You can find the user guide in the official Kubernetes documentation.
The detailed design of the project can be found in the following docs:
For the broader view of monitoring in Kubernetes take a look into Monitoring architecture
Compatibility matrix:
| Metrics Server | Metrics API group/version | Supported Kubernetes version |
|---|---|---|
| 0.3.x | metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1 |
1.8+ |
| 0.2.x | metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1 |
1.8+ |
| 0.1.x | metrics/v1alpha1 |
1.7 |
In order to deploy metrics-server in your cluster run the following command from the top-level directory of this repository:
# Kubernetes 1.7
$ kubectl create -f deploy/1.7/
# Kubernetes > 1.8
$ kubectl create -f deploy/1.8+/You can also use this helm chart to deploy the metric-server in your cluster (This isn't supported by the metrics-server maintainers): https://github.com/helm/charts/tree/master/stable/metrics-server
If you want to test metric-server in a minikube cluster, please follow the steps below:
$ minikube version
minikube version: v1.2.0
# disable the metrics-server addon for minikube in case it was enabled, because it installs the metric-server@v0.2.1
$ minikube addons disable metrics-server
# now start a new minikube
$ minikube delete; minikube start --extra-config=kubelet.authentication-token-webhook=true
🔥 Deleting "minikube" from virtualbox ...
💔 The "minikube" cluster has been deleted.
😄 minikube v1.2.0 on linux (amd64)
🔥 Creating virtualbox VM (CPUs=2, Memory=2048MB, Disk=20000MB) ...
🐳 Configuring environment for Kubernetes v1.15.0 on Docker 18.09.6
▪ kubelet.authentication-token-webhook=true
🚜 Pulling images ...
🚀 Launching Kubernetes ...
⌛ Verifying: apiserver proxy etcd scheduler controller dns
🏄 Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube"
# deploy the latest metric-server
$ kubectl create -f deploy/1.8+/
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:aggregated-metrics-reader created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server:system:auth-delegator created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server-auth-reader created
apiservice.apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io created
serviceaccount/metrics-server created
deployment.extensions/metrics-server created
service/metrics-server created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
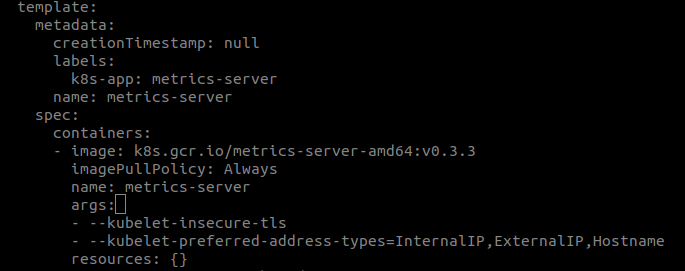
# edit metric-server deployment to add the flags
# args:
# - --kubelet-insecure-tls
# - --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
$ kubectl edit deploy -n kube-system metrics-serverMetrics Server supports all the standard Kubernetes API server flags, as
well as the standard Kubernetes glog logging flags. The most
commonly-used ones are:
-
--logtostderr: log to standard error instead of files in the container. You generally want this on. -
--v=<X>: set log verbosity. It's generally a good idea to run a log level 1 or 2 unless you're encountering errors. At log level 10, large amounts of diagnostic information will be reported, include API request and response bodies, and raw metric results from Kubelet. -
--secure-port=<port>: set the secure port. If you're not running as root, you'll want to set this to something other than the default (port 443). -
--tls-cert-file,--tls-private-key-file: the serving certificate and key files. If not specified, self-signed certificates will be generated, but it's recommended that you use non-self-signed certificates in production. -
--kubelet-certificate-authority: the path of the CA certificate to use for validate the Kubelet's serving certificates.
Additionally, Metrics Server defines a number of flags for configuring its behavior:
-
--metric-resolution=<duration>: the interval at which metrics will be scraped from Kubelets (defaults to 60s). -
--kubelet-insecure-tls: skip verifying Kubelet CA certificates. Not recommended for production usage, but can be useful in test clusters with self-signed Kubelet serving certificates. -
--kubelet-port: the port to use to connect to the Kubelet (defaults to the default secure Kubelet port, 10250). -
--kubelet-preferred-address-types: the order in which to consider different Kubelet node address types when connecting to Kubelet. Functions similarly to the flag of the same name on the API server.