In this work, we introduce AdaPrompt, a framwork that retrieves data from large raw text for continual pre-training prompt-based systems.
AdaPrompt: Adaptive Model Training for Prompt-based NLP
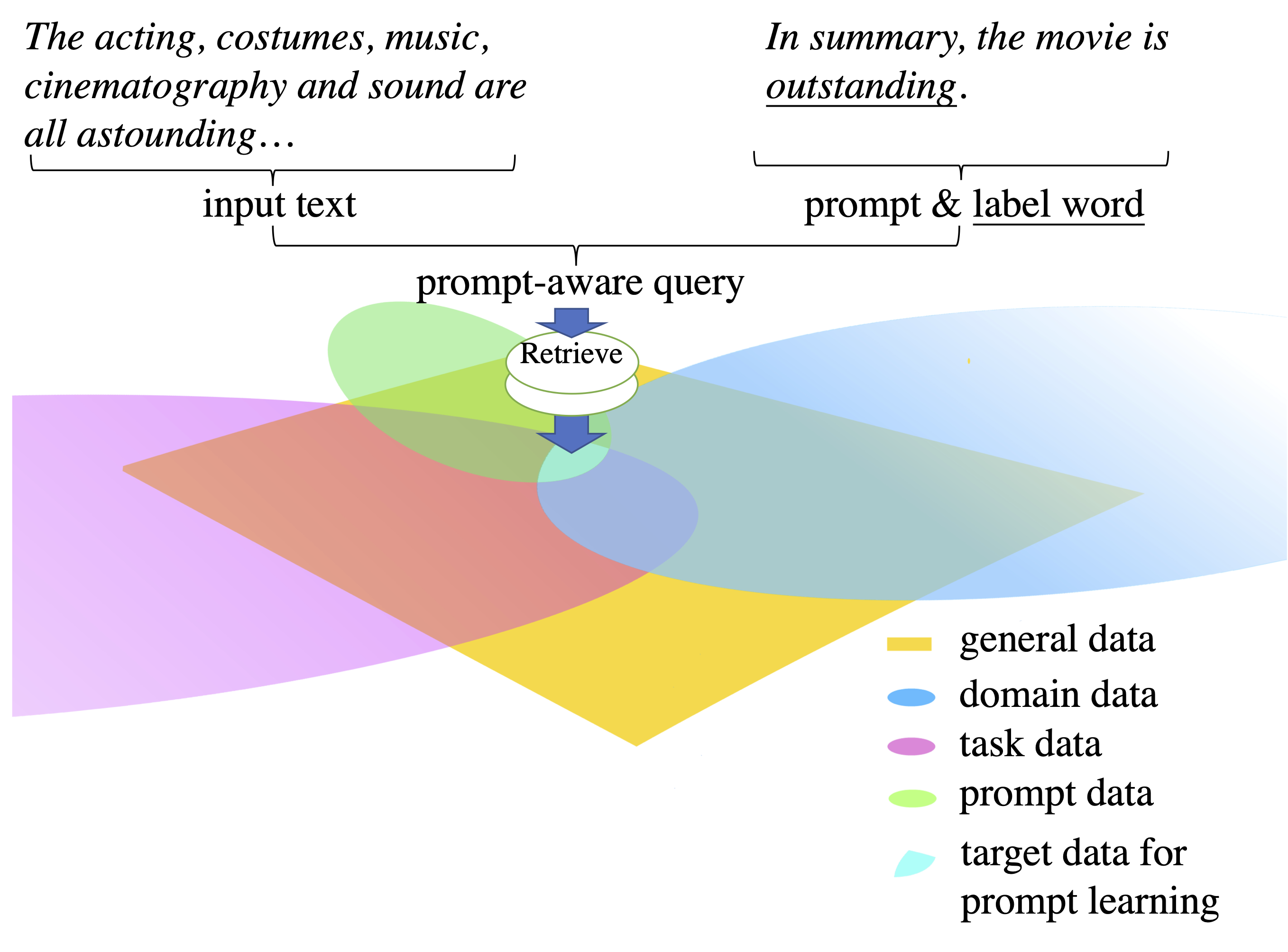
AdaPrompt aims to improve the model performance when using small language models (such as BERT) for prompt learning in a low-resource setting. The main idea is to adapt a PLM to a strong prompt-based model for an end task by exploring knowledge from its raw input data.
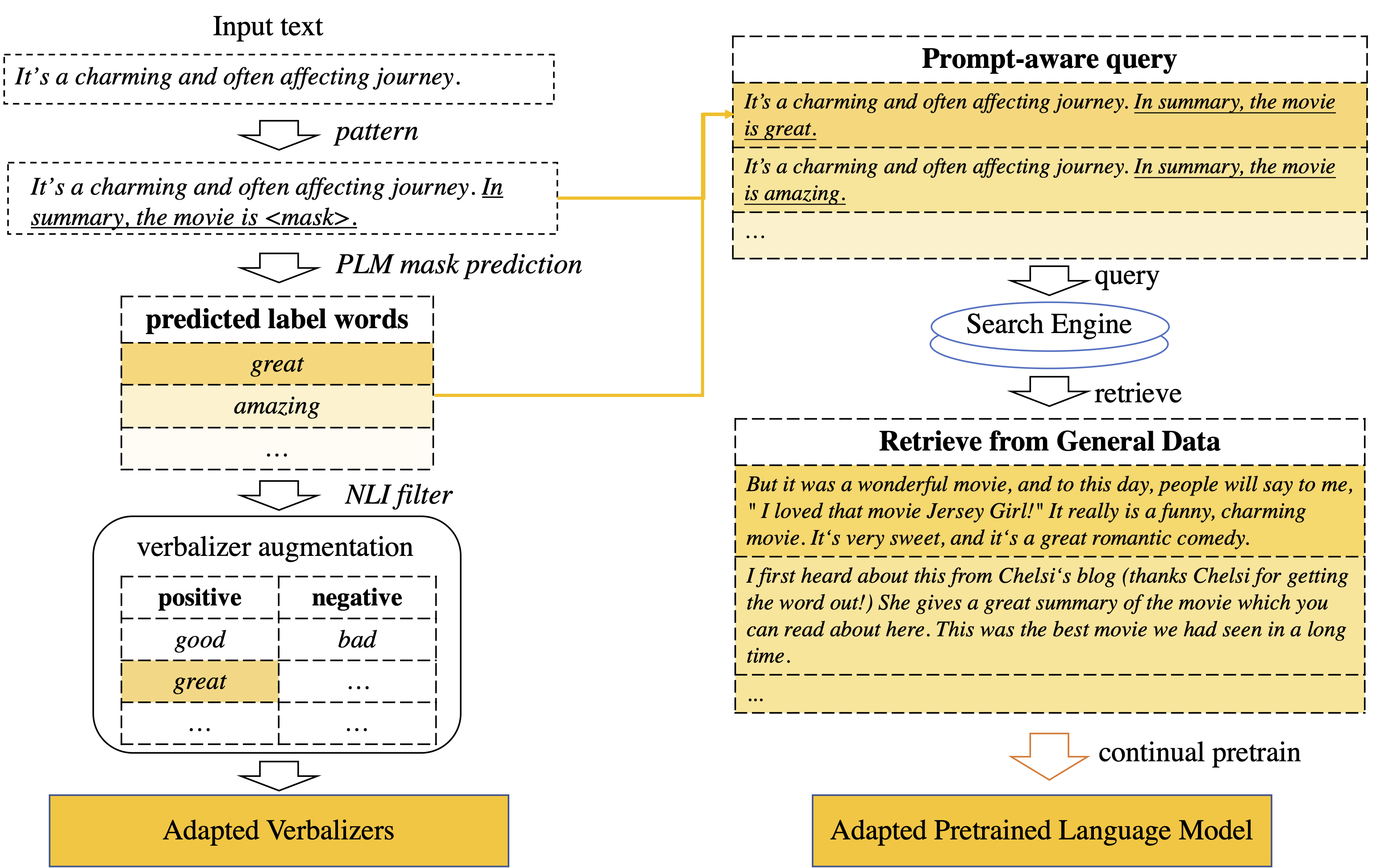
The overall procedure is shown in the above figure.
- First, we use the Roberta-large to give labels on those samples using prompt as shown in the paper.
In particular, for example, given a sentence
"I like the movie", we first convert all data into"X. In summary, the movie is <MASK>.", i.e."I like the movie. In summary, the movie is <MASK>,". - Then we use a language model (e.g., Roberta large) to label them and obtain the top-K words to have the sentences like:
"X. In summary, the movie is good","X. In summary, the movie is great","X. In summary, the movie is interesting", etc. - These sentences will be then used as queries to retrieve raw data using the Elastic. For elastic (https://www.elastic.co/), we index the data which is used for Roberta pretaining on sentence level.
- After having the retrieved data, we first deduplicate them, and use them for continual pretraining (https://github.com/allenai/dont-stop-pretraining).
- Now, we assume the model has gained more related knowledge for prompt-based learning on downstream tasks. For PET experiments, we use the code from https://github.com/timoschick/pet.
This process can be framed in an iterative way.
As regular prompt- based method defines the verbalizer that maps predicted label word into task classes, such as “good” for positive and “bad” for negative. However, predefined verbalizer can be limited. To expand this verbalizer, we first infer top-|O| label words at mask token position over all inputs in test set. Then, we filter the predicted words and obtain a set of high frequent words C as candidates for verbalizer augmentation. Then, we propose a new method for exploring useful verbalizer words by using knowl- edge from a Natural Language Entailment model.
If you find our paper interesting, please kindly cite our paper:
@inproceedings{chen-etal-2022-adaprompt,
title = "{A}da{P}rompt: Adaptive Model Training for Prompt-based {NLP}",
author = "Chen, Yulong and
Liu, Yang and
Dong, Li and
Wang, Shuohang and
Zhu, Chenguang and
Zeng, Michael and
Zhang, Yue",
editor = "Goldberg, Yoav and
Kozareva, Zornitsa and
Zhang, Yue",
booktitle = "Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2022",
month = dec,
year = "2022",
address = "Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2022.findings-emnlp.448",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2022.findings-emnlp.448",
pages = "6057--6068",
abstract = "Prompt-based learning, with its capability to tackle zero-shot and few-shot NLP tasks, has gained much attention in the community. The main idea is to bridge the gap between NLP downstream tasks and language modeling (LM), by mapping these tasks into natural language prompts, which are then filled by pre-trained language models (PLMs).However, for prompt learning, there are still two salient gaps between NLP tasks and pretraining. First, prompt information is not necessarily sufficiently present during LM pre-training. Second, task-specific data are not necessarily well represented during pre-training. We address these two issues by proposing AdaPrompt, adaptively retrieving external data for continual pretraining of PLMs by making use of both task and prompt characteristics. In addition, we make use of knowledge in Natural Language Inference models for deriving adaptive verbalizers.Experimental results on five NLP benchmarks show that AdaPrompt can improve over standard PLMs in few-shot settings. In addition, in zero-shot settings, our method outperforms standard prompt-based methods by up to 26.35{\%} relative error reduction.",
}