| NRP | Name |
|---|---|
| 5025211015 | Muhammad Daffa Ashdaqfillah |
Success Validation
-- Tabel 'users'
CREATE TABLE users (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(255),
email varchar(255) UNIQUE,
email_verified_at timestamp,
password varchar(255),
remember_token varchar(100),
created_at timestamp DEFAULT current_timestamp,
updated_at timestamp DEFAULT current_timestamp ON UPDATE current_timestamp
);
-- Tabel 'dokters'
CREATE TABLE dokters (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(128),
email varchar(255),
phone_number varchar(20),
age integer,
height numeric(6, 2),
weight numeric(6, 2),
password varchar(255),
profile_picture varchar(255),
remember_token varchar(100),
created_at timestamp DEFAULT current_timestamp,
updated_at timestamp DEFAULT current_timestamp ON UPDATE current_timestamp
);
-- Tabel 'pasiens'
CREATE TABLE pasiens (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(128),
email varchar(255),
phone_number varchar(20),
age integer,
height numeric(6, 2),
weight numeric(6, 2),
password varchar(255),
profile_picture varchar(255),
remember_token varchar(100),
created_at timestamp DEFAULT current_timestamp,
updated_at timestamp DEFAULT current_timestamp ON UPDATE current_timestamp
);
-- Tabel 'rekams'
CREATE TABLE rekams (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
pasien_id integer REFERENCES pasiens (id),
dokter_id integer REFERENCES dokters (id),
kondisi varchar(255),
suhu varchar(20),
picture varchar(255),
created_at timestamp DEFAULT current_timestamp,
updated_at timestamp DEFAULT current_timestamp ON UPDATE current_timestamp
);To initiate Laravel Breeze, you can follow the following steps:
-
Open the terminal and navigate to your Laravel project directory.
-
Run the following command to install Laravel Breeze:
composer require laravel/breeze --dev
-
After the installation process is complete, run the following command to initiate Laravel Breeze:
php artisan breeze:install
-
Laravel Breeze will create all the necessary basic authentication features, including user authentication, registration, and password reset, which are powered by Laravel Fortify.
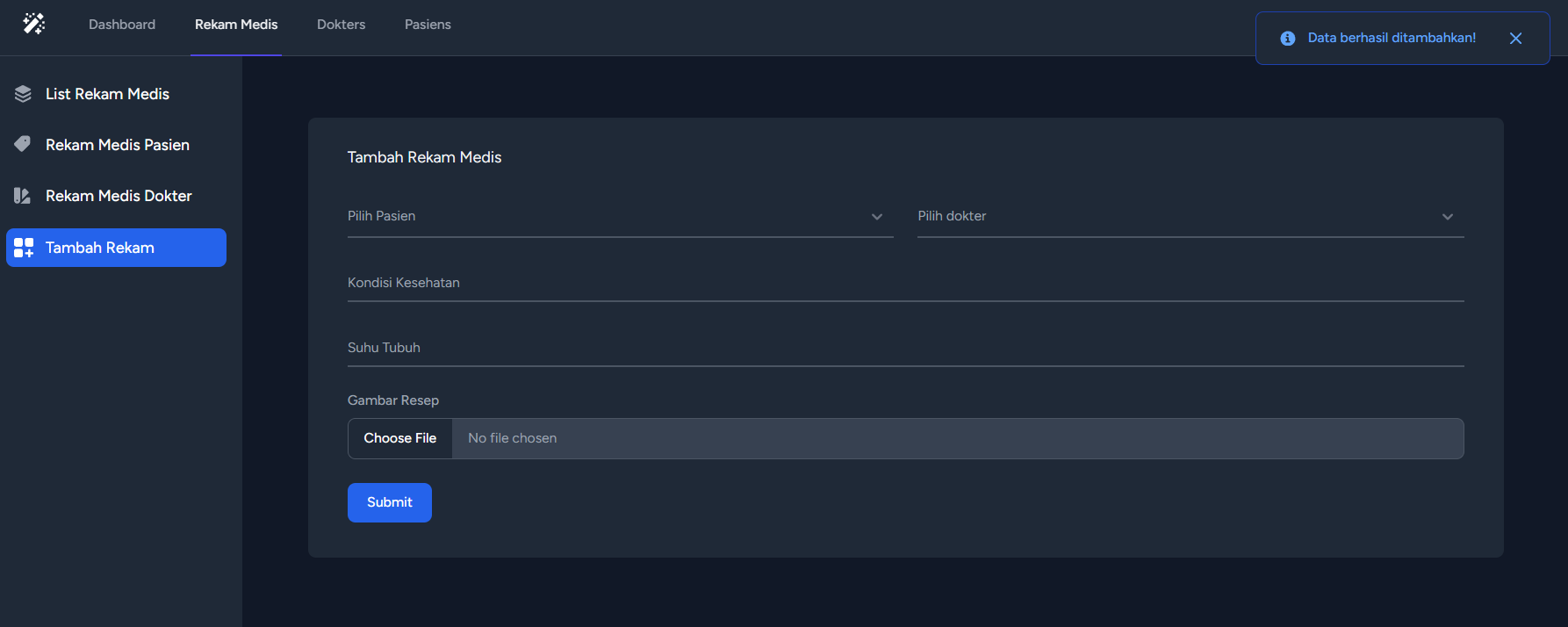
public function store(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'pasien' => 'required|string|max:255',
'dokter' => 'required|string|max:255',
'kondisi' => 'required|string|max:255',
'suhu' => 'required|string|max:255',
'picture' => 'required|image|mimes:jpeg,png,jpg|max:2048',
]);
$rekam = new Rekam();
$rekam->pasien = $request->input('pasien');
$rekam->dokter = $request->input('dokter');
$rekam->kondisi = $request->input('kondisi');
$rekam->suhu = $request->input('suhu');
if ($request->hasFile('picture')) {
$picturePath = $request->file('picture')->store('public/pictures');
$rekam->picture = str_replace('public/', '', $picturePath);
}
$rekam->save();
return redirect()->route('admin.rekam.create')->with('status', 'Data berhasil ditambahkan!');
}
public function create()
{
$pasien = Pasien::all();
$dokter = Dokter::all();
return view('admin.rekam.create', [
'pasien' => $pasien,
'dokter' => $dokter,
]);
}The provided code is a snippet from a PHP Laravel application. It contains two functions: store() and create().
The store() function is responsible for handling the request to store a record (rekam medis) in the application's database. It first validates the incoming request data using the validate() method, which ensures that certain fields are required and meet certain criteria (e.g., maximum length, file type, etc.).
After validating the request, a new instance of the Rekam model is created, and the request input values are assigned to the corresponding model properties (pasien, dokter, kondisi, suhu). If the request contains a file (picture), it is stored in the public/pictures directory and the file path is saved in the picture property of the Rekam model.
Finally, the Rekam model instance is saved to the database, and the user is redirected to the admin.rekam.create route with a success message.
The create() function is responsible for rendering the view for creating a new record. It fetches all the available Pasien and Dokter models from the database and passes them to the view as variables.
These functions are part of a larger application that manages medical records (rekam medis) and allows administrators to create new records and associate them with patients (pasien) and doctors (dokter).
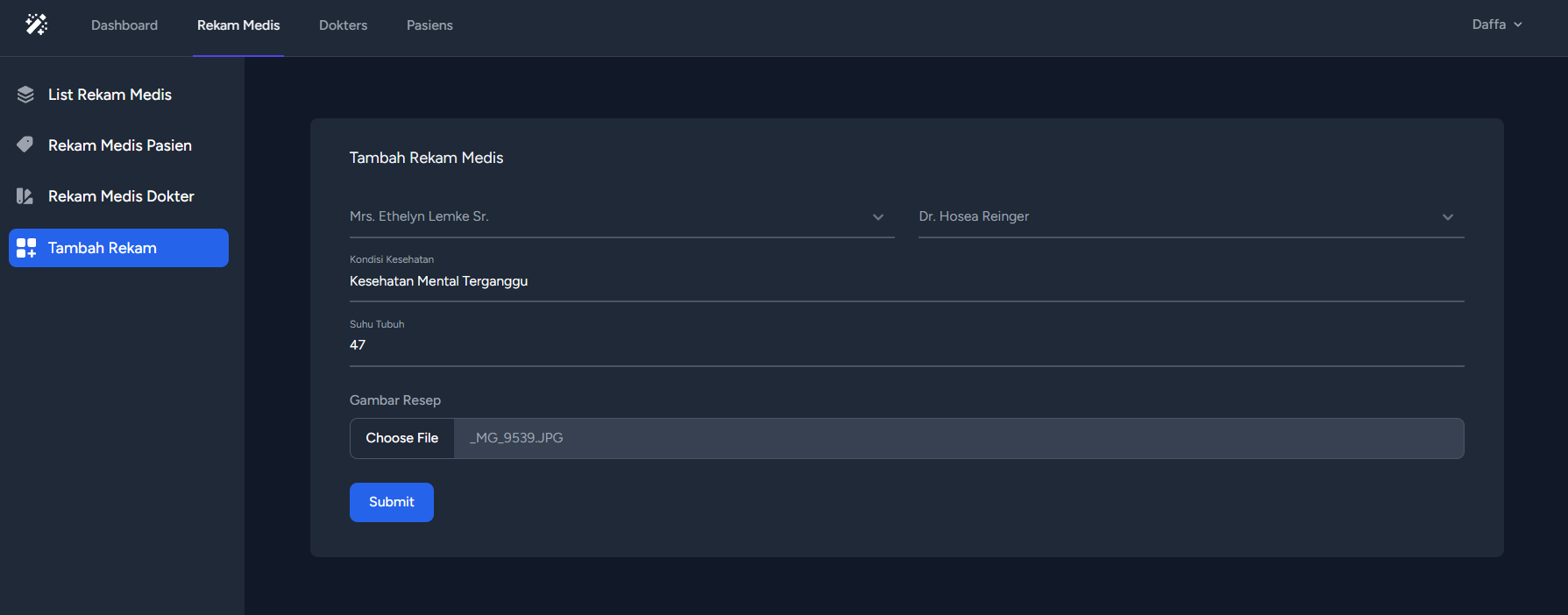
<div>
@include('layouts.Sidebar')
<div class="p-4 sm:ml-64">
<div class="py-12">
<div class="max-w-7xl mx-auto sm:px-6 lg:px-8">
<div class="bg-white dark:bg-gray-800 overflow-hidden shadow-sm sm:rounded-lg">
<div class="py-7 px-10 text-gray-900 dark:text-gray-100">
{{ __("Tambah Rekam Medis") }}
</div>
<form class="px-10 pb-6" action="{{ route('admin.rekam.store') }}" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data">
@csrf
<div class="grid md:grid-cols-2 md:gap-6">
<div class="relative z-0 w-full mb-6 group">
<select name="pasien" id="pasien" class="block bg-transparent py-2.5 px-0 w-full text-sm border-0 border-b-2 border-gray-300 appearance-none text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-400 dark:border-gray-600 dark:focus:border-blue-500 focus:outline-none focus:ring-0 focus:border-blue-600 peer">
<option value="" selected disabled> Pilih Pasien </option>
@foreach($pasien as $pasien)
<option value="{{ $pasien->id }}">{{ $pasien->name }}</option>
@endforeach
</select>
<!-- <label for="pasien" class="peer-focus:font-medium absolute text-sm text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-400 duration-300 transform -translate-y-6 scale-75 top-3 -z-10 origin-[0] peer-focus:left-0 peer-focus:text-blue-600 peer-focus:dark:text-blue-500 peer-placeholder-shown:scale-100 peer-placeholder-shown:translate-y-0 peer-focus:scale-75 peer-focus:-translate-y-6">pasien rekam</label> -->
</div>
<div class="relative z-0 w-full mb-6 group">
<select name="dokter" id="dokter" class="block bg-transparent py-2.5 px-0 w-full text-sm border-0 border-b-2 border-gray-300 appearance-none text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-400 dark:border-gray-600 dark:focus:border-blue-500 focus:outline-none focus:ring-0 focus:border-blue-600 peer">
<option value="" selected disabled> Pilih dokter </option>
@foreach($dokter as $dokter)
<option value="{{ $dokter->id }}">{{ $dokter->name }}</option>
@endforeach
</select>
</div>
</div>
<div class="relative z-0 w-full mb-6 group">
<input type="text" name="kondisi" id="kondisi" class="block py-2.5 px-0 w-full text-sm text-gray-900 bg-transparent border-0 border-b-2 border-gray-300 appearance-none dark:text-white dark:border-gray-600 dark:focus:border-blue-500 focus:outline-none focus:ring-0 focus:border-blue-600 peer" placeholder=" " required />
<label for="kondisi" class="peer-focus:font-medium absolute text-sm text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-400 duration-300 transform -translate-y-6 scale-75 top-3 -z-10 origin-[0] peer-focus:left-0 peer-focus:text-blue-600 peer-focus:dark:text-blue-500 peer-placeholder-shown:scale-100 peer-placeholder-shown:translate-y-0 peer-focus:scale-75 peer-focus:-translate-y-6">Kondisi Kesehatan</label>
</div>
<div class="relative z-0 w-full mb-6 group">
<input type="text" name="suhu" id="suhu" class="block py-2.5 px-0 w-full text-sm text-gray-900 bg-transparent border-0 border-b-2 border-gray-300 appearance-none dark:text-white dark:border-gray-600 dark:focus:border-blue-500 focus:outline-none focus:ring-0 focus:border-blue-600 peer" placeholder=" " required />
<label for="suhu" class="peer-focus:font-medium absolute text-sm text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-400 duration-300 transform -translate-y-6 scale-75 top-3 -z-10 origin-[0] peer-focus:left-0 peer-focus:text-blue-600 peer-focus:dark:text-blue-500 peer-placeholder-shown:scale-100 peer-placeholder-shown:translate-y-0 peer-focus:scale-75 peer-focus:-translate-y-6">Suhu Tubuh</label>
</div>
<div class="relative z-0 w-full mb-6 group">
<label class="block mb-2 text-sm font-medium text-gray-500 dark:text-gray-400" for="picture">Gambar Resep</label>
<input value="{{old('picture')}}" name="picture" id="picture" class="block w-full text-sm text-gray-900 border border-gray-300 rounded-lg cursor-pointer bg-gray-50 dark:text-gray-400 focus:outline-none dark:bg-gray-700 dark:border-gray-600 dark:placeholder-gray-400" aria-describedby="picture_help" type="file">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="text-white bg-blue-700 mb-3 hover:bg-blue-800 focus:ring-4 focus:outline-none focus:ring-blue-300 font-medium rounded-lg text-sm w-full sm:w-auto px-5 py-2.5 text-center dark:bg-blue-600 dark:hover:bg-blue-700 dark:focus:ring-blue-800">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>The form is using the POST method and the route "admin.rekam.store". It also includes CSRF protection.
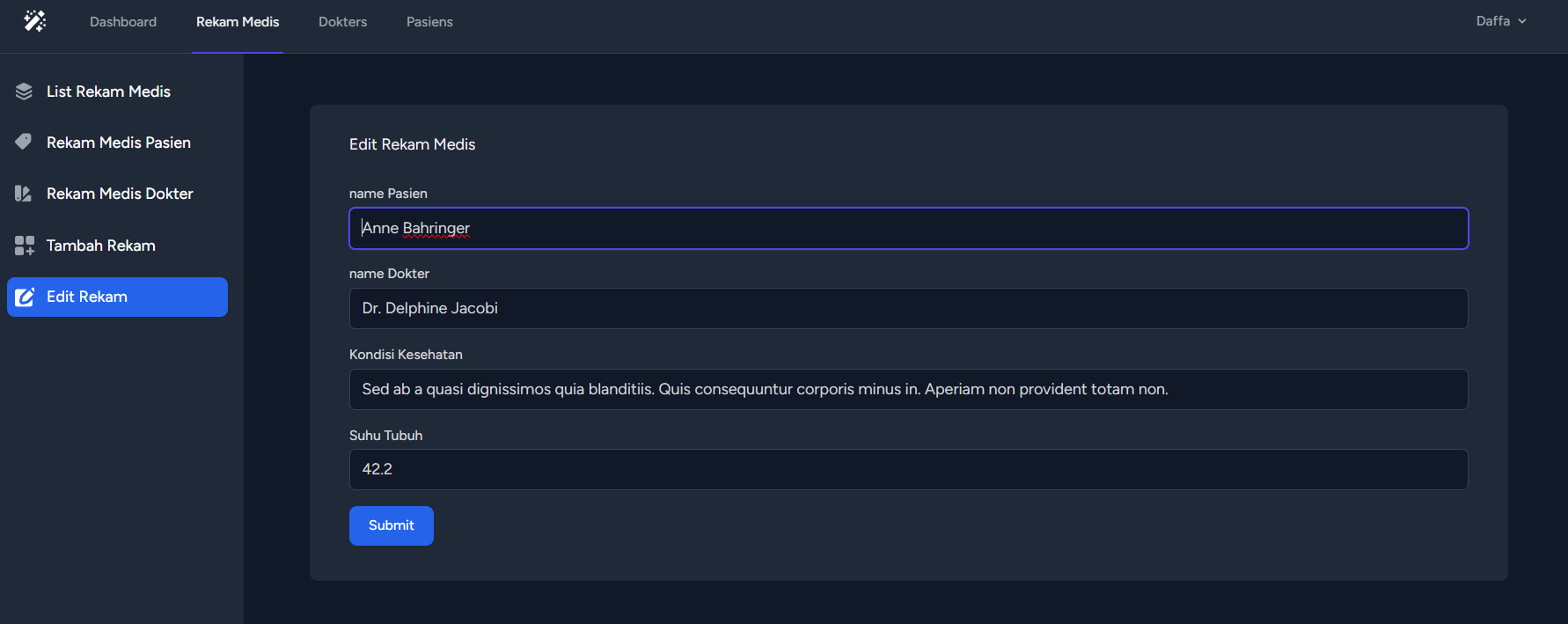
public function edit($id)
{
$rekam = DB::table('rekams')
->join('pasiens', 'rekams.pasien', '=', 'pasiens.id')
->join('dokters', 'rekams.dokter', '=', 'dokters.id')
->select('rekams.*', 'pasiens.name as name_pasien', 'dokters.name as name_dokter')
->where('rekams.id', '=', $id)
->first();
if (!$rekam) {
return redirect()->route('admin.rekam.list')->with('error', 'Item' . $id . ' not found');
}
return view('admin.rekam.edit', [
'title' => 'Edit Rekam',
'rekam' => $rekam,
]);
}
public function update(Request $request, $id)
{
$rekam = Rekam::find($id);
$name = $rekam->name;
if (!$rekam) {
return redirect()->route('admin.rekam.list')->with('error', 'Item' . $name . ' not found');
}
$validated = $request->validate([
'pasien' => 'required|string|max:255',
'dokter' => 'required|string|max:255',
'kondisi' => 'required|string|max:255',
'suhu' => 'required|numeric|between:35,45.5',
]);
$rekam->pasien = $validated['pasien'];
$rekam->dokter = $validated['dokter'];
$rekam->kondisi = $validated['kondisi'];
$rekam->suhu = $validated['suhu'];
$rekam->save();
return back()->with('status', 'Items ' . $name . ' updated successfully');
}The edit() function is responsible for retrieving the data of a specific record (rekam) from the database and rendering the view for editing that record. It takes the ID of the record as a parameter.
Inside the function, the DB::table() method is used to perform a query that joins the rekams, pasiens, and dokters tables based on their foreign key relationships. It selects the necessary columns from each table and restricts the result to the record with the specified ID. The first() method is then called to retrieve the first matching record.
If the record is not found, the function redirects the user to the admin.rekam.list route with an error message.
If the record is found, the function returns the admin.rekam.edit view, passing the necessary data to the view.
The update() function is responsible for handling the request to update a record (rekam) in the database. It takes the request object and the ID of the record as parameters.
Inside the function, the Rekam::find() method is used to retrieve the specific record from the database based on the ID. If the record is not found, the function redirects the user to the admin.rekam.list route with an error message.
If the record is found, the request data is validated using the validate() method, which ensures that certain fields are required and meet certain criteria (e.g., maximum length, numeric values within a certain range).
After validation, the properties of the rekam model instance are updated with the validated data. The save() method is then called to save the changes to the database.
Finally, the function redirects the user back to the previous page with a success message.
public function show() : View
{
$rekams = DB::table('rekams')
->join('pasiens', 'rekams.pasien', '=', 'pasiens.id')
->join('dokters', 'rekams.dokter', '=', 'dokters.id')
->select('rekams.*', 'pasiens.name as name_pasien', 'dokters.name as name_dokter')
->get();
return view('admin.rekam.list', [
'rekams' => $rekams,
]);
}- The
show()function returns an instance of theViewclass. - Inside the function, it uses the
DBfacade to interact with the database. - The
join()method is used to join therekams,pasiens, anddokterstables based on their respective foreign key relationships. - The
select()method is used to specify the columns to be retrieved from the joined tables. - The
get()method retrieves all the matching records from the database. - The retrieved data is then passed to the
listview located atadmin/rekam/list. - The
rekamsvariable is assigned the value of the retrieved records.
This code is likely part of a larger application that handles medical records and is used to display a list of records along with associated patient and doctor information in the admin.rekam.list view.
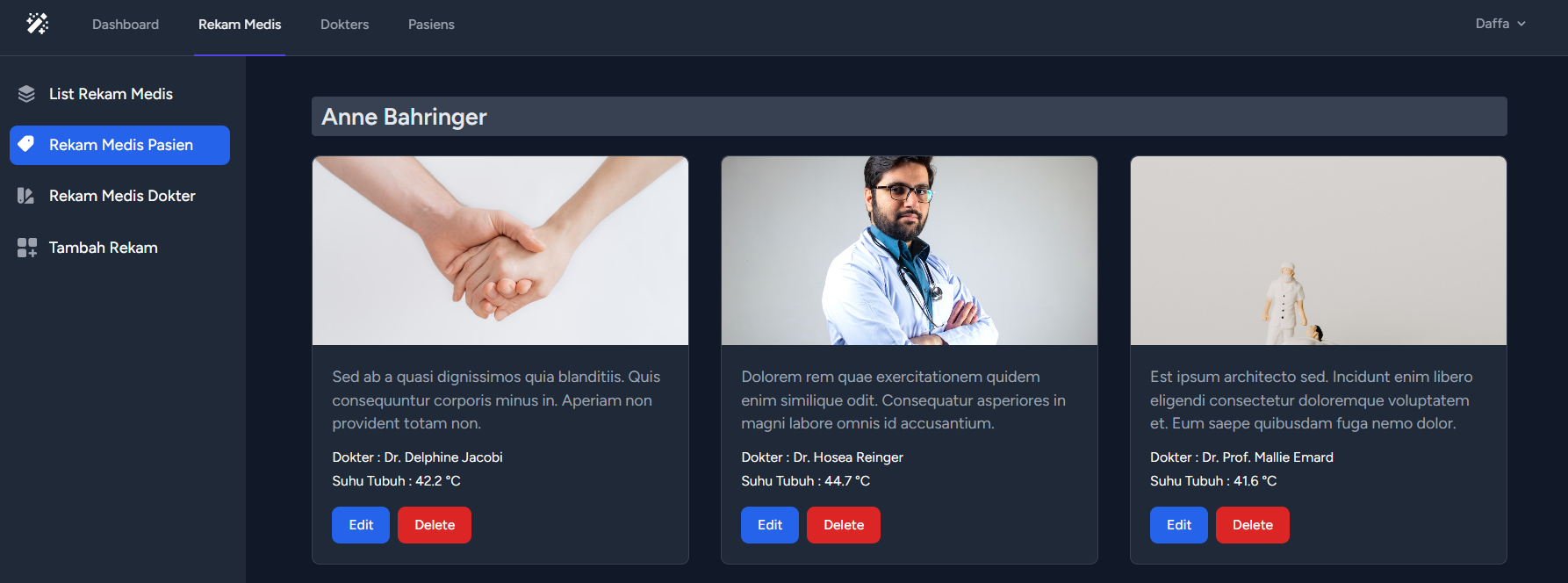
public function pasien() : View
{
$rekams = DB::table('rekams')
->join('pasiens', 'rekams.pasien', '=', 'pasiens.id')
->join('dokters', 'rekams.dokter', '=', 'dokters.id')
->select('rekams.*', 'pasiens.name as name_pasien', 'dokters.name as name_dokter')
->orderBy('pasiens.name') // Urut berdasarkan name pasien
->get();
return view('admin.rekam.pasien', [
'rekams' => $rekams,
]);
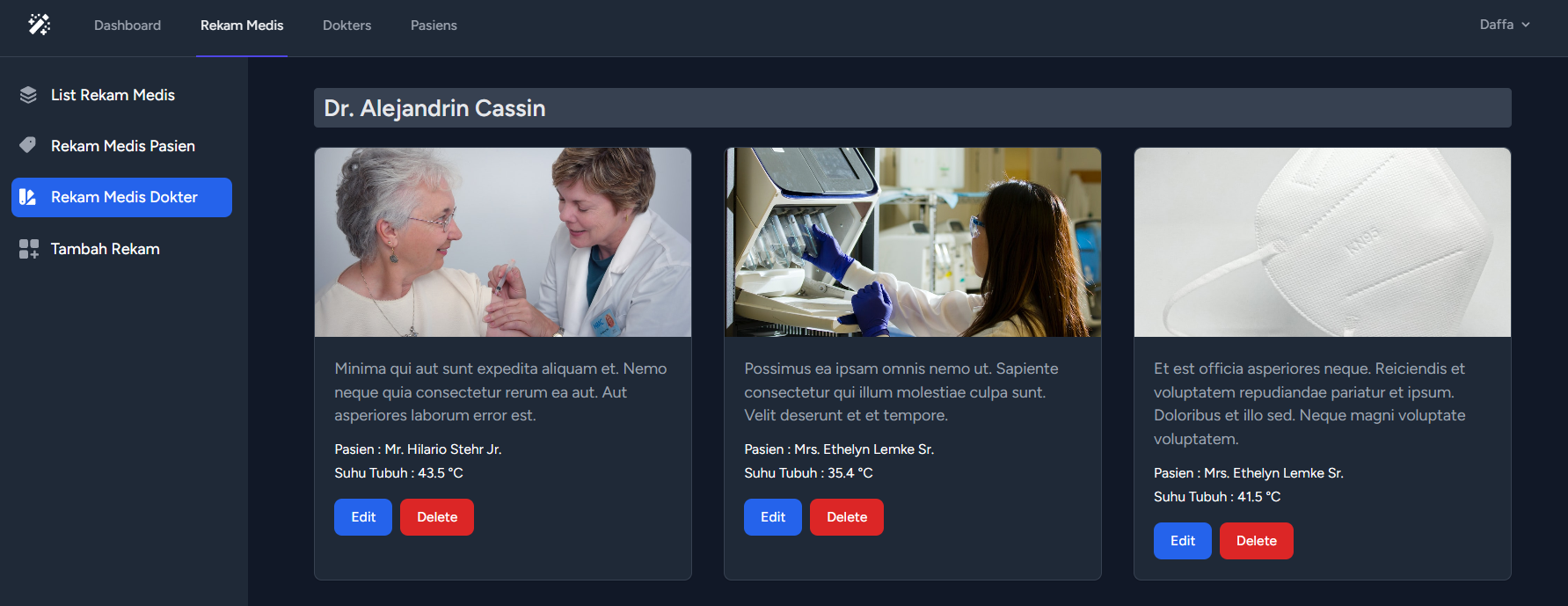
}public function dokter() : View
{
$rekams = DB::table('rekams')
->join('pasiens', 'rekams.pasien', '=', 'pasiens.id')
->join('dokters', 'rekams.dokter', '=', 'dokters.id')
->select('rekams.*', 'pasiens.name as name_pasien', 'dokters.name as name_dokter')
->orderBy('dokters.name') // Urut berdasarkan name dokter
->get();
return view('admin.rekam.dokter', [
'rekams' => $rekams,
]);
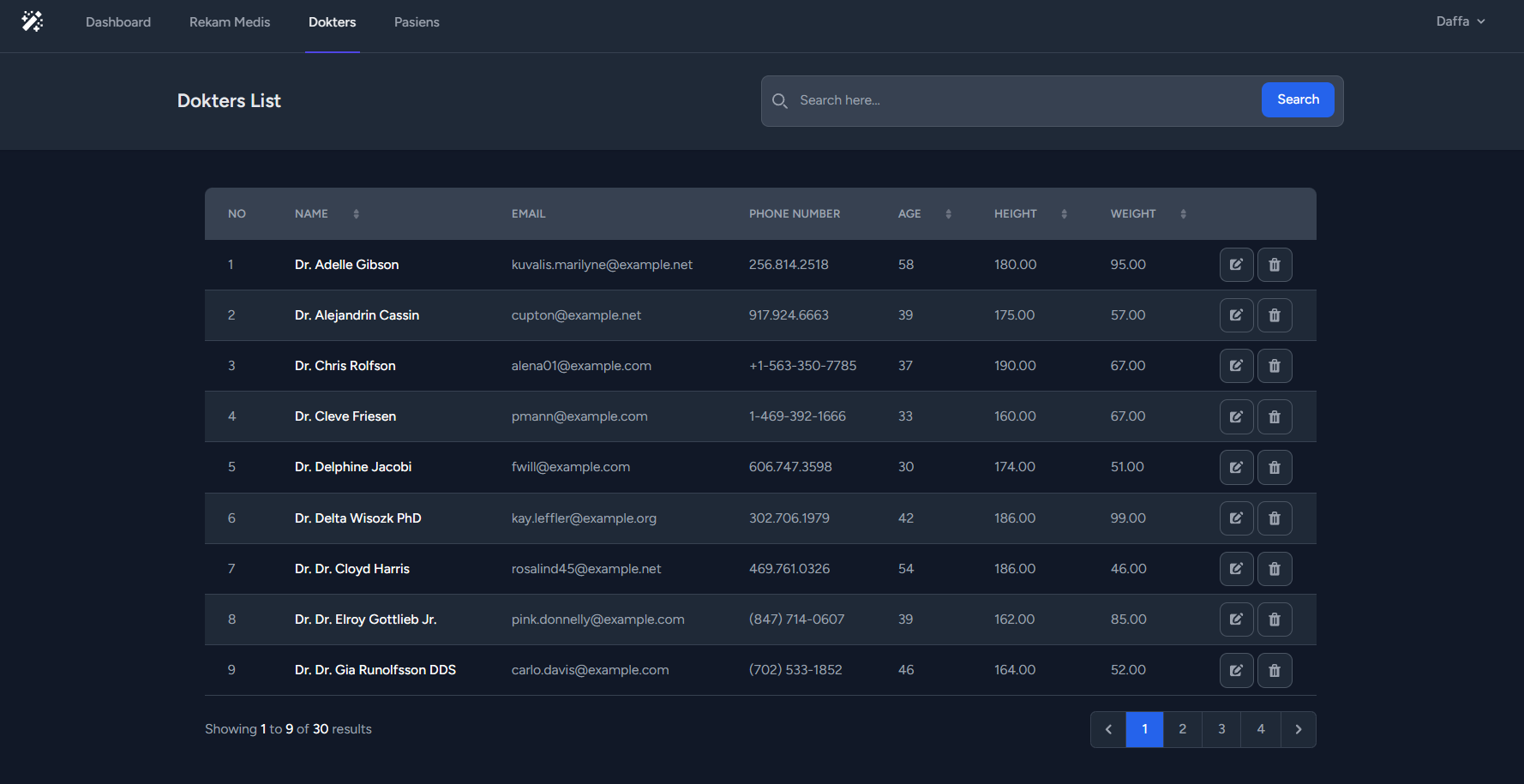
}public function getDokterList(Request $request)
{
$pagination = 9;
$query = Dokter::query();
if ($request->has('query')) {
$search_text = $request->input('query');
$query->where(function ($q) use ($search_text) {
$q->where('name', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('email', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('phone_number', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('age', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('height', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('weight', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%");
});
}
if ($request->has('sort_by')) {
$sort_by = $request->input('sort_by');
if ($sort_by === 'name_asc') {
$query->orderBy('name', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'name_desc') {
$query->orderBy('name', 'desc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'age_asc') {
$query->orderBy('age', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'age_desc') {
$query->orderBy('age', 'desc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'height_asc') {
$query->orderBy('height', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'height_desc') {
$query->orderBy('height', 'desc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'weight_asc') {
$query->orderBy('weight', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'weight_desc') {
$query->orderBy('weight', 'desc');
}
} else {
$query->orderBy('name', 'asc');
}
$dokters = $query->paginate($pagination);
return view('admin.dokters', [
'title' => 'Dokters',
'dokters' => $dokters,
'query' => $request->input('query'),
'sort_by' => $request->input('sort_by'),
]);
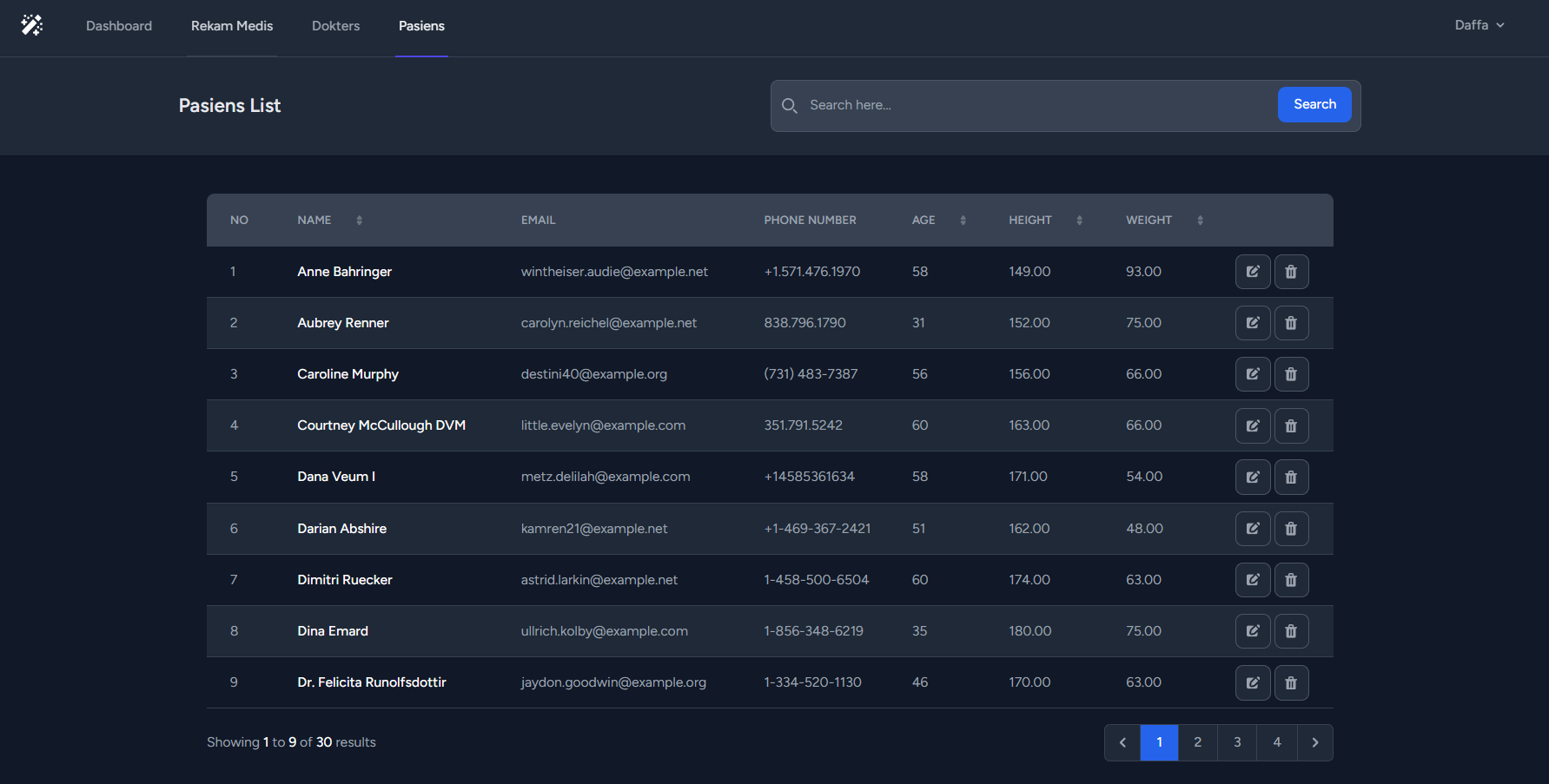
}public function getPasienList(Request $request)
{
$pagination = 9;
$query = Pasien::query();
if ($request->has('query')) {
$search_text = $request->input('query');
$query->where(function ($q) use ($search_text) {
$q->where('name', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('email', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('phone_number', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('age', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('height', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('weight', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%");
});
}
if ($request->has('sort_by')) {
$sort_by = $request->input('sort_by');
if ($sort_by === 'name_asc') {
$query->orderBy('name', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'name_desc') {
$query->orderBy('name', 'desc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'age_asc') {
$query->orderBy('age', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'age_desc') {
$query->orderBy('age', 'desc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'height_asc') {
$query->orderBy('height', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'height_desc') {
$query->orderBy('height', 'desc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'weight_asc') {
$query->orderBy('weight', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'weight_desc') {
$query->orderBy('weight', 'desc');
}
} else {
$query->orderBy('name', 'asc');
}
$pasiens = $query->paginate($pagination);
return view('admin.pasiens', [
'title' => 'Pasiens',
'pasiens' => $pasiens,
'query' => $request->input('query'),
'sort_by' => $request->input('sort_by'),
]);
}In this code, the function starts by setting the pagination limit to 9 and initializing the query for retrieving patients from the database. It then checks if there is a search query provided in the request and adds conditions to the query to filter the patients based on the search text. The search is performed on fields like name, email, phone number, age, height, and weight.
Next, the function checks if there is a sorting parameter (sort_by) in the request. If so, it applies the corresponding sorting order to the query based on the value of sort_by. For example, if sort_by is set to 'name_asc', the patients will be sorted in ascending order by their name. If no sorting parameter is specified, the default sorting order is ascending by name.
After setting up the search and sorting conditions, the function retrieves the paginated results using the paginate method on the query. The number of results per page is determined by the pagination limit set earlier.
Finally, the function returns a view called 'admin.pasiens' with various data, including the title, the paginated patient results, the search query, and the sorting parameter. This view can be used to display the patients' list in the admin panel.
if ($request->has('sort_by')) {
$sort_by = $request->input('sort_by');
if ($sort_by === 'name_asc') {
$query->orderBy('name', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'name_desc') {
$query->orderBy('name', 'desc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'age_asc') {
$query->orderBy('age', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'age_desc') {
$query->orderBy('age', 'desc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'height_asc') {
$query->orderBy('height', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'height_desc') {
$query->orderBy('height', 'desc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'weight_asc') {
$query->orderBy('weight', 'asc');
} elseif ($sort_by === 'weight_desc') {
$query->orderBy('weight', 'desc');
}
} else {
$query->orderBy('name', 'asc');
}
}If the sort_by parameter exists in the request, the code checks its value and applies the corresponding sorting logic to the query.
Here's how the code works:
- If the
sort_byvalue isname_asc, the query is sorted by thenamecolumn in ascending order. - If the
sort_byvalue isname_desc, the query is sorted by thenamecolumn in descending order. - If the
sort_byvalue isage_asc, the query is sorted by theagecolumn in ascending order. - If the
sort_byvalue isage_desc, the query is sorted by theagecolumn in descending order. - If the
sort_byvalue isheight_asc, the query is sorted by theheightcolumn in ascending order. - If the
sort_byvalue isheight_desc, the query is sorted by theheightcolumn in descending order. - If the
sort_byvalue isweight_asc, the query is sorted by theweightcolumn in ascending order. - If the
sort_byvalue isweight_desc, the query is sorted by theweightcolumn in descending order. - If the
sort_byparameter does not exist in the request, the query is sorted by thenamecolumn in ascending order by default.
This code segment can be used in a larger codebase to dynamically sort query results based on user-defined sorting preferences.
if ($request->has('query')) {
$search_text = $request->input('query');
$query->where(function ($q) use ($search_text) {
$q->where('name', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('email', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('phone_number', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('age', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('height', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%")
->orWhere('weight', 'LIKE', "%$search_text%");
});
}The search filter is applied using the where method with a callback function. The callback function uses the LIKE operator to perform a partial match search on multiple columns of a table. It checks if the 'name', 'email', 'phone_number', 'age', 'height', or 'weight' columns contain the text specified in the $search_text variable.
Overall, this code enables searching for records in a database table based on a user-provided search query.
$pagination = 9;
$dokters = $query->paginate($pagination);The provided code is related to pagination in a web application. It appears to set the number of items per page to 9 using the variable $pagination. The $query object is then used to paginate the results, assigning the paginated items to the $dokters variable.
This code snippet is part of a larger codebase and is likely used to display a list of items, such as doctors, in a paginated manner on a web page.
return back()->with('status', 'Dokter updated successfully');In the controller, this code is typically used after performing an action, such as updating a record in a database. It redirects the user back to the previous page (using the back() function) and stores a status message in the session with the key 'status'. In this case, it sets the message to 'Dokter updated successfully'.
@if(Session::get('status') != null)
<div id="alert-1" class="flex items-center p-4 mb-4 z-40 text-sm text-blue-800 border border-blue-300 rounded-lg bg-blue-50 dark:bg-gray-800 dark:text-blue-400 dark:border-blue-800 md:px-6" role="alert" style="position: fixed; top: 20px; right: 20px;">
<svg class="flex-shrink-0 w-4 h-4" aria-hidden="true" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 20 20">
<path d="M10 .5a9.5 9.5 0 1 0 9.5 9.5A9.51 9.51 0 0 0 10 .5ZM9.5 4a1.5 1.5 0 1 1 0 3 1.5 1.5 0 0 1 0-3ZM12 15H8a1 1 0 0 1 0-2h1v-3H8a1 1 0 0 1 0-2h2a1 1 0 0 1 1 1v4h1a1 1 0 0 1 0 2Z"/>
</svg>
<span class="sr-only">Info</span>
<div class="ml-3 mr-6 text-sm font-medium">
{{ \Illuminate\Support\Facades\Session::get('status') }}
</div>
<button type="button" class="ml-auto -mx-1.5 -my-1.5 bg-blue-50 text-blue-500 rounded-lg focus:ring-2 focus:ring-blue-400 p-1.5 hover:bg-blue-200 inline-flex items-center justify-center h-8 w-8 dark:bg-gray-800 dark:text-blue-400 dark:hover:bg-gray-700" data-dismiss-target="#alert-1" aria-label="Close">
<span class="sr-only">Close</span>
<svg class="w-3 h-3" aria-hidden="true" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" fill="none" viewBox="0 0 14 14">
<path stroke="currentColor" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round" stroke-width="2" d="m1 1 6 6m0 0 6 6M7 7l6-6M7 7l-6 6"/>
</svg>
</button>
</div>
@endisset
@foreach($errors->all() as $error)
<div id="alert-2" class="mx-auto w-full px-8 z-40 overflow-x-auto lg:px-56 md:px-14 flex items-center p-4 mb-4 text-red-800 rounded-lg bg-red-50 dark:bg-gray-800 dark:text-red-400" role="alert">
<svg class="flex-shrink-0 w-4 h-4" aria-hidden="true" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" fill="currentColor" viewBox="0 0 20 20">
<path d="M10 .5a9.5 9.5 0 1 0 9.5 9.5A9.51 9.51 0 0 0 10 .5ZM9.5 4a1.5 1.5 0 1 1 0 3 1.5 1.5 0 0 1 0-3ZM12 15H8a1 1 0 0 1 0-2h1v-3H8a1 1 0 0 1 0-2h2a1 1 0 0 1 1 1v4h1a1 1 0 0 1 0 2Z"/>
</svg>
<span class="sr-only">Info</span>
<div class="ml-3 text-sm font-medium">
{{ $error }}
</div>
<button type="button" class="ml-auto -mx-1.5 -my-1.5 bg-red-50 text-red-500 rounded-lg focus:ring-2 focus:ring-red-400 p-1.5 hover:bg-red-200 inline-flex items-center justify-center h-8 w-8 dark:bg-gray-800 dark:text-red-400 dark:hover:bg-gray-700" data-dismiss-target="#alert-2" aria-label="Close">
<span class="sr-only">Close</span>
<svg class="w-3 h-3" aria-hidden="true" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" fill="none" viewBox="0 0 14 14">
<path stroke="currentColor" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round" stroke-width="2" d="m1 1 6 6m0 0 6 6M7 7l6-6M7 7l-6 6"/>
</svg>
</button>
</div>
@endforeachIn the view code, it checks if there is a 'status' message in the session. If a 'status' message is found, it displays a styled alert box with the message.
Here's what's happening in the view code:
- The
@ifdirective checks whether the 'status' message is not null. - If the 'status' message exists, it displays an alert box with the message.
- The alert box includes a blue background, an SVG icon, the status message, and a close button.
- The alert box is positioned fixed to the top-right corner of the page.
Additionally, there is another section in the code that handles error messages ($errors->all()) and displays them in a similar manner but with a red background. It iterates through each error message and creates an alert box for each error.
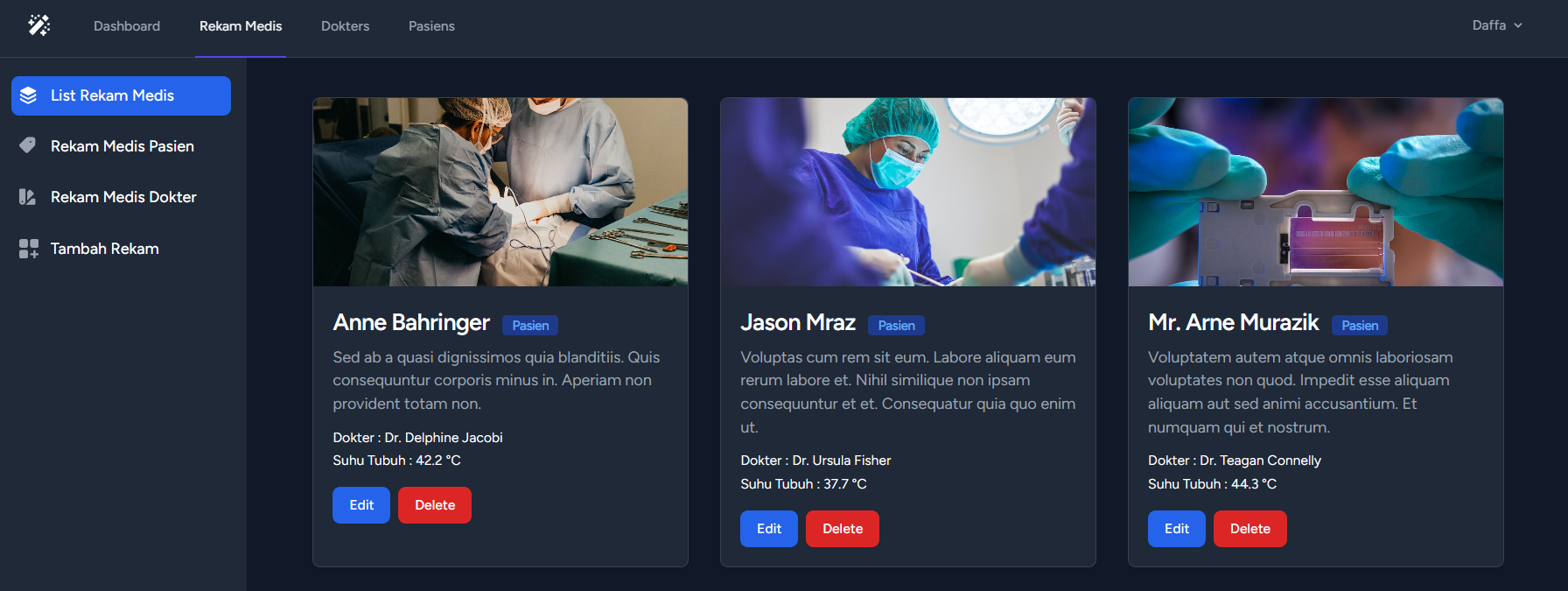
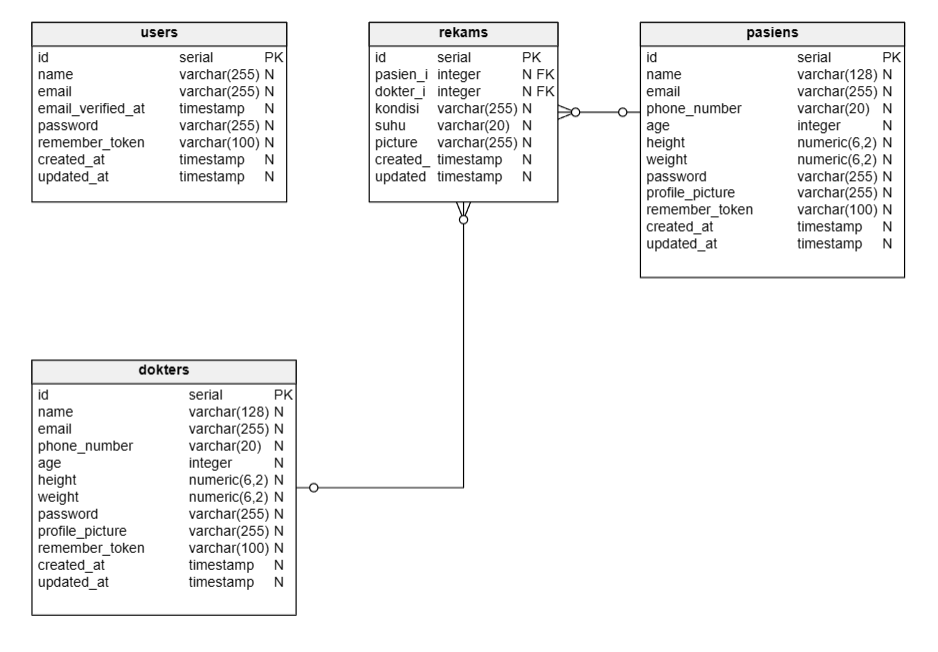
This midexam project is done using Laravel. For login, register, and logout sessions, we are using the built-in Breeze feature from Laravel. In this project, there are 4 tables: user table, patient table, doctor table, and medical record table. The medical record table uses foreign keys from the doctor and patient tables.
The implementation in this project includes: Login, Register, Logout, Listing, Sorting, Searching, Pagination, and Validation Status.