GUEB is a static analyzer performing use-after-free detection on binary. The tool is still under development, any commentary / help are welcome.
In summary, GUEB performs a value analysis on binary code, which tracks pointers and the states of the heap objects. When GUEB detects the use of a freed pointer, it extracts the sub-graph representation of the use-after-free.
If you want to try GUEB easily (and skip the compilation part): here you will find a virtual machine with everything installed (login/pass: gueb/gueb) (md5 : 53458b32fee721717455902920b3c6f7), (note that you still need to provide IDA pro and to configure BinNAvi with it).
GUEB will not work on a 32 bits machine (for now). It was tested on a Ubuntu 14.04 64 bits. You need ocaml in version 4.02 installed.
On Ubuntu 14.04:
add-apt-repository ppa:avsm/ppa
apt-get update
apt-get install ocaml m4 opam
opam init
eval `opam config env`
You also need to install piqi:
opam update
opam install piqi
Then you can compile the code
cd src
export PATH=$PATH:~/.opam/system/bin/ && make
Be sure that you have Java 8 installed, if not: (tested on Ubuntu)
add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
apt-get update
apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
Note that if you have differents version of Java installed, you can set the default version of Java to be used with:
update-alternatives --config java
Finally you need jython in version 2.7.0. Jython works better when installed that with the standalone .jar version.
GUEB uses REIL as intermediate representation (see BinNavi) :

First, you need to extract the REIL representation of the binary, from the BinNavi database to a protobuf file. A jython script is provided in export/gui.py.
You need to modify the first lines of export/export_probotuf.py with the right path of instalation and your BinNavi database information.
Then run
cd export
jython gui.py
Chosse the proper module on the first windows.
The second and the third windows allow you to specify all the wrappers to malloc and free.
Two files will be create, the first one is the protobuf file, the second one is the list of functions with no caller (that you can use as entry points on GUEB).
Then you can launch GUEB:
gueb -reil reil_file -func func_name -output-dir results
If a use-after-free is found, results of the analysis will be located in results/func_name/ (as a dot file)
In ./example there are two file :
- gnome-nettool : the protobuf file of gnome-nettool
- gnome-nettool-entry-points : a text file containing all the entry-points of the analysis (all functions without caller)
You can launch GUEB on all the possible entry points:
gueb -reil gnome-nettool -funcs-file gnome-nettool-entry-points -output-dir results -type 2
-type 2 launches the analysis on a set of entry points and is needed with -funcs-file. Be sure to create the directory results prio GUEB execution.
GUEB will detect 5 use-afte-free (4 false positives, 1 true positive).
The real one is located in info_nic_changed :
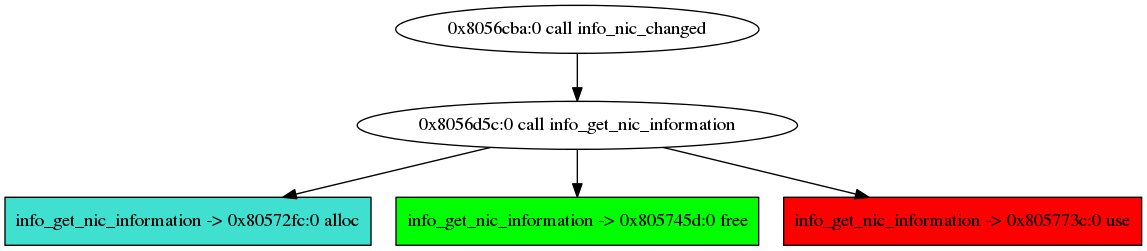 From this tree, we can suspect that the root of the use-after-free is located in the function info_get_nic_information.
We can export the sub-graph of info_get_nic_information leading to the use-after-free:
From this tree, we can suspect that the root of the use-after-free is located in the function info_get_nic_information.
We can export the sub-graph of info_get_nic_information leading to the use-after-free:
gueb -reil gnome-nettool -func info_get_nic_information -flow-graph-dot
A second dot file will be created :
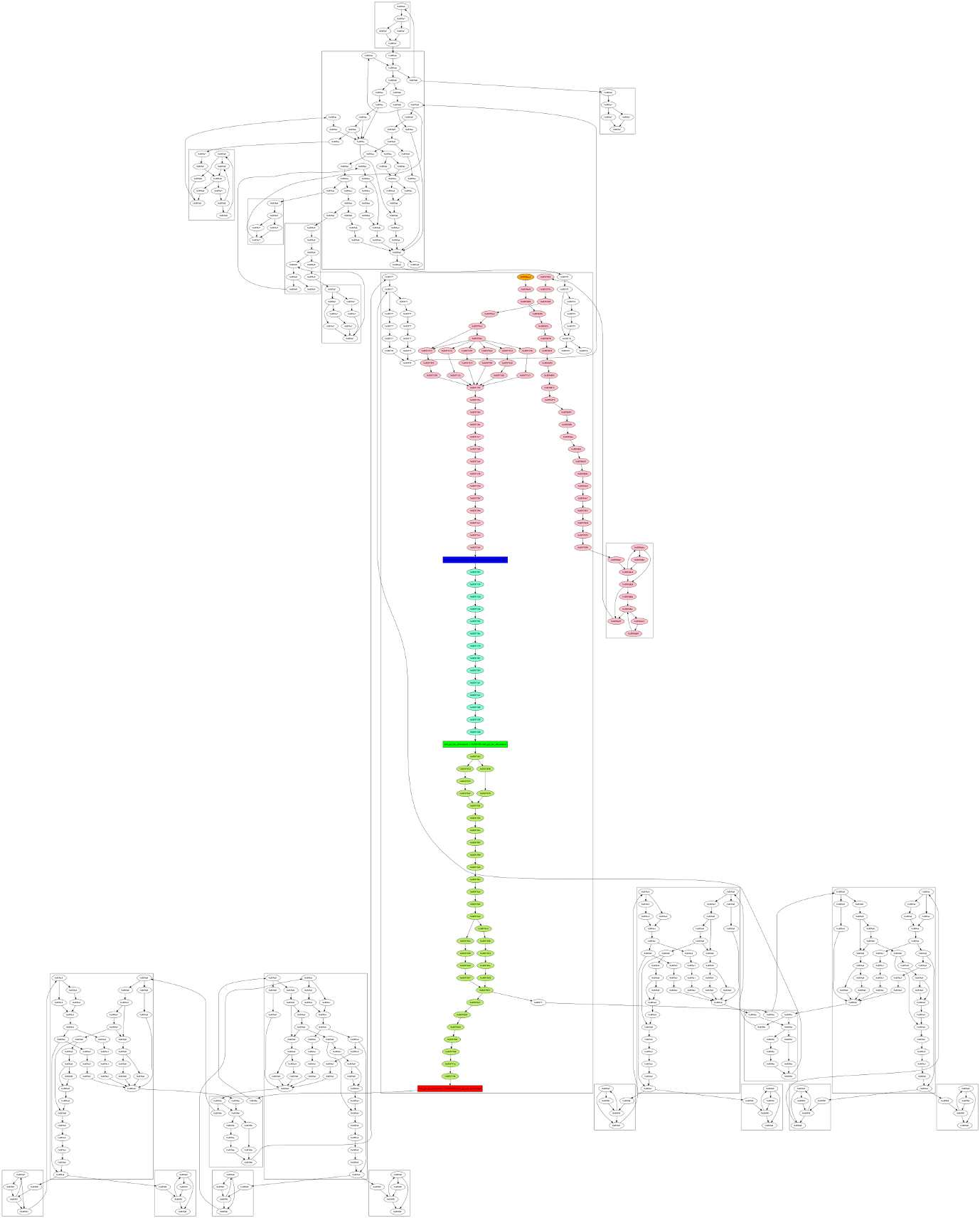
- The node orange is the entry point of the first function
- The blue node is the allocation site
- The green node is the free site
- The red node is the use site
- Others nodes in color represent the sub-graph leading to the use-after-free
- Nodes of the same function are grouped into boxes
You can create a representation that do not include any arc between the ret instructions of the functions and their callers, with :
gueb -reil gnome-nettool -func info_get_nic_information -flow-graph-dot -flow-graph-call-disjoint
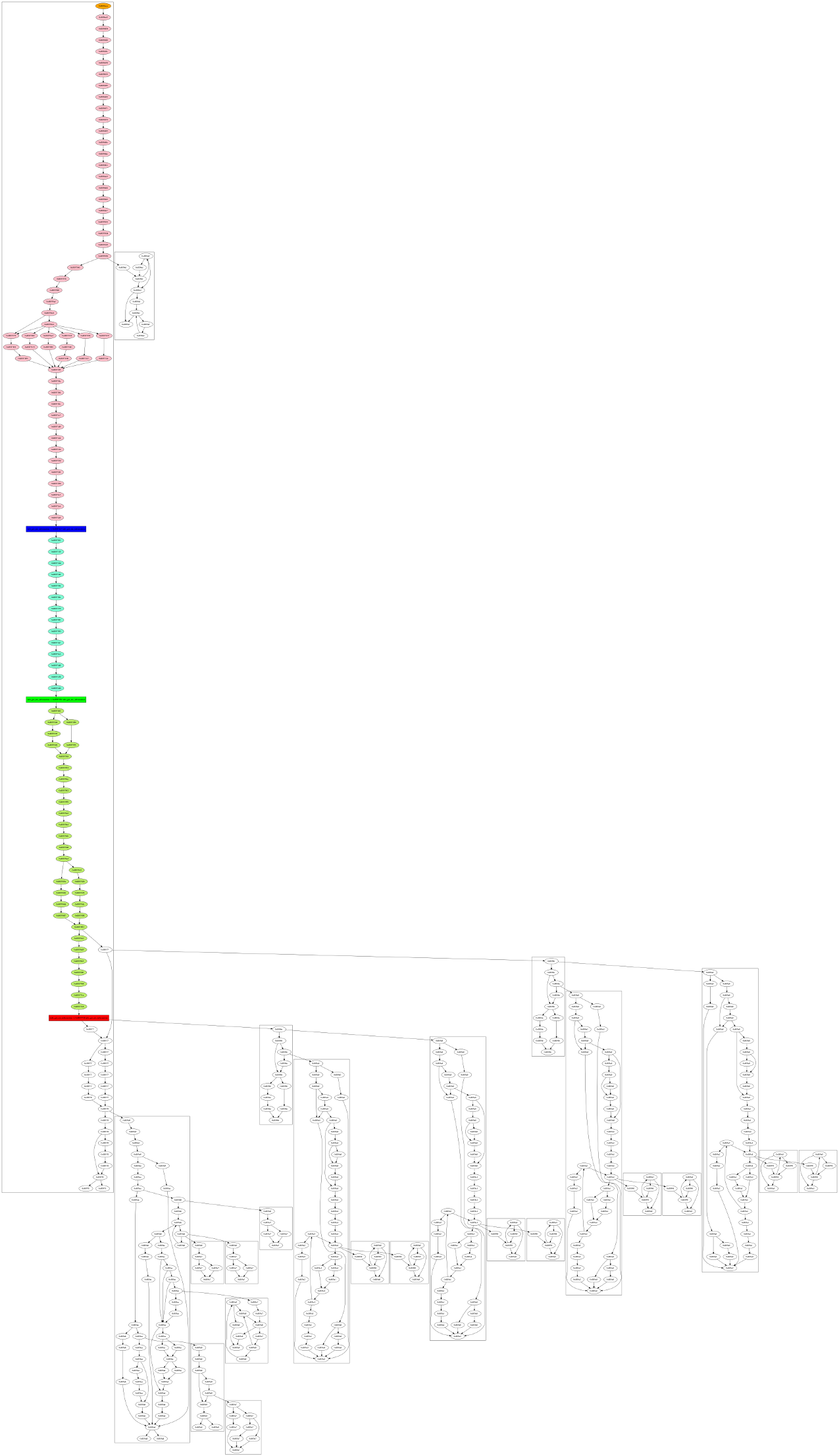 This representation can be easier to understand.
This representation can be easier to understand.
You can find more options with
gueb -help
- Calling convention: for now gueb supports only cdecl
- GUEB is still a prototype, large binaries are out of scope of the analysis
Some user reported a trouble to build piqilib. During piqi installation, piqilib can be installed in version 0.6.6 with opam. If so, please update your piqilib at the version 0.6.12.
- Jasper-JPEG-200 (CVE-2015-5221)
- openjpeg (CVE-2015-8871)
- gnome-netool : https://bugzilla.gnome.org/show_bug.cgi?id=753184
- bind (https://fossies.org/diffs/bind/9.10.2-P4_vs_9.10.3/CHANGES-diff.html ( 4179. [bug] Fix double frees in getaddrinfo() in libirs. [RT #40209] )
- accel-ppp (http://accel-ppp.org/forum/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=581)
- giflib (CVE-2016-3177)
Feist Josselin (josselin.feist [SPAM] gmail.com)
This tool is a part of my thesis: Finding the needle in the heap : combining binary analysis techniques to trigger use-after-free
Benjamin Farinier (CEA) for this advice in Ocaml.