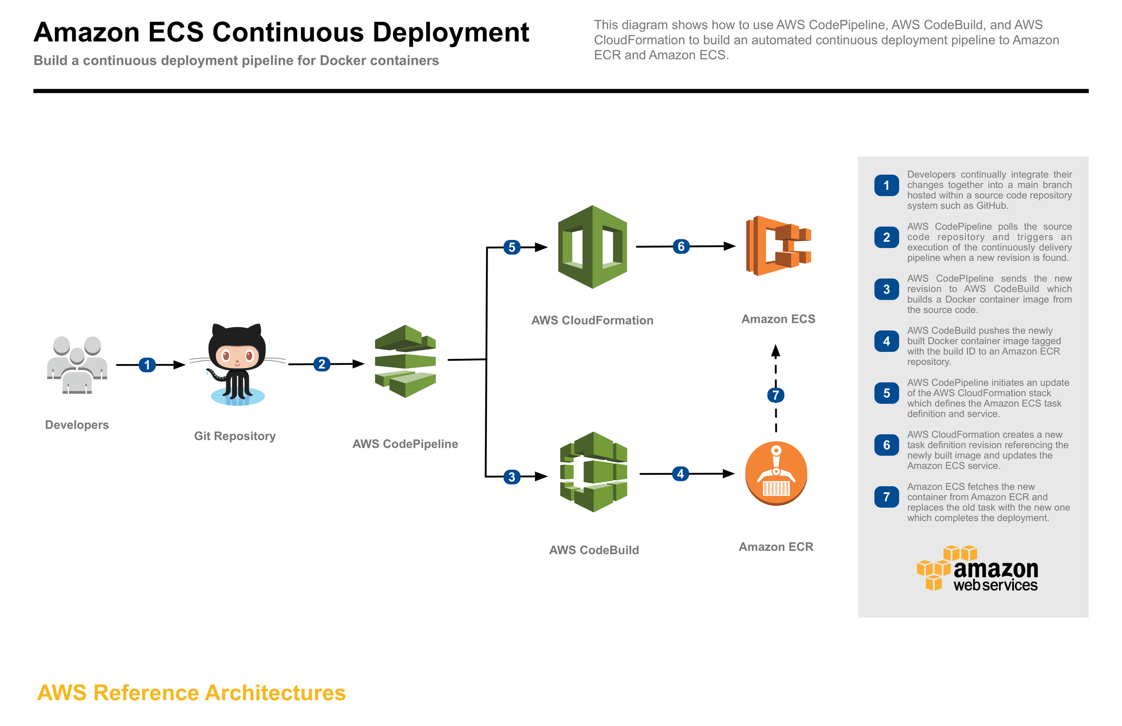
The ECS Continuous Deployment reference architecture demonstrates how to achieve continuous deployment of an application to Amazon ECS using AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeBuild, and AWS CloudFormation. With continuous deployment, software revisions are deployed to a production environment automatically without explicit approval from a developer, making the entire software release process automated.
Launching this AWS CloudFormation stack provisions a continuous deployment process that uses AWS CodePipeline to monitor a GitHub repository for new commits, AWS CodeBuild to create a new Docker container image and to push it into Amazon ECR, and AWS CloudFormation to deploy the new container image to production on Amazon ECS.
Fork the Amazon ECS sample app GitHub repository into your GitHub account.
From your terminal application, execute the following command (make sure to replace <your_github_username> with your actual GitHub username):
git clone https://github.com/<your_github_username>/ecs-demo-php-simple-appThis creates a directory named ecs-demo-php-simple-app in your current directory, which contains the code for the Amazon ECS sample app.
Choose Deploy to AWS to launch the template in your account.
This reference architecture can only be deployed to Regions which have all necessary services such as AWS CodePipeline and AWS CodeBuild. See the Region Table for more details.
The CloudFormation template requires the following parameters:
- GitHub configuration
- Repo: The repo name of the sample service.
- Branch: The branch of the repo to deploy continuously.
- User: Your username on GitHub.
- Personal Access Token: Token for the user specified above. (https://github.com/settings/tokens)
The CloudFormation stack provides the following output:
- ServiceUrl: The sample service that is being continuously deployed.
- PipelineUrl: The continuous deployment pipeline in the AWS Management Console.
After the CloudFormation stack is created, the latest commit to the GitHub repository is run through the pipeline and deployed to ECS. Open the PipelineUrl to watch the first revision run through the CodePipeline pipeline. After the deploy step turns green, open the URL from ServiceUrl which loads a page similar to this:
To test continuous deployment, make a change to src/index.php in the ecs-demo-php-simple-app repository and push it to GitHub. CodePipeline detects the change, builds the new application, and deploys it to your cluster automatically. After the pipeline finishes deploying the revision, reload the page to see the changes made.
To remove all resources created by this example, do the following:
- Delete the main CloudFormation stack which deletes the substacks and resources.
- Manually delete resources which may contain files:
- S3 bucket:
ArtifactBucket - ECR repository:
Repository
The following sections explains all of the resources created by the CloudFormation template provided with this example.
Resources that compose the deployment pipeline include the CodeBuild project, the CodePipeline pipeline, an S3 bucket for deployment artifacts, and all necessary IAM roles used by those services.
An ECS task definition, service, IAM role, and ECR repository for the sample application. This template is used by the CodePipeline pipeline to deploy the sample service continuously.
An ECS cluster backed by an Auto Scaling group of EC2 instances running the Amazon ECS-optimized AMI.
An Application Load Balancer to be used for traffic to the sample application.
A VPC with two public subnets on two separate Availability Zones, an internet gateway, and a route table with a default route to the public internet.
This reference architecture sample is licensed under Apache 2.0.