Project for the Principles for Software Composition exam, a.y. 23/24.
The program relies on the Ebitengine library, which on some platforms has external dependencies. Those should be installed following the instructions. On NixOS, all dependencies can be downloaded by activating the shell.nix file with nix-shell.
Then, the program can be compiled and run with the command go run ..
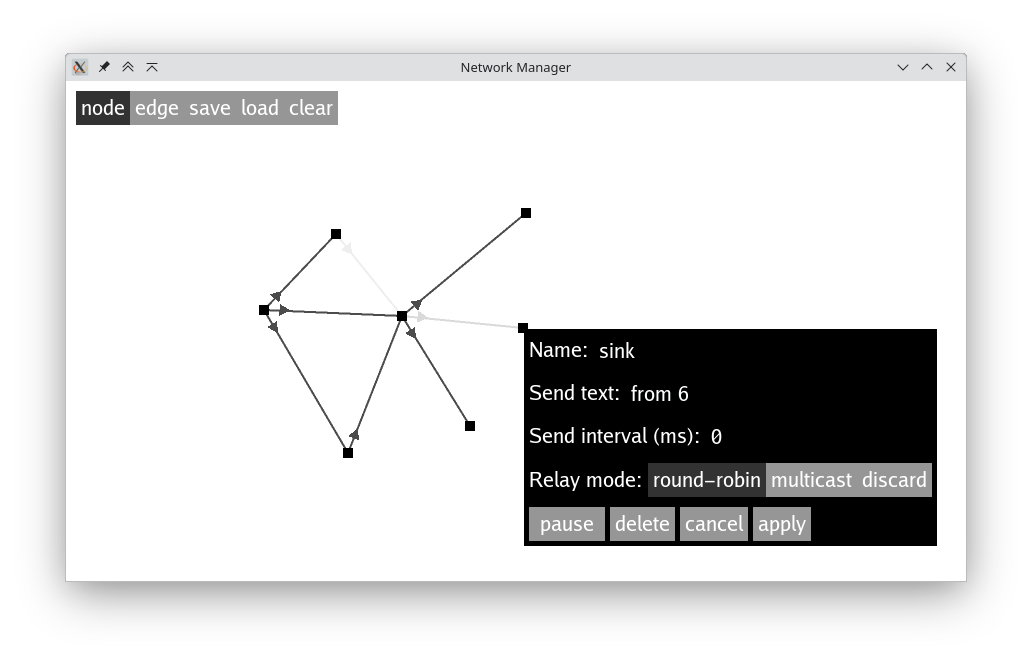
The programs allows the creation of a network through a graphical interface. The user can select one of two tools:
- Node tool
- when this tool is selected, a left click will create a new node, or open the control panel of the node under the mouse pointer.
- Edge tool
- with this tool, the user can left click on two different nodes to create a channel between them, or remove the existing channel if they were already connected. Channels are directional, as indicated by the small triangles in the UI.
The user can also hold down the right mouse button to pan the view.
Through the node control panel, several parameters can be set for each node:
- display name;
- send text and interval;
- relay mode (round-robin, multicast, discard);
and the node can be paused or deleted.
When a node is created, a corresponding coroutine is spawned that performs two tasks:
- It generates periodically (according to the send interval) a new message, containing the send text, and it sends it to all output channels of the node.
- It forwards incoming messages to the output channels, according to the relay mode (round-robin, multicast, discard).
The activity of the nodes is logged to standard output. Log messages start with the current date and time, followed by the display name and unique ID of the node, and then the logged text.
In the UI, the channels are drawn with a shade of gray that gets darker the more they are used.
The user can also save and load networks to/from files on disk using the dedicated buttons.
Networks can be saved and loaded from text files with the following syntax:
NET ::= 'digraph network {\n' (NODE | CHAN)* '}'
NODE ::= ID '[label=' NAME '] //' SEND_TEXT SEND_INTERVAL RELAY_MODE PAUSED X Y '\n'
CHAN ::= ID '->' ID '\n'
ID, SEND_INTERVAL, X, Y ::= <integer>
NAME, SEND_TEXT ::= <string>
RELAY_MODE ::= 0 | 1 | 2
PAUSED ::= 'true' | 'false'
Each node must have an unique ID. The strings NAME and SEND_TEXT must be between double quotes; they may contain escaped double quotes (\"). SEND_INTERVAL is in milliseconds. The channels are written as <src id> -> <dst id>.
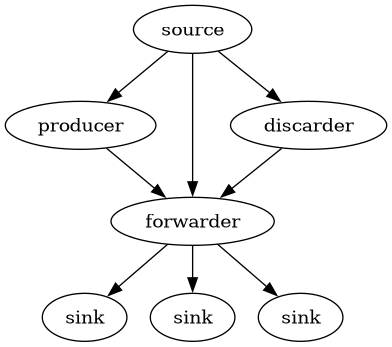
For an example, see example.dot.
Such files are valid DOT programs, and can be turned into graphs of the network topology with the command:
dot -Tpng example.dot > example.pngwhich for the provided example produces the following image: