The rapid advances in technology of the last decades are characterized by a proportionate increase in its complexity, a fact that makes it a necessity to search for ways to constitute our interaction with it familiar and friendly. The recent spectacular growth in machine learning and artificial intelligence has led to high expectations for natural human-robot interaction. Therefore, communication via natural language is an important next objective which has recently led to the development of various systems of natural language understanding.
Programmable general purpose robots, such as NAO, can be utilized for everyday personal use. The ability to program such machines without technical knowledge through the use of natural language can result in a significant improvement of their usefulness.
This diploma thesis aims to recognize inside a natural language text actions that belong to a predefined list and map them to an already existing robotic platform. It is not attempted to synthesize a fully working algorithm that reflects the logic of the text; rather, a static mapping of the given sentences to actions is performed. The output of the system could be processed by an independent application for the final production of executable code.
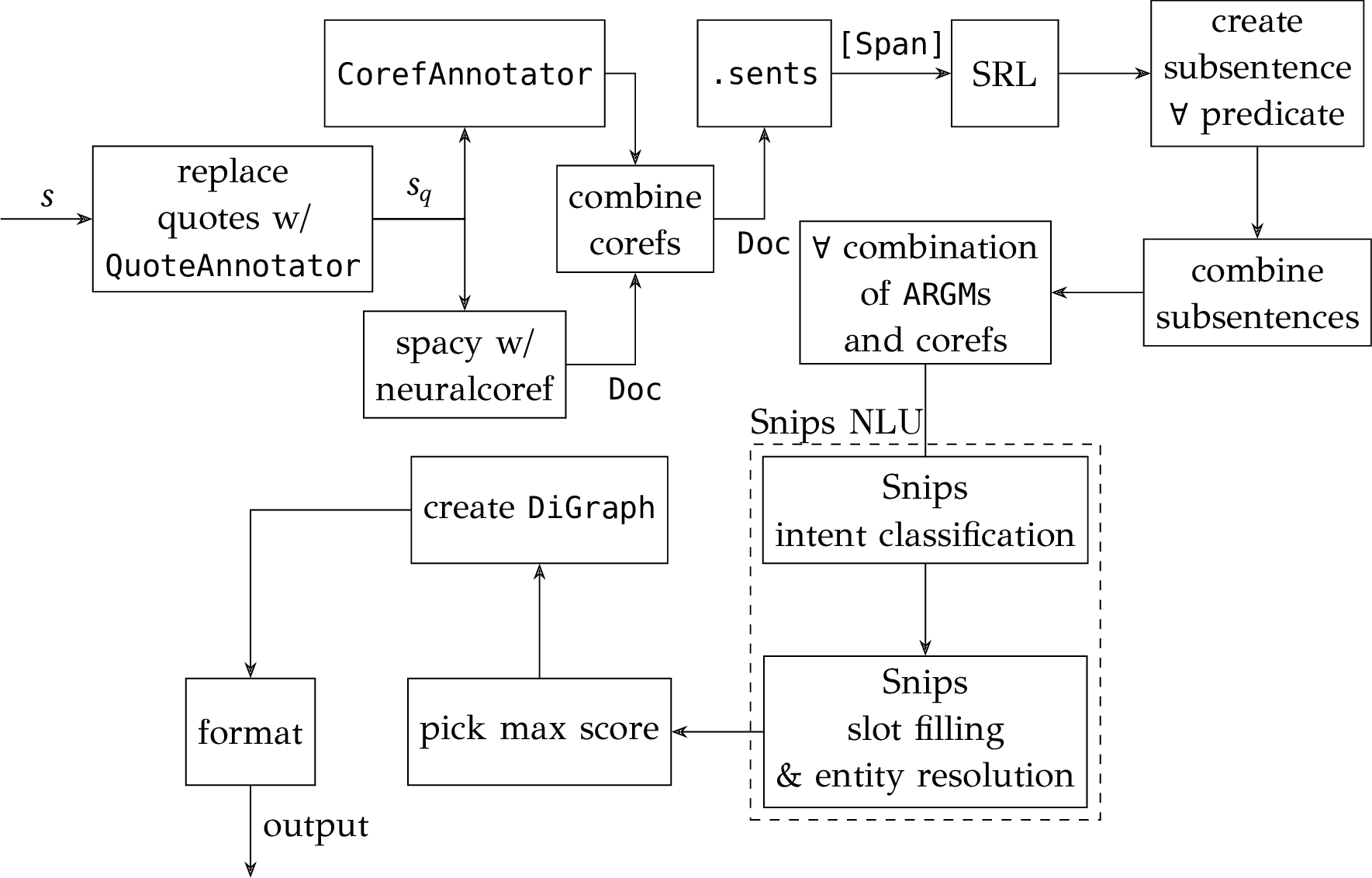
For the above-mentioned purposes, we have developed a natural language understanding (NLU) system, r4a-nao-nlp, that recognizes the supported actions of the R4A-NAO meta-model. We have implemented a modular software pipeline that segments the text using semantic role labeling to identify multiple user intents per sentence. In addition, the system utilizes the results of coreference resolution throughout the text to enhance the performance of intent classification and slot filling in sentences that include mentions. Since the dataset for training the NLU system had to be created from scratch, our approach has been designed to cope with a low-data regime; there are no requirements in the dataset for sentences that combine multiple intents since that would result in polynomial growth of the dataset size. The final output of our pipeline is a directed graph that encompasses all detected actions and connects them with the original conjunctions of the text.
This implementation benefits from its modularity since the used models, with the exception of those that perform intent classification and slot filling, come pre-trained on much larger datasets and concern major natural language processing tasks and therefore are bound to improve with the further development of the related technology. We believe that our approach can be utilized, without the need to increase training data, by task-oriented dialog systems or other related applications that often lack the ability to recognize multiple intents per sentence.
In conclusion, we have developed a system that can prove useful to the final user who can obtain optimal results if they learn about its limitations and idiosyncrasies. This procedure is not considered to demand technical or esoteric knowledge on r4a-nao-nlp.
- Install the package and its dependencies:
pip install -e . - Download spacy models:
python -m spacy download en_core_web_md && python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm - (For training) Download the
enlanguage resources for snips:python -m snips_nlu download en