Java 21 Virtual Threads and Structured Concurrency Java Threads and Scalability
Task types
Concurrency and Parallelism
Non Blocking IO
Introduce Project Loom
%%{ init: { 'flowchart': { 'curve': 'cardinal' } } }%%
flowchart LR
subgraph External World
browser(("Browser"))
end
subgraph Typical Web Application
application["\nWeb Application\n(Process)\n"]
database_1[(Database 1)]
database_2[(Database 2)]
ms_1{{"Microservice 1\n(Process)"}}
ms_2{{"Microservice 2\n(Process)"}}
end
application --> external_api
browser -->|User Request| application
browser -->|User Request| application
browser -->|User Request| application
application <--> database_1
application <--> database_2
application <--> ms_1
application <--> ms_2
Loading
Process Per Request (CGI)
flowchart LR
web-server["Web Server\n(Process)"]
handler-1["User 1 Handler\nCGI Script\n(Process)"]
handler-2["User 2 Handler\nCGI Script\n(Process)"]
handler-3["User 3 Handler\nCGI Script\n(Process)"]
external-call["\n\n\n\n\n\n "]
external-call -->|User 1 Request| web-server
external-call -->|User 2 Request| web-server
external-call -->|User 3 Request| web-server
web-server <-->|" (1) Start Process "| handler-1
web-server <-->|" (2) Start Process "| handler-2
web-server <-->|" (3) Start Process "| handler-3
Loading
Process is heavyweight
Limited number of processes per machine
Scalability issues
Cannot support large number of users
Expensive Process startup and termination time
Difficult to share data or communicate between Processes
FastCGI
Pooling of Processes
CGI processes are started upfront for performance
flowchart LR
user-request["\n\n\n\n\n"]
subgraph web-application["fa:fa-internet-explorer Web Application"]
thread-1-start(("start"))
thread-1-finish(("end"))
thread-2-start(("start"))
thread-2-finish(("end"))
thread-3-start(("start"))
thread-3-finish(("end"))
end
user-request -->|User 1 Request| web-application
user-request -->|User 2 Request| web-application
user-request -->|User 3 Request| web-application
thread-1-start -->|" 1. Thread process "| thread-1-finish
thread-2-start -->|" 2. Thread process "| thread-2-finish
thread-3-start -->|" 3. Thread process "| thread-3-finish
Loading
Threads are lightweight
Can handle larger number of concurrent users
Can share data or communicate between threads
Improved Performance
No extra process to deal with
Easy to understand
Easy to debug
Concurrency and Parallelism
Multiple independent tasks are making progress but may not execute at the same time
Appearance of simultaneous execution (parallelism)
Concurrency is about dealing with lots of things at once
CPU time slicing
Multiple dependent sub-tasks are executing at the same time
Multiple cores needed
No parallelism in single core
Sequential execution of code
Easy to understand
Easy to debug
Does not wait for call to complete
Callbacks, Futures...
More complex to understand
In java, user Threads
Default stack size 1M
As number of users increase, memory usage increases
There is a max limit to the max threads
Depends on VM or Machine Memory
Much more socket connections can be supported
This prevents optimum scalability
IO Bound Tasks
Paralyzes the OS thread for a longer time than necessary
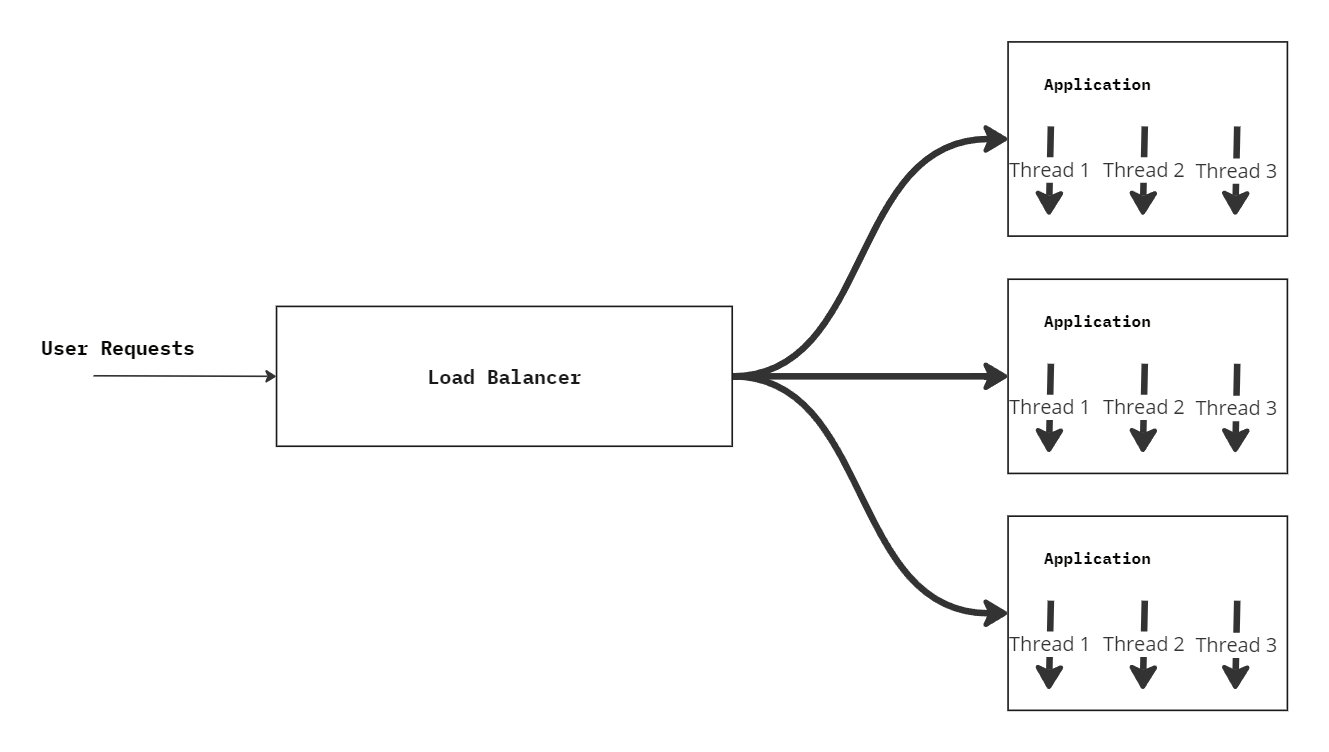
{Optimized Scalable Application} + {Vertial Scaling} + {Horizontal Scaling}
Increase resources
CPU, Memory, Disk Space, etc...
Limit to scaling
Increases cost
Cloud Environment
Increase number of Application (Instances) nodes
No limit
Costly
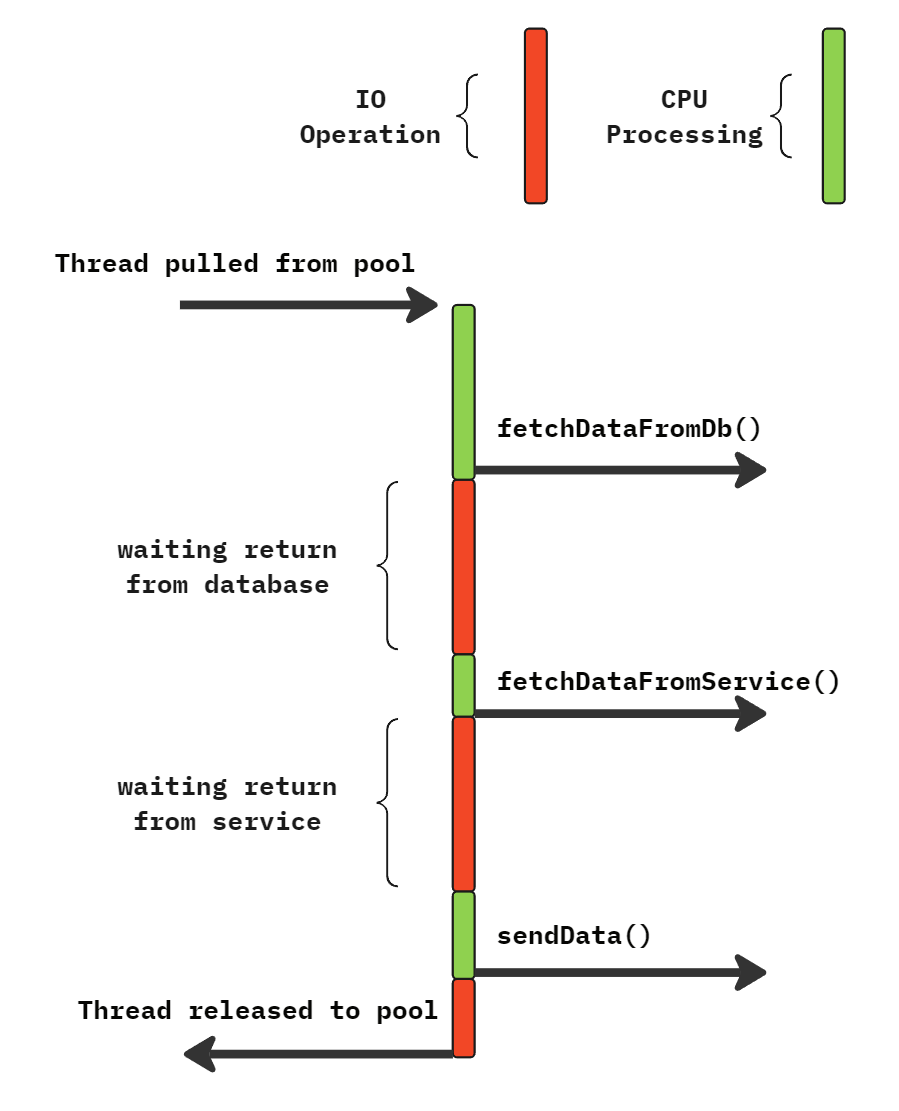
Pseudo Code For Blocking IO
// Fetch some data from DB
var data1 = fetchDataFromDB (dbUrl );
// Fetch some data from Microservice
var data2 = fetchDataFromService (serviceUrl );
// Process all data
var combinedData = processAndCombine (data1 , data2 );
// Send data to user
sendData (combinedData );
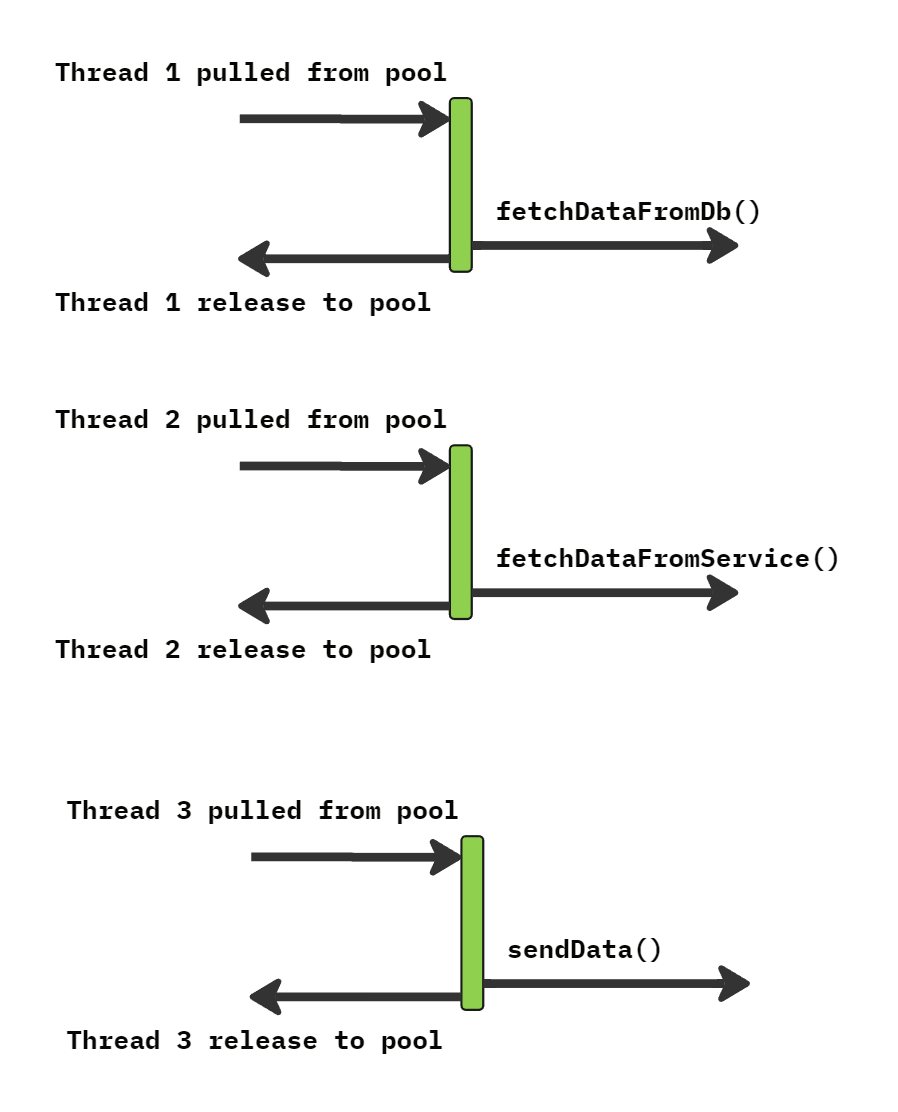
Non-Blocking IO program flux
// Non Blocking: Fetch some data from DB
return fetchDataFromDb (dbUrl , data1 -> {
// Non Blocking: Fetch some data from Microservice
return fetchDataFromService (serviceUrl , data2 -> {
// Process all data and send
var combinedData = processAndCombine (data1 , data2 );
return sendData (combinedData );
});
});
Lightweight threads (Extends the Thread Class)
Fast creation time
Exhibits same behaviour as Platform Threads
Scales to millions of instances
No need for Thread Pool
Can block on IO with no scalability issues
Optimal concurrency
Code can still be sequential
Existing code will benefit from using Virtual Thread
Combine with Future's and CompletableFuture's
Blocking with native frames on Stack (JNI)
Control memory per stack
Reduce ThreadLocal's usage
No deep recursions