A TypeScript language service plugin for CSS Modules.
To install with Yarn:
yarn add -D typescript-plugin-css-modulesTo install with npm:
npm install -D typescript-plugin-css-modulesOnce installed, add this plugin to your tsconfig.json:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"plugins": [{ "name": "typescript-plugin-css-modules" }]
}
}If you're using Visual Studio Code, please also follow these instructions.
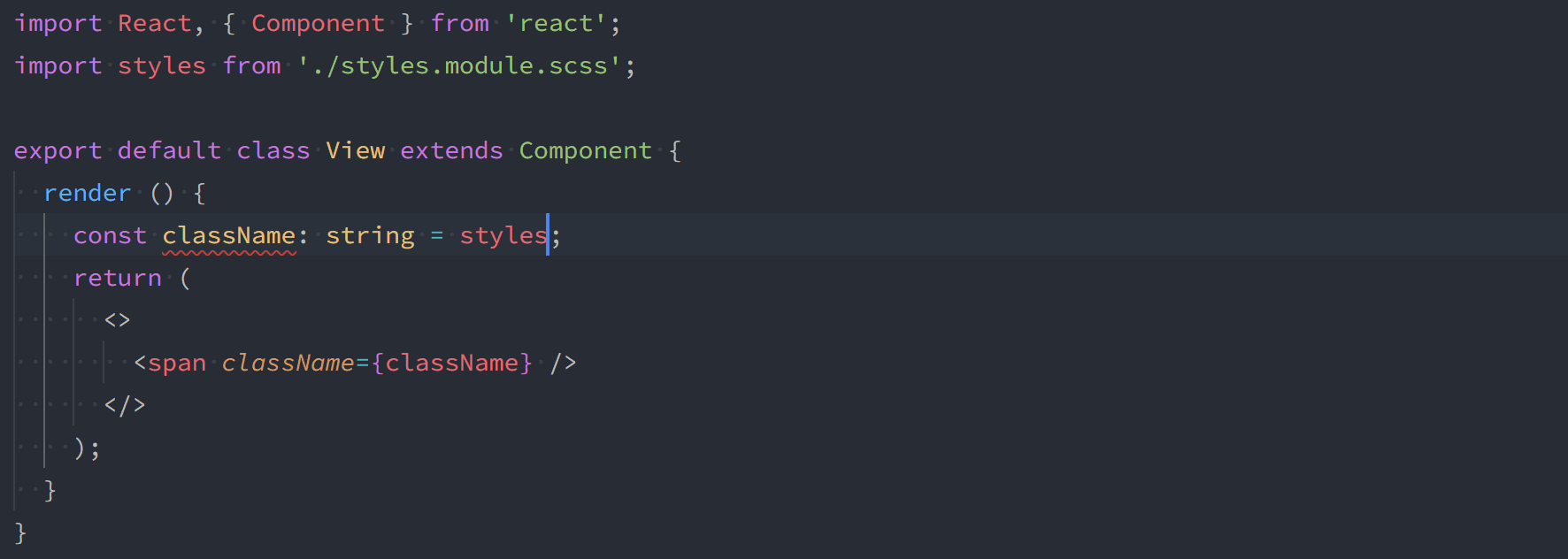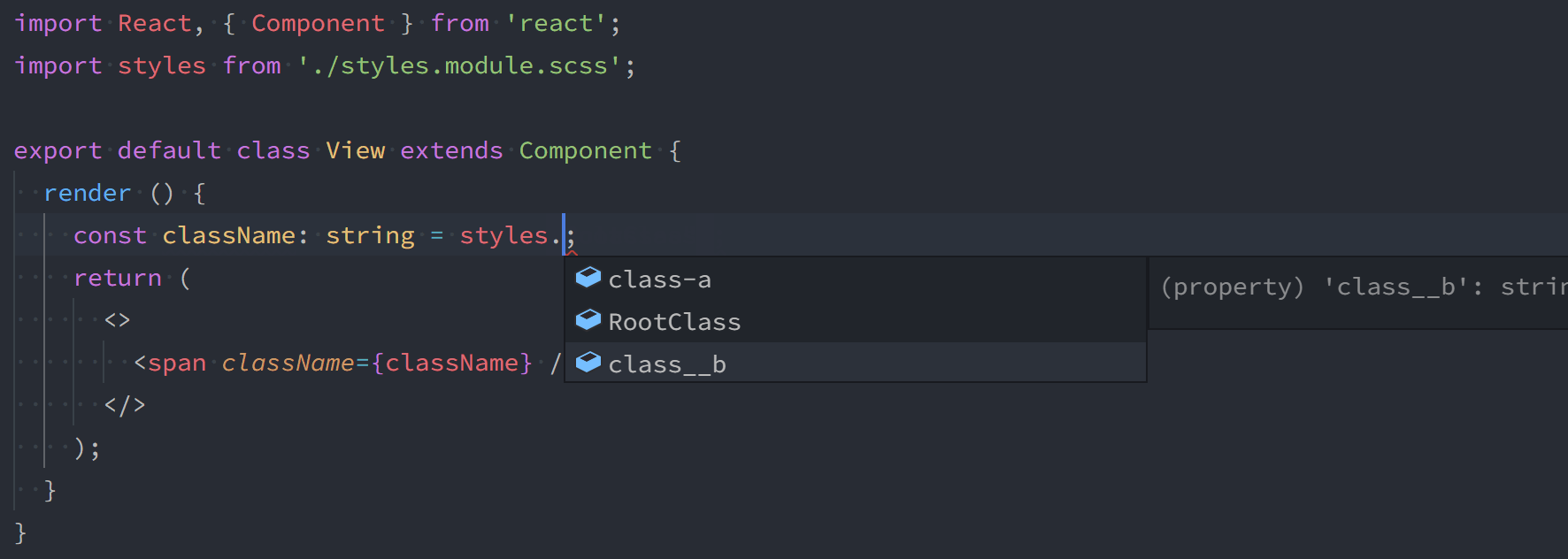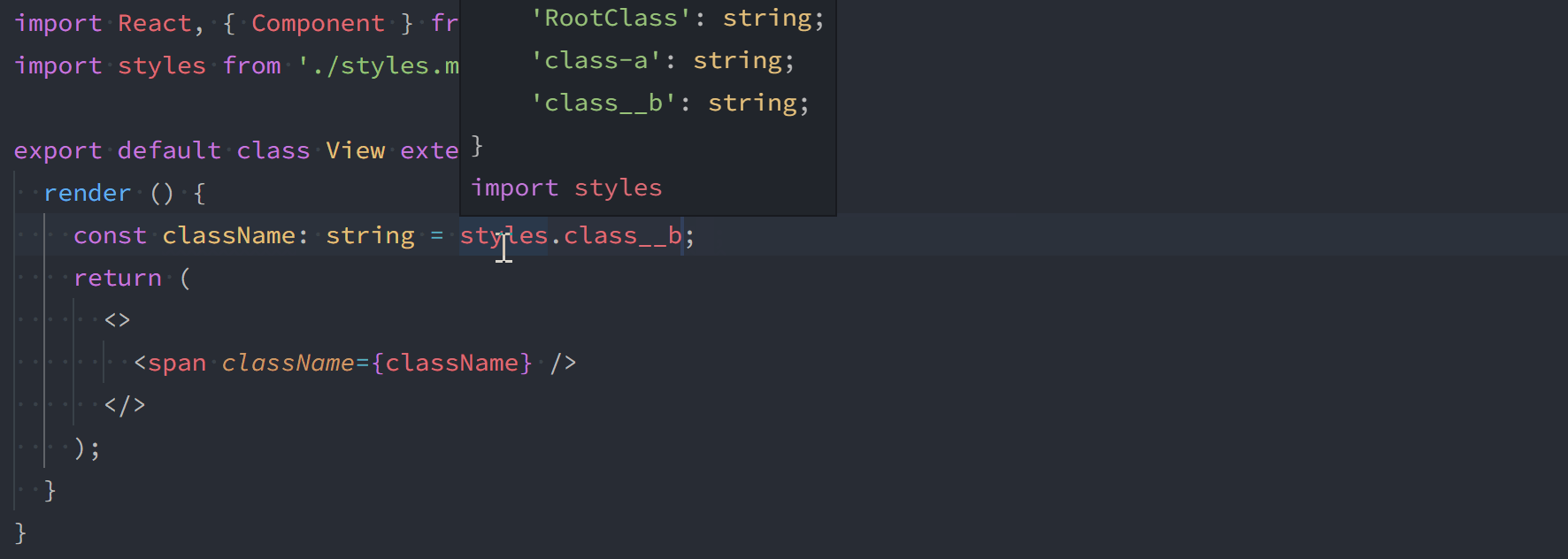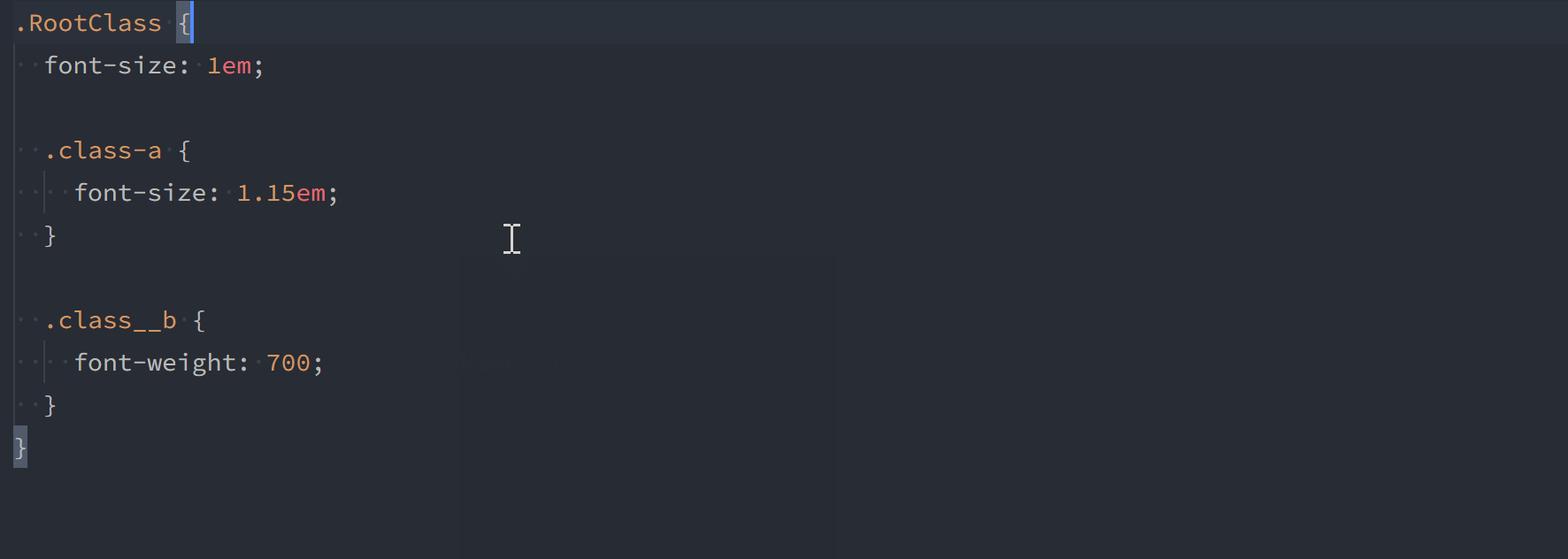
A default export is always provided for your CSS module.
import styles from 'my.module.css';
const a = styles.myClass;
const b = styles['my_other-class'];As of version 1.1.0, you can also use named exports for classes that don't contain hyphens or underscores. You can still access other classes via the default export.
import styles, { myClass } from 'my.module.css';
const a = myClass;
const b = styles['my_other-class'];Please note that no options are required. However, depending on your configuration, you may need to customise these options.
| Option | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
classnameTransform |
asIs |
See classnameTransform below. |
customMatcher |
"\\.module\\.(c|le|sa|sc)ss$" |
Changes the file extensions that this plugin processes. |
customRenderer |
false |
See customRenderer below. |
customTemplate |
false |
See customTemplate below. |
dotenvOptions |
{} |
Provides options for dotenv. |
postCssOptions |
{} |
See postCssOptions below. |
rendererOptions |
{} |
See rendererOptions below. |
{
"compilerOptions": {
"plugins": [
{
"name": "typescript-plugin-css-modules",
"options": {
"classnameTransform": "dashes",
"customMatcher": "\\.m\\.css$",
"customRenderer": "./myRenderer.js",
"dotenvOptions": {},
"postCssOptions": {},
"rendererOptions": {}
}
}
]
}
}Implements the behaviour of the localsConvention css-loader option.
Options available are: 'asIs', 'camelCase', 'camelCaseOnly', 'dashes', and 'dashesOnly'.
The customRenderer is an advanced option, letting you provide the CSS renderer.
When a custom renderer is provided, not other renderers will be used.
The path to the customRenderer must be relative to the project root (i.e. ./myRenderer.js).
The custom renderer itself should be a JavaScript file. The function will be called with three arguments: a css string, an options object and an compilerOptions object that is defined in tsconfig.json the tsc used. (see options.ts). It must be synchronous, and must return valid CSS.
module.exports = (css, { fileName, logger }) => {
try {
// ...process your css here.
return renderedCss;
} catch (error) {
logger.error(error.message);
}
};You can find an example custom renderer in our test fixtures (customRenderer.js).
The internal logger is provided for debugging.
Note: If you are working with webpack and
less-loader, you can choose resolver that webpack provided and webpack will resolve the@importfile path that start with~, but~is not support by less natively, and the plugin will break down, then we can useless-plugin-aliasesnpm package make it works again, more details can find here and here
The customTemplate is an advanced option, letting you provide a template for the generated TypeScript declarations.
When a custom template is provided, its output is used as the virtual declaration (*.d.ts) file.
The path to the customTemplate must be relative to the project root (i.e. ./customTemplate.js).
The custom renderer itself should be a JavaScript file. The function will be called with two arguments: a dts string, and an options object (see options.ts). It must be synchronous, and must return a valid TypeScript declaration (as found in a .d.ts file).
module.exports = (dts, { classes, fileName, logger }) => {
try {
// ...generate your template here.
return customTemplate;
} catch (error) {
logger.error(error.message);
}
};You can find an example custom template in our test fixtures (customTemplate.js).
The internal logger is provided for debugging.
The classes object represents all the classnames extracted from the CSS Module. They are available if you want to add a custom representation of the CSS classes.
| Option | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
useConfig |
false |
Set to true to load plugins from your PostCSS config. |
excludePlugins |
false |
Only sync plugins are supported. Use this to set an array of async plugins to exclude (i.e. ['postcss-mixins']) |
| Option | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
less |
{} |
Set renderer options for Less. |
sass |
{} |
Set renderer options for Sass. |
For convenience,
includePathsfor Sass are extended, not replaced. The defaults are the path of the current file, and'node_modules'.
To use this plugin with Visual Studio Code, you should set your workspace's version of TypeScript, which will load plugins from your tsconfig.json file.
For instructions, see: Using the workspace version of TypeScript.
If you aren't using any plugin options, you can simple add this plugin to "typescript.tsserver.pluginPaths" in settings. You cannot provide plugin options with this approach.
{
"typescript.tsserver.pluginPaths": ["typescript-plugin-css-modules"]
}Note: Create React App users can skip this section if you're using react-scripts@2.1.x or higher.
If your project doesn't already have global declarations for CSS Modules, you will need to add these to help TypeScript understand the general shape of the imported CSS during build.
Where you store global declarations is up to you. An example might look like: ./src/custom.d.ts.
The below is an example that you can copy or modify. If you use a customMatcher, you'll need to modify this.
declare module '*.module.css' {
const classes: { [key: string]: string };
export default classes;
}
declare module '*.module.scss' {
const classes: { [key: string]: string };
export default classes;
}
declare module '*.module.sass' {
const classes: { [key: string]: string };
export default classes;
}
declare module '*.module.less' {
const classes: { [key: string]: string };
export default classes;
}For troubleshooting and debugging, you can view the TypeScript Server Log in Visual Studio Code by entering Typescript: Open TS Server log in the command palette.
If you're not using Visual Studio Code or are having trouble with the above method, you can set the TSS_LOG environment variable.
You can include these logs with any issues you open for this project.
This project was inspired by a Create React App issue
and built on prior work from css-module-types.