Quantum Machine Learning for FinTech and Time Series Data
Quantum Neural Networks for FinTech Time Series Function Fitting
This repository is for developing quantum neural network models for fitting one-dimensional time series data and noisy signals. It is modified from the model presented in PennyLane Function fitting with a quantum neural network. We modify the code presented in the default notebook downloaded from PennyLane so that it works using synthetic data created by the user, and we train a model on several years worth of drug sales data.
In this very basic setup, there were only 4-layers in the quantum neural network, initialized with random weights. The model went through 50 iterations and had the following training data:
Iter: 1 | Cost: 0.4366430
Iter: 2 | Cost: 0.4130995
Iter: 3 | Cost: 0.4401763
Iter: 4 | Cost: 0.4843044
Iter: 5 | Cost: 0.5272264
Iter: 6 | Cost: 0.5590949
Iter: 7 | Cost: 0.5756194
Iter: 8 | Cost: 0.5762956
Iter: 9 | Cost: 0.5631025
Iter: 10 | Cost: 0.5394853
Iter: 11 | Cost: 0.5095363
Iter: 12 | Cost: 0.4773198
Iter: 13 | Cost: 0.4463337
Iter: 14 | Cost: 0.4191397
Iter: 15 | Cost: 0.3972019
Iter: 16 | Cost: 0.3809405
Iter: 17 | Cost: 0.3699549
Iter: 18 | Cost: 0.3633300
Iter: 19 | Cost: 0.3599337
Iter: 20 | Cost: 0.3586456
Iter: 21 | Cost: 0.3584964
Iter: 22 | Cost: 0.3587285
Iter: 23 | Cost: 0.3588033
Iter: 24 | Cost: 0.3583769
Iter: 25 | Cost: 0.3572647
Iter: 26 | Cost: 0.3554029
Iter: 27 | Cost: 0.3528146
Iter: 28 | Cost: 0.3495813
Iter: 29 | Cost: 0.3458197
Iter: 30 | Cost: 0.3416648
Iter: 31 | Cost: 0.3372562
Iter: 32 | Cost: 0.3327294
Iter: 33 | Cost: 0.3282081
Iter: 34 | Cost: 0.3238007
Iter: 35 | Cost: 0.3195972
Iter: 36 | Cost: 0.3156676
Iter: 37 | Cost: 0.3120615
Iter: 38 | Cost: 0.3088088
Iter: 39 | Cost: 0.3059200
Iter: 40 | Cost: 0.3033888
Iter: 41 | Cost: 0.3011936
Iter: 42 | Cost: 0.2993004
Iter: 43 | Cost: 0.2976666
Iter: 44 | Cost: 0.2962437
Iter: 45 | Cost: 0.2949811
Iter: 46 | Cost: 0.2938298
Iter: 47 | Cost: 0.2927447
Iter: 48 | Cost: 0.2916878
Iter: 49 | Cost: 0.2906292
Iter: 50 | Cost: 0.2895481
Iter: 51 | Cost: 0.2884328
Iter: 52 | Cost: 0.2872799
Iter: 53 | Cost: 0.2860931
Iter: 54 | Cost: 0.2848812
Iter: 55 | Cost: 0.2836566
Iter: 56 | Cost: 0.2824333
Iter: 57 | Cost: 0.2812253
Iter: 58 | Cost: 0.2800452
Iter: 59 | Cost: 0.2789039
Iter: 60 | Cost: 0.2778094
Iter: 61 | Cost: 0.2767668
Iter: 62 | Cost: 0.2757787
Iter: 63 | Cost: 0.2748451
Iter: 64 | Cost: 0.2739643
Iter: 65 | Cost: 0.2731328
Iter: 66 | Cost: 0.2723465
Iter: 67 | Cost: 0.2716004
Iter: 68 | Cost: 0.2708895
Iter: 69 | Cost: 0.2702092
Iter: 70 | Cost: 0.2695549
Iter: 71 | Cost: 0.2689228
Iter: 72 | Cost: 0.2683099
Iter: 73 | Cost: 0.2677134
Iter: 74 | Cost: 0.2671316
Iter: 75 | Cost: 0.2665631
Iter: 76 | Cost: 0.2660070
Iter: 77 | Cost: 0.2654630
Iter: 78 | Cost: 0.2649310
Iter: 79 | Cost: 0.2644110
Iter: 80 | Cost: 0.2639034
Iter: 81 | Cost: 0.2634083
Iter: 82 | Cost: 0.2629260
Iter: 83 | Cost: 0.2624569
Iter: 84 | Cost: 0.2620009
Iter: 85 | Cost: 0.2615582
Iter: 86 | Cost: 0.2611285
Iter: 87 | Cost: 0.2607117
Iter: 88 | Cost: 0.2603074
Iter: 89 | Cost: 0.2599152
Iter: 90 | Cost: 0.2595346
Iter: 91 | Cost: 0.2591651
Iter: 92 | Cost: 0.2588059
Iter: 93 | Cost: 0.2584567
Iter: 94 | Cost: 0.2581168
Iter: 95 | Cost: 0.2577857
Iter: 96 | Cost: 0.2574629
Iter: 97 | Cost: 0.2571479
Iter: 98 | Cost: 0.2568405
Iter: 99 | Cost: 0.2565402
Iter: 100 | Cost: 0.2562468
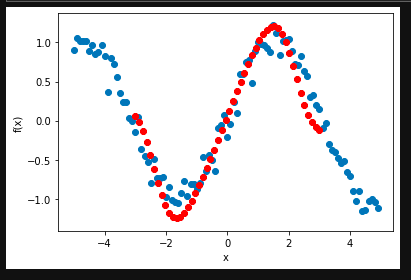
After training the quantum neural network learns to smooth the noisy sine function as can be seen in the red plots:
This example illustrates an implementation of optical quantum computing and training an optical based quantum neural network. For more information on photonic quantum computing see the Strawberry Fields documentation. Strawberry Fields is a full-stack library for design, simulation, optimization, and quantum machine learning of continuous-variable circuits that is fully integrated into PennyLane. For more information on more general quantum nodes, see the PennyLane documentation.
In later examples of applications of quantum machine learning to FinTech, we will also be investigating quantum walks. Quantum walks are a quantum analogue to random walks and have substantially reduced the time-consumption in Monte Carlo simulations for mixing of Markov chains as reported by Ashley Montanaro (2015). These quantum algorithms are applied for investment strategies in wealth management and trading.