Data Facility Admin
Admin system for the Data Facility.
Why
DFAdmin was created to organize the core entities of a Data Facility such as Datasets, People and Projects. It is used as a core component on ADRF, being the orchestrator of IAM. Read more on the ADRF Framework, Data Model and DFAdmin whitepaper.
Features
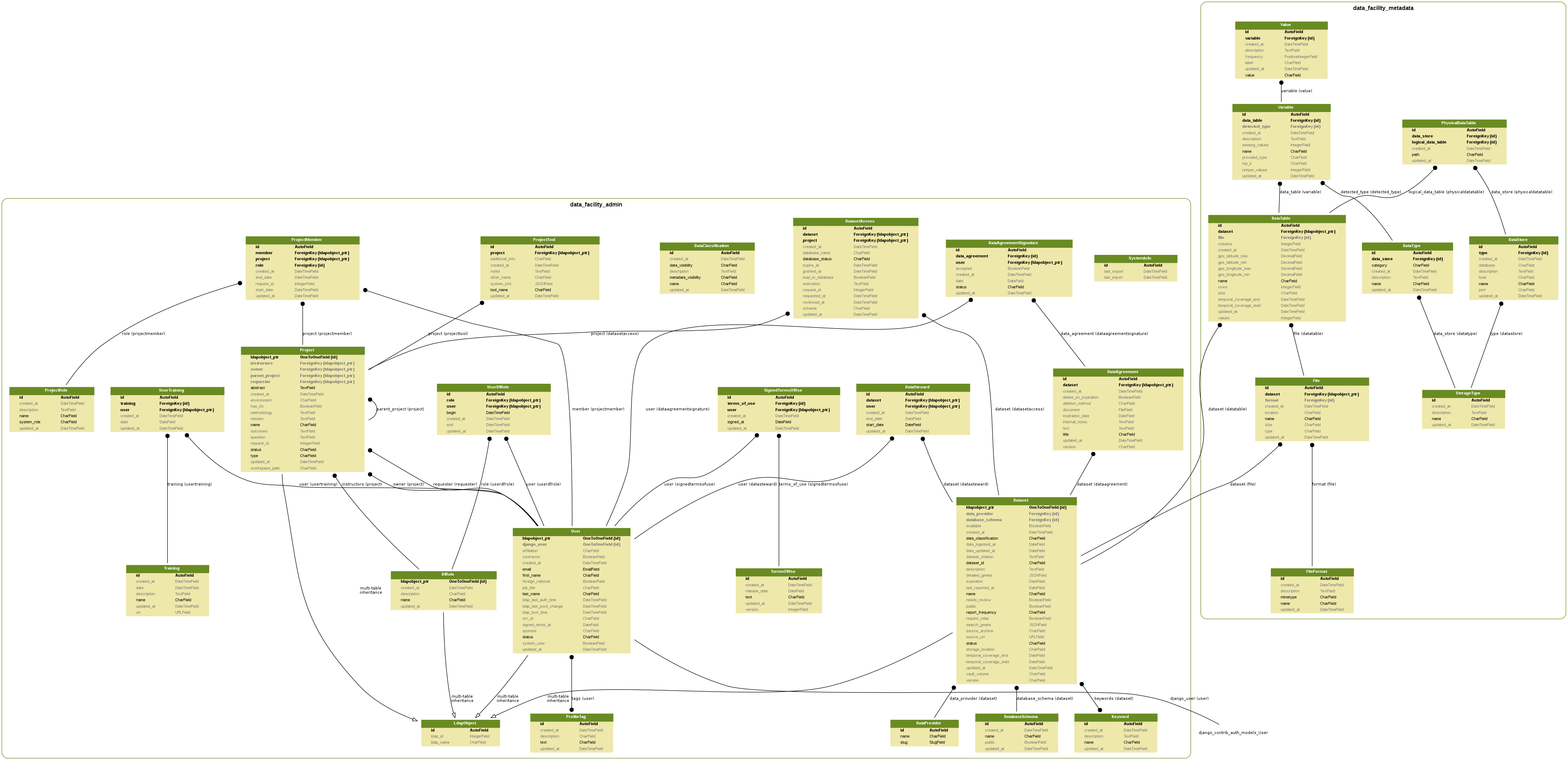
Data Model
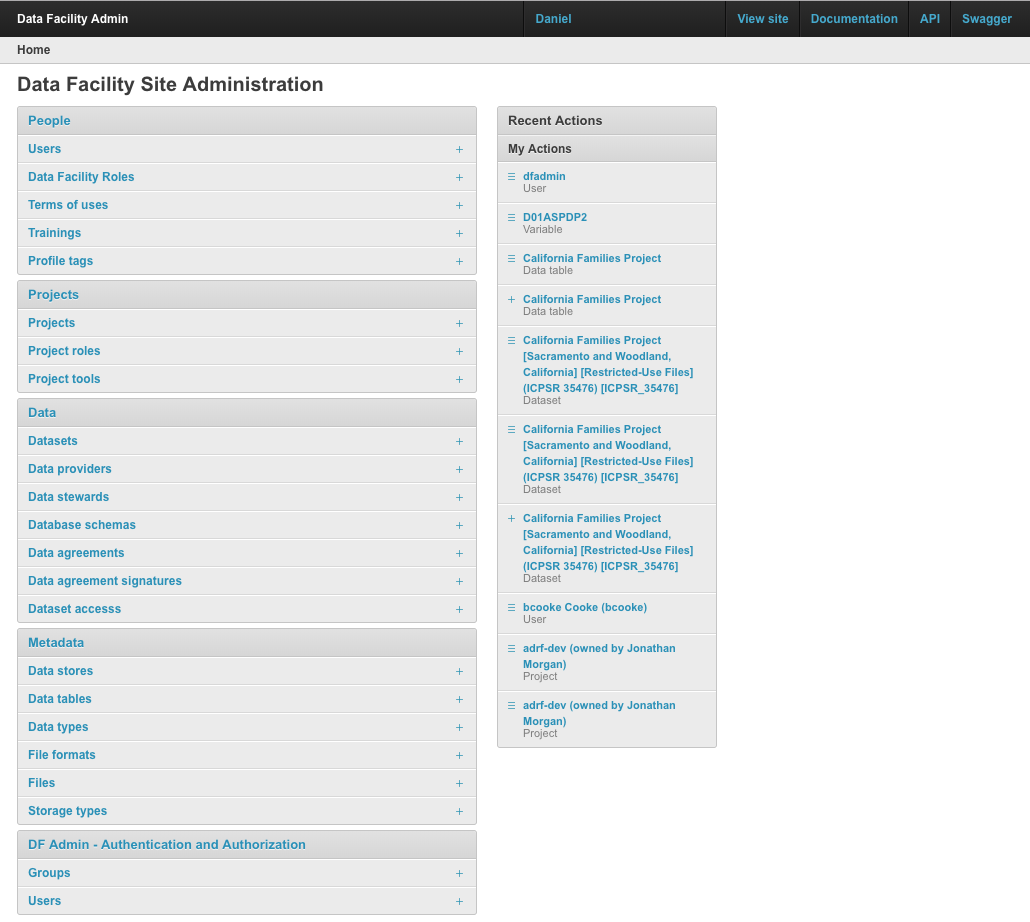
Screenshots
Requirements
- Docker (v 17.12.0)& Docker Compose
- Wait-for-it. After git clone, run
make git-submodules-init
Teste on MacOX: Docker version 17.12.0-ce, build c97c6d6
Deploy - with Docker
Two containers are used:
- web: to run the web application and Django management tasks.
- db: is a PostgreSQL database with a local folder mounted as the data volume.
Copy the code to the desired server and run:
make deploy-build-latest: used to build the containers on the first time and to update the web container when needed.make depoy-up: used to run start the containers.
Development
Prepare the application and database
- Run
ln -s local.env .envto symlink the local dev configuration - Run the containers
docker-compose up -d - Prepare the database with the data backup and migrate
make dev-db-restoreor justmake db-migrateif you don't have a previous db backup to use. - Create the super user:
docker-compose exec web ./manage.py createsuperuser(if you restored the dev db it might already have a super user withdfadmin/dfadmincredentials) - Run tests (
make test) to make sure all is right.
Cheers! Go to http://localhost:8000 and check the DF Admin website.
Running tests
You can run tests with the following:
make test: to run tests creating the database (necessary on the first run)
Clean the database (Postgres)
This will wipe out everything (tables, sequences and views; the whole schema): dev-db-clear
Access
Now access the <host>:8000/admin and you should be prompted for login credentials.
Before commit
Before commit your changes, please:
- Run tests:
make test - Run code checks:
make code-check
LDAP Control
(needs update)
When you write users and groups in LDAP, we should know some information like objectClass, loginShell, HomeDirectory, uidNumber, and gidNumber. All the groups that exist in LDAP should come from DF Admin. We should have the Django models Group, Dataset, and Project in DF Admin. These models should use the same sequence to set their id value, and we should use this id to set the gidNumber in LDAP. We should use the id of the Django model User as the uidNumber. The groups and users in LDAP should be created only by DF Admin. The rest of the necessary information necessary to create groups and users in LDAP should be processed by a script using conventions.
Troubleshooting
wait for it not found: Make sure you initialized the submodules. (see requirements above)
Documentation
Reference the folder documentation.
UML Class Diagram
A class diagram can be generated automatically based on the models with django_model_graph.sh
source env/bin/activate
make docsRelease
Please check the RELEASE documentation when preparing a release.
Keycloak Integration
Postman Collections: https://www.getpostman.com/collections/1b72e4b52b9e5ad42d3c
Getting KeyCloak PubKey (It needs to have the "----BEGIN..." And "-----END...") (PEM format): https://www.getpostman.com/collections/1b72e4b52b9e5ad42d3c
References:
https://zapier.com/engineering/apikey-oauth-jwt/ https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/an-introduction-to-oauth-2 http://getblimp.github.io/django-rest-framework-jwt/#additional-settings https://auth0.com/blog/building-modern-applications-with-django-and-vuejs/