- Read and understand travis config
- Read and understand docker-compose file
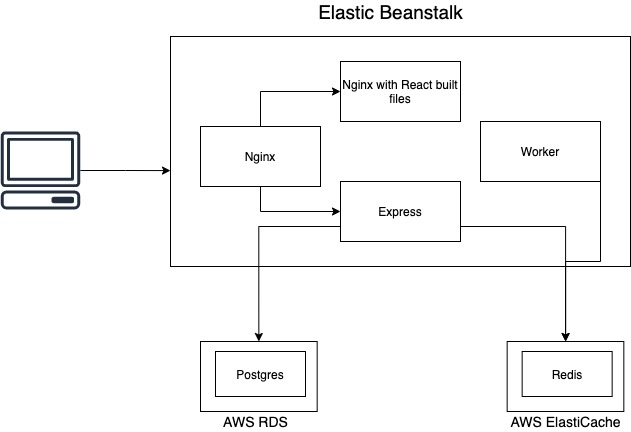
- To deploy multiple container running on one EC2 instance using Elastic Beanstalk, we need a
Dockerrun.aws.jsonconfiguration file, which is specific to Elastic Beanstalk. - When writting the configuration file, note that we have to specify
AWSEBDockerrunVersion=2, because version 2 is to handle multiple container. The format differs significantly from the previous version 1. - Further reading: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/create_deploy_docker_ecs.html
-
To handle path routing/load balancing we can use Nginx, which can be used by simply writting a config file, in this application it is the
nginx/default.conffile. -
Further reading: https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/load-balancer/http-load-balancer/
-
Inside the file, we have 2 kind of directives,
upstreamandserver- Theupstreamdirective is to specify a group of server that will handle the traffic. - Below is a group named client and only consists of 1 server client host on port 3000, noted that theserverdirective here is diferent from the outerserverdirective. Here, theserveris just a list of server (in this application, the server name is taken from the container name set by thedocker-compose.ymlfile) that will handle the traffic passed to this group.upstream client { server client:3000; }- Theserver(outer) directive is to list all the path routing config to a virtual server running on Nginx. Thelocationis followed by a template of incoming traffic, and theproxy_passindicates theupstreamgroup that will handle that request. - In the snippet below, the server will route all request prefix with/apito theapiupstream group and the remaining requests will be handle by theclientupstream group.server { location / { proxy_pass http://client; } location /api { proxy_pass http://api; } }