This repository contains an example of a Fullstack Supergraph with GraphOS.
In order to run the project locally, you'll need node>=14 installed on your development machines.
🏃♂️🕐 Powered by GraphOS
GraphOS automatically provisions and hosts a serverless cloud router for this example. Clients query the router instead of individual subgraphs, which enables the router to automatically collect operation metrics and usage data that you can then visualize in Apollo Studio.
Create your free serverless cloud router with GraphOS by signing up for free here.
GraphOS makes it possible to expose a public set of docs for your supergraph that anyone can use! Check out this supergraph's example and try running some queries.
You can create operation collections in the Apollo Studio Explorer, enabling you to save, organize, and share your frequently used GraphQL operations. There is an operation collection for the Website's grouped queries.
Deployed on Netlify, try @defer
This fullstack application contains a simple React app that utilizes @apollo/client to query GraphOS.
If you would like to run the website locally, setup the website:
cd website
npm installTo start a local copy of the app on port 3000:
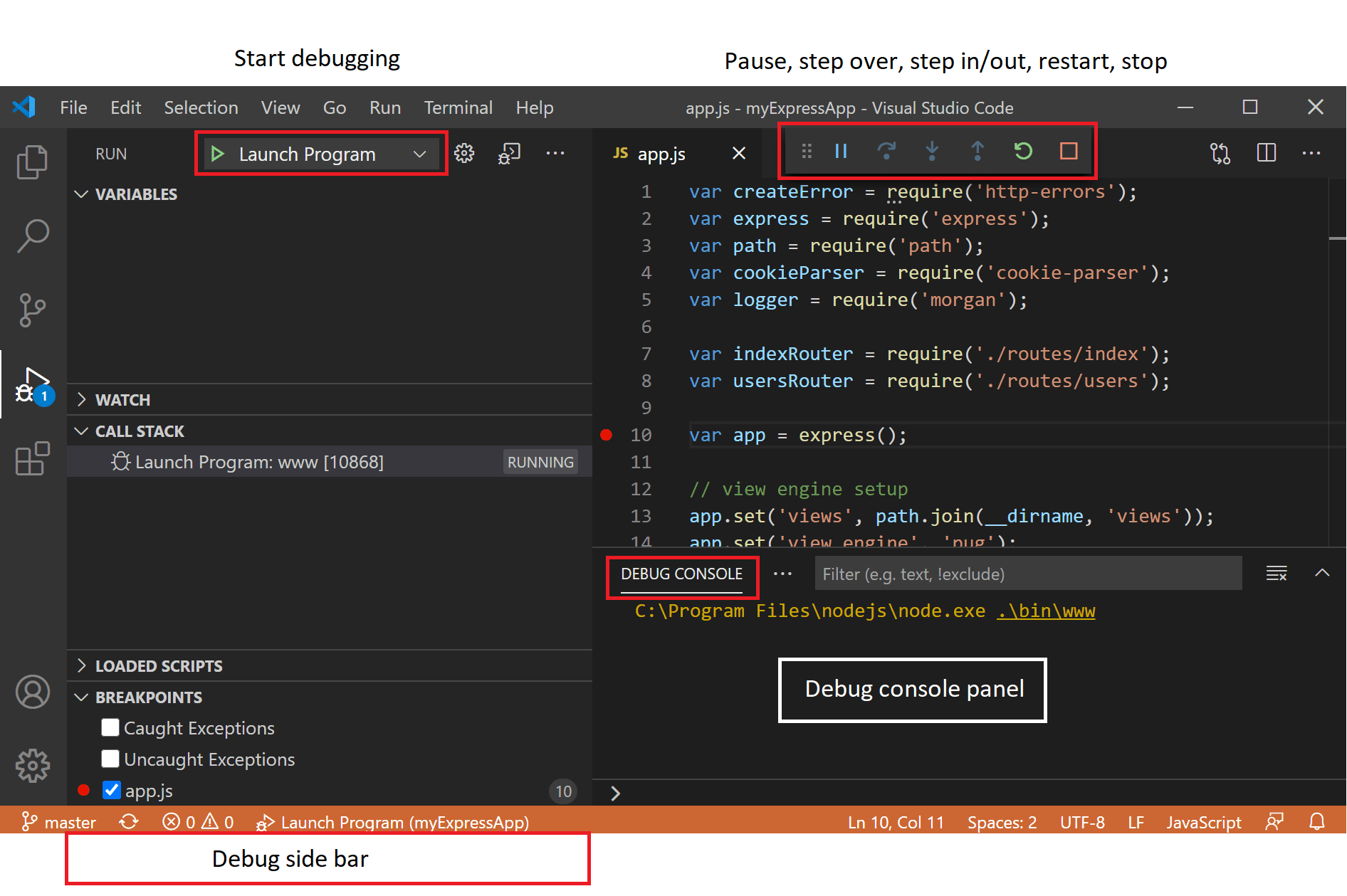
npm startTo debuge the instance, open VS Code and use the launch configuration available in the Debug panel:
code .All of the subgraph projects are located in the subgraphs folder. There are currently five subgraphs: orders, products, reviews, shipping, users. Each subgraph is currently built with @apollo/server and hosted on Railway
All of the subgraphs in this example have GitHub Action workflows to interact with GraphOS. We created separate workflows to isolate each subgraphs tests and deploys. It was easy enough to do this using paths for each subgrpah folder.
This README
We keep this repositories README in sync with GraphOS in case anyone visits our public Explorer referenced above. We are using the Rover CLI to do this in this example, but you can also using the public GraphOS Platform API if you want.
Schema Checks
Certain changes to your graph's schema (such as removing a field or type) might break one of your application's clients. GraphOS provides schema checks to help you identify breaking changes before you make them, and to help you identify when a potentially dangerous change won't break anything.
To try out schema checks on this repository:
- Navigate to the products subgraph
- Edit the file and remove the
mediaUrlfiled from theProducttype - Create a new PR and commit
- GitHub Actions will trigger in PR and fail due to schema checks
Deploying Subgraph changes with Launches
In GraphOS, a launch represents the complete process of making a set of updates to a supergraph, usually initiated by changes to one of its subgraphs.
For this example we've kept it simple and have the minimum of what you want, keeping the main branch of this repository in sync with the main variant in GraphOS. Each variant of a supergraph has its own subgraph schemas, supergraph schema, change history, and metrics. You might have a staging or pre-production environment and that's exactly what variants are for!
You can easily deploy all of the subgraphs to Railway by clicking the button above—just configure your first subgraph with the repo you want to clone this to, and click into the rest to accept the defaults. Once all of the subgraphs are deployed, create a new supergraph in GraphOS pointing to the users subgraph, then add new subgraphs in this order:
reviewsproductsordersshipping
Once your last deploy finishes in Studio, you can test it out by running a query like this:
fragment ProductFragment on Product {
averageRating
reviews {
content
rating
}
}
query GetProductDetails {
products {
id
title
description
mediaUrl
...ProductFragment @defer
}
}