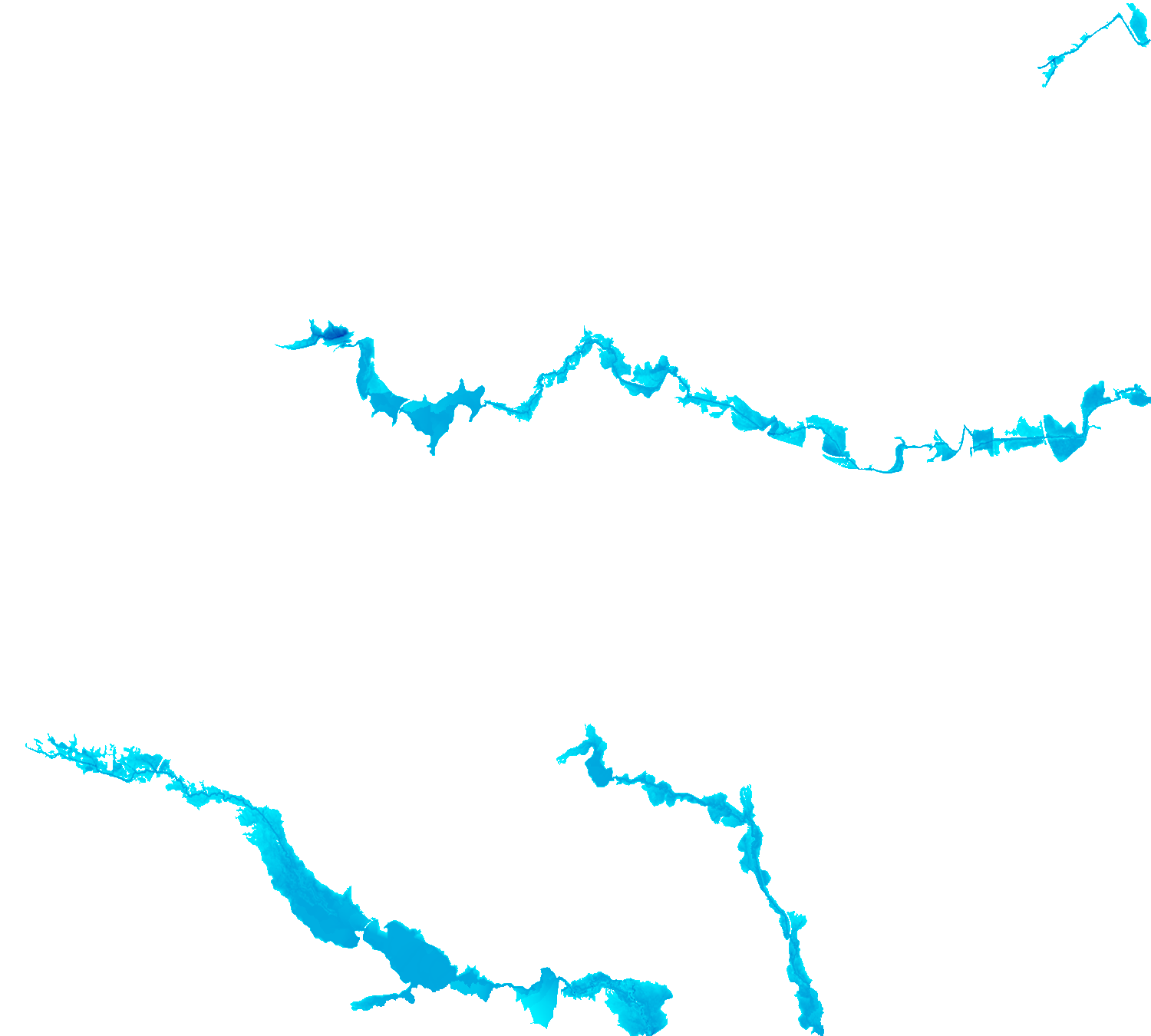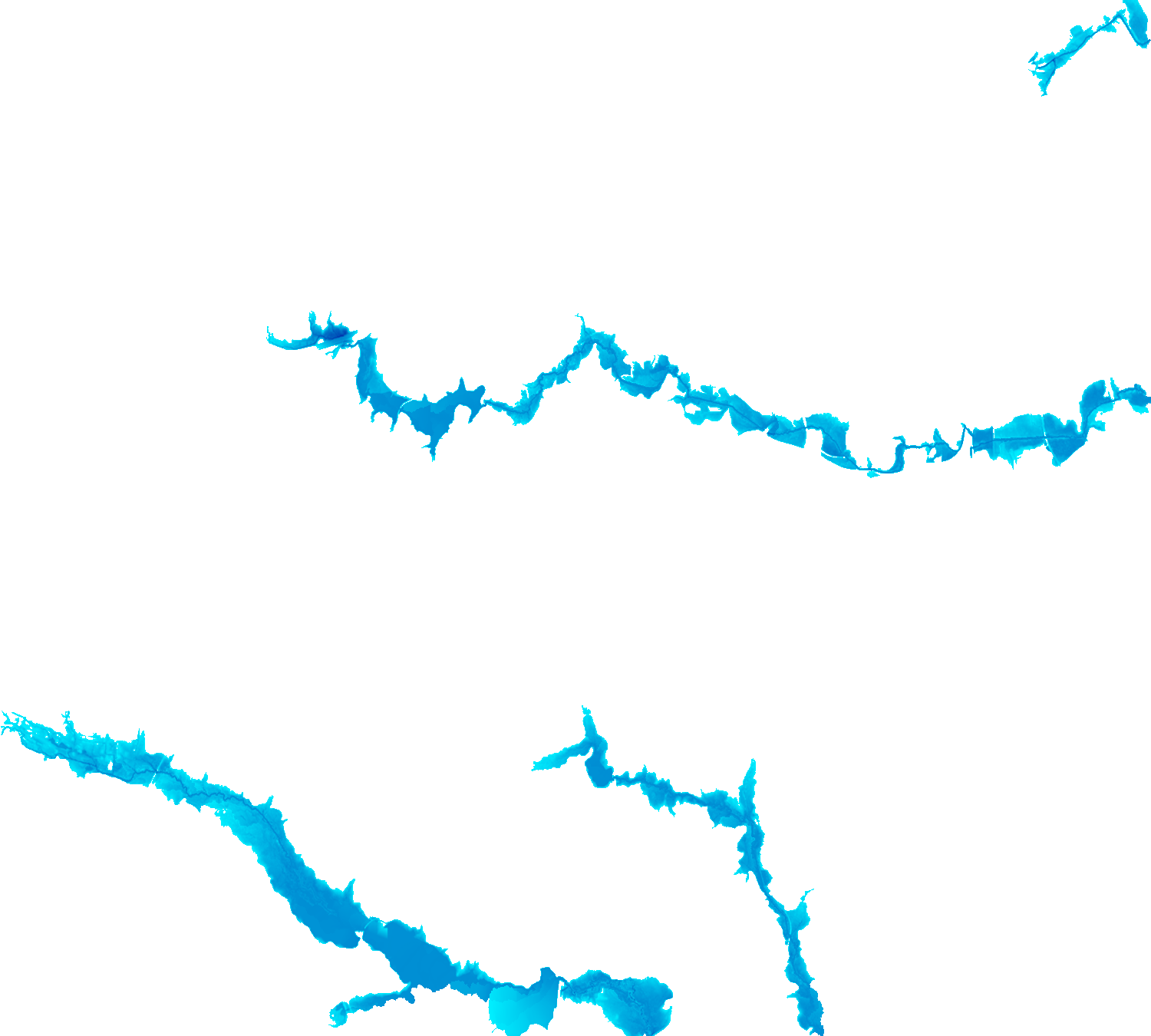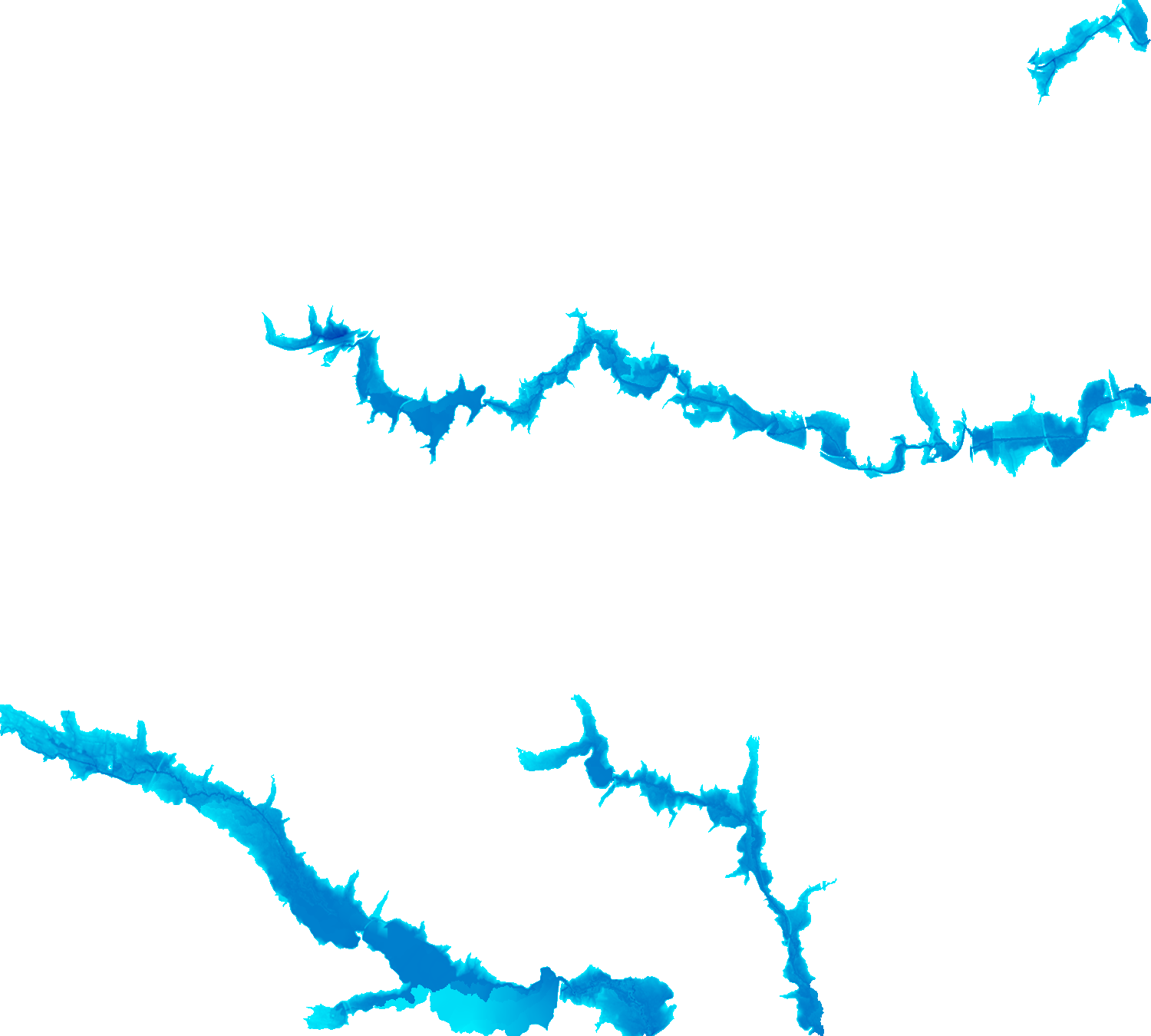 |
SIMWE is a spatially-distributed hydrological model designed to simulate flash floods (Hofierka & Knutová, 2015). SIMWE is implemented as a GRASS GIS module called r.sim.water and requires an elevation raster, as well as the partial derivatives slope and aspect to run. To run the computational region must first be set using g.region. Once the computational region is set, calculate the partial derivatives using v.surf.rst or r.slope.aspect. Now r.sim.water can be used to calculate the overland flow and discharge (GIS/MEA582: Geospatial Modeling and Analysis).
Condensed script from From GIS/MEA582: Geospatial Modeling and Analysis.
https://ncsu-geoforall-lab.github.io/geospatial-modeling-course/grass/simwe.html.
# GRASS Location: nc_spm_08_grass7
g.region rural_1m res=2 -p
v.surf.rst -d input=elev_lid792_bepts elevation=elev_lid792_2m slope=dx_2m aspect=dy_2m tension=15 smooth=1.5 npmin=150
r.sim.water -t elevation=elev_lid792_2m dx=dx_2m dy=dy_2m rain_value=50 infil_value=0 man_value=0.05 depth=wdp_2m discharge=disch_2m nwalkers=100000 niterations=120 output_step=20Set Your MapBox Token
echo MapboxAccessToken="'<YourMapBoxToken>'" > .envYou can use either NPM or Yarn
npm install
npm startyarn install
yarn startnpm run deployIf this does not work for you add
[alias]
stpp = subtree push --prefix
to ~/.gitconfig
Download: GRASS GIS Data: North Carolina sample data set
GRASS GIS manual: r.stream.distance. (n.d.). Retrieved January 23, 2019, from https://grass.osgeo.org/grass74/manuals/addons/r.stream.distance.html
From GRASS GIS novice to power user (workshop at FOSS4G Boston 2017) - GRASS-Wiki. (n.d.). Retrieved January 23, 2019, from https://grasswiki.osgeo.org/wiki/From_GRASS_GIS_novice_to_power_user_(workshop_at_FOSS4G_Boston_2017)#Computational_region
Hofierka, J., & Knutová, M. (2015). Simulating spatial aspects of a flash flood using the Monte Carlo method and GRASS GIS: a case study of the Malá Svinka Basin (Slovakia). Open Geosciences, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1515/geo-2015-0013
GIS/MEA582: Geospatial Modeling and Analysis. (n.d.). Retrieved January 23, 2019, from https://ncsu-geoforall-lab.github.io/geospatial-modeling-course/grass/simwe.html
Nobre, A. D., Cuartas, L. A., Hodnett, M., Rennó, C. D., Rodrigues, G., Silveira, A., … Saleska, S. (2011). Height Above the Nearest Drainage – a hydrologically relevant new terrain model. Journal of Hydrology, 404(1), 13–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.051
GRASS GIS manual: r.lake. (n.d.). Retrieved January 23, 2019, from https://grass.osgeo.org/grass76/manuals/r.lake.html
GRASS GIS manual: t.rast.univar. (n.d.). Retrieved January 23, 2019, from https://grass.osgeo.org/grass76/manuals/t.rast.univar.html
GRASS GIS manual: r.lake.series. (n.d.). Retrieved January 23, 2019, from https://grass.osgeo.org/grass74/manuals/addons/r.lake.series.html
GRASS GIS 7.4.5svn Reference Manual: Topic hydrology. (n.d.). Retrieved January 23, 2019, from https://grass.osgeo.org/grass74/manuals/topic_hydrology.html