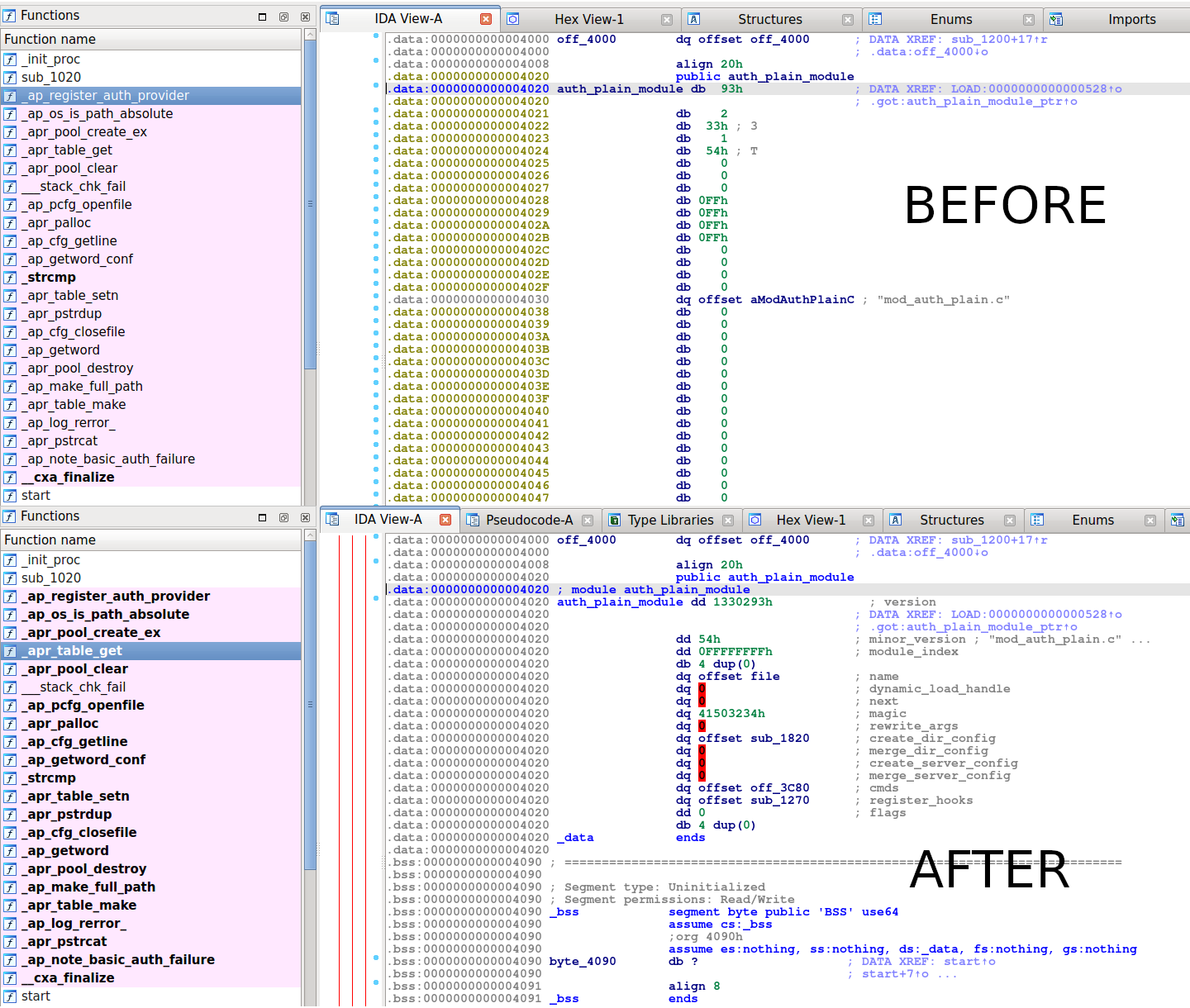
Creating a Type Information Library makes it easier to reverse engineer binaries by providing IDA with detailed and acurate information about types.
Types include:
- function prototypes
- structures
- enums
The main point is that IDA will apply function prototypes to the imports and include the relevant data types in the database.
As an example, we will create a TIL file which can help reversing Apache modules.
Everything here will be done on a Debian Sid, amd64 from March 2021, but most of it will work on most Linux distros.
We need the source code of the libraries we want to analyze. My target used Apache 2.2, so let's fetch it:
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/httpd/httpd-2.2.34.tar.bz2
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/httpd/httpd-2.2.34.tar.bz2.asc
curl https://downloads.apache.org/httpd/KEYS | gpg2 --import
gpg2 --verify httpd-2.2.34.tar.bz2.asc httpd-2.2.34.tar.bz2
The archive contains things we want to include in our TIL:
- the headers for writing modules
- the Apache Runtime (apr) lib
First, we need to do a ./configure to have the right headers generated.
Of course, this phase will need to reflect the configuration that was used
by your target.
In my case, the binary was compiled with GCC: (GNU) 3.2.3 20030502 (Red Hat Linux 3.2.3-56), which
is ancient. But in theory, there should not be real differences in ABI between a recent and old
GCC compiler on Linux amd64, so let's proceed anyway.
First, we need to get the right configuration for the compiler options in tilib: depending on
the architecture and target ABI, the structures padding, type sizes, etc. will vary.
This is the "documentation":
$ ./tilib -C?
-C... specifies the compiler information
It has the -Cx# form, where # - value, x is one of the following:
c-compiler id, m-model, p-sizeof(near*), g-defalign (0/1/2/4/8/6 for16)
b-sizeof(bool), e-sizeof(enum), i-sizeof(int), s-sizeof(short)
l-sizeof(long), L-sizeof(longlong), R-explicit stack offsets
v-calling convention, B-bitness (3 for 32 or 6 for 64), D-sizeof(long double)
8-4 byte alignment for 8byte scalars (__int64/double) inside structures (y/n)
a-shorthand for cmpgbeislLvB8. The default is us40144248i3n
Compiler ids: Pointer sizes:
0 or u: Unknown 1: sizeof(near*)=1, sizeof(far*)=2
1 or v: Visual C++ 2: sizeof(near*)=2, sizeof(far*)=4
2 or b: Borland C++ 4: sizeof(near*)=4, sizeof(far*)=6
3 or w: Watcom C++ 8: sizeof(near*)=8, sizeof(far*)=8
6 or g: GNU C++ Memory models:
7 or a: Visual Age C++ s: small (code=near, data=near)
8 or d: Delphi l: large (code=far, data=far)
c: compact (code=near, data=far)
m: medium (code=far, data=near)
Calling conventions:
i: invalid s: stdcall u: unknown (default)
v: void p: pascall
c: cdecl r: fastcall
e: (...) t: thiscall
For example, BCC small model v3.1: -Cabs2122224
GNU C++: -Cags44444248u
As you can see, -C is difficult to master. Here's how to read the
-Cags44444 which you can find in tilib's gcc.cfg:
; from GCC 32 config:
; -Cags44444
; cmpgbeislLvB8 (expansion for for "Ca")
; us40144248i3n (default)
; gs44444
; |||||||||||||_ 8bytes scalars alignment
; ||||||||||||__ bitness
; |||||||||||___ calling convention
; ||||||||||____ sizeof(longlong)
; |||||||||_____ sizeof(long) :
; ||||||||______ sizeof(short) : 4
; |||||||_______ sizeof(int) : 4
; ||||||________ sizeof(enum) : 4
; |||||_________ sizeof(bool) : 4
; ||||__________ defalign: 4
; |||___________ pointer size: 4
; ||____________ mem model: small
; |_____________ compiler: gcc
- Use
sizes.c cp gcc.cfg gcc64.cfg- Update
gcc64.cfg
Note: the (updated) gcc64.cfg was provided by Igor Skochinsky from Hex-Rays, I just added the comments.
First we need to make a top level header which includes everything: apache_all.h.
Then, we will preprocess it using gcc -E to preprocess everything and facilitate
the ingestion by tilib.
Then we begin the loop of fixing errors and warnings.
The most important hacks are:
- Adding
#define __asm__(arg)to ourapache_all.hfile, to "nop" inline asm - Adding
-D__extension__= \to thetilibcall, which will "nop" the unsupported__extension__keyword - Adding
"-D__builtin_va_list=void *"which will work around the need for the internal definition ofva_list - Add
-D__UNKNOWN_ATTR__=UNKNOWN_ATTRingcc64.cfg
Of course the command line options could be included in the .cfg file.
See make_til.sh for the final result.
Identify which structures have no "size" in the .til file:
$ tilib -l apache22-debian64.til | grep "FFFFFFFF struct"
[...]
FFFFFFFF struct ap_conf_vector_t;
FFFFFFFF struct ap_filter_provider_t;
FFFFFFFF struct apr_allocator_t;
FFFFFFFF struct apr_bucket_alloc_t;
[...]
some are opaque by "design", such as ap_conf_vector_t, others should be added
in the apache_all.h file by copy pasting.
The TIL file should be put inside til/pc in IDA dir to be discovered.
After loading the TIL file (Shift-F11, Insert), and defining the module export as module, note
how all the Apache related imports are now in bold, with their types defined: