Contact Russell Hamilton (darogan@gmail.com)
Protoocol to process the fastq files direct from the sequencer, prior to running through McCarroll lab's DropSeq Tools (https://github.com/broadinstitute/Drop-seq/releases).
Custom Transcriptome for alignment is provided on this repository https://github.com/darogan/TSC_Custom_Transcriptome.
BBTools from https://jgi.doe.gov/data-and-tools/software-tools/bbtools/ Install amd make available on PATH, instructions provided on source website above.
Cutadapt from https://cutadapt.readthedocs.io/en/stable/
fastp from https://github.com/OpenGene/fastp
Demultiplexing of raw fastq files into Nextera indexed fastq files is performed using a custom script (dropseq_demultiplex.sh). The script contains all Nextera index name:sequence pairs to be used in the sequencing runs and calls demuxbyname.sh from BBTools (v39.05, CITATION_1).
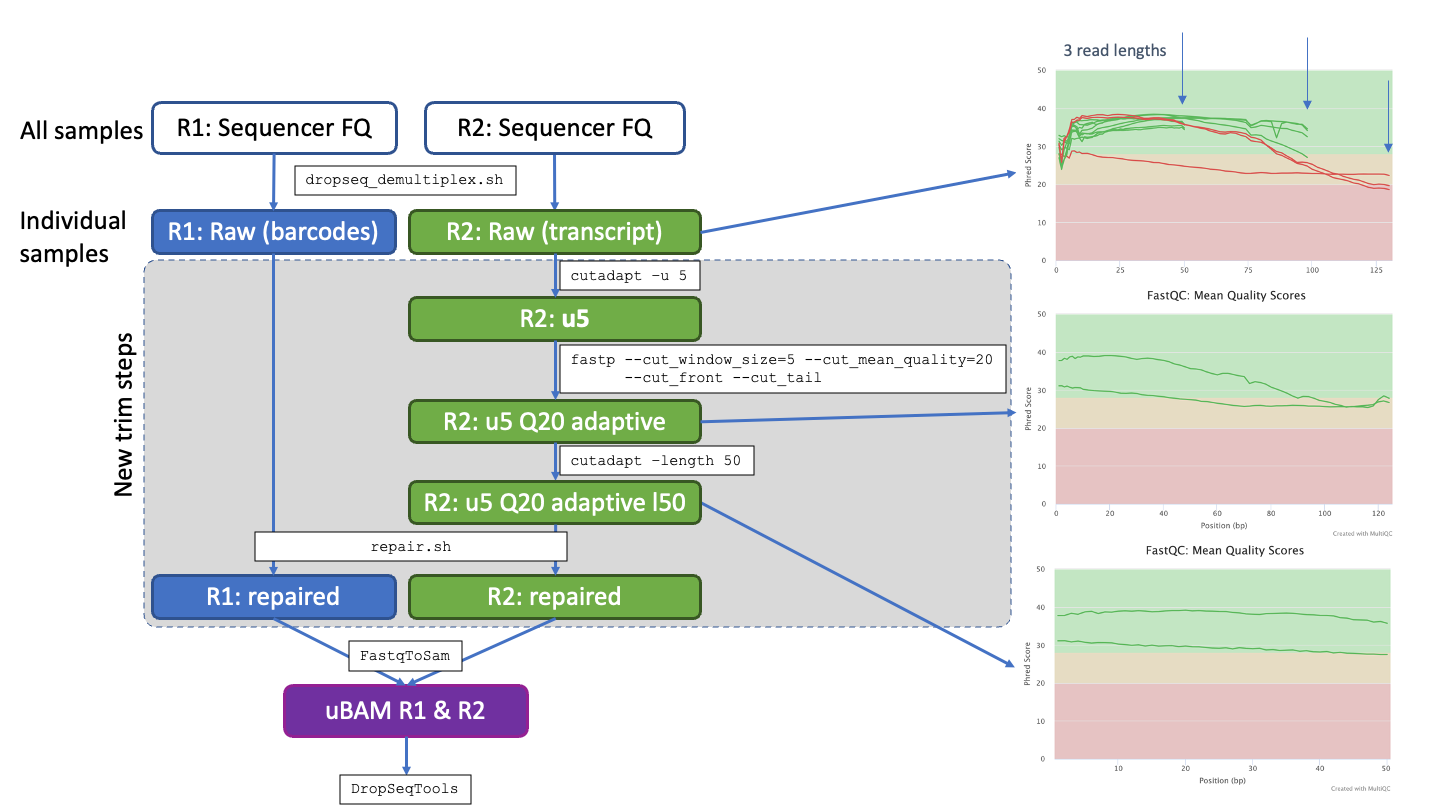
Trimming fastq files from different sequencing runs with varying read lengths is performed with a custom protocol making calls to Cutadapt (v4.0, CITATION_2), fastp (v0.23.4, CITATION_3) and BBTools (v39.05, CITATION_1). Read 1 contains the sequences barcodes, read 2 the transcript sequences. Steps performed are 1. removal of first 5bp from Read 2; 2. adaptive trimming to high quality (Q20) runs within Read 2 reads, lower quality start and end or reads removed; 3. trimming of all Read 2 reads to a fixed length determined by the shortest read cycles used across sequencing runs (i.e. 50bp); 4. Final step is to re-pair read 1 and read 2 fastq files so they contain the same compliment of reads and in the same order.
All custom code and detailed instructions for demultiplexing and trimming provided at https://github.com/darogan/DropSeq_Demultiplex_Trimming
Citations
[1] http://sourceforge.net/projects/bbmap/
[2] Martin, M. (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.journal, 17:1, 10-12, doi:https://doi.org/10.14806/ej.17.1.200
[3] Chen, S. (2023) Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. iMeta 2: e107. https://doi.org/10.1002/imt2.107
A custom script dropseq_demultiplex.sh provides a full set of nextera index pairs used in the project e.g. N701:TAAGGCGA. For each sample, statistics on read counts R1 and R2 are provided. For each sample, the extracted index pairs are used to run demuxbyname.sh from BBTools.
Check whether the fastq files use "NoIndex" or "UnspecifiedIndex" and set IDXSTR accordingly
Run dropseq_demultiplex.sh from within the same directory as the paired fastq files.
Output is paired fastq files with the N7XX as part of the filename
In order to deal with varying read lengths from different seqeuncing runs and reduce the batch effects. A trimming protocol was developed to unify to a single read length consistent for all fastq files across a project.
The schematic below outlines the steps involved for an example of processing fastq files with three different read lengths (e.g. 50, 100, 130nt). Indididual steps are detailed below, note Read 1 contains the barcode, so trimming focused on read 2 before re-pairing the read 1 and read 2 files to match.
Remove a fixed number of bases (set at 5) from Read 2 using e.g.
cutadapt -u 5 -o output.fastq input.fastq
Run adaptive quality trimming using fastp to trim the read to contain runs passing Q20. This uses a rolling window of size 5bp along the entire read. Low quality bases bookending this high quality section are removed
fastp --cut_window_size=5 --cut-mean_quality=20 --cut_front --cut_tail
Trim the reads down to a fixed length, set to the shortest read length from the input fastq files in this case 50bp with e.g.
cutadapt -length 50 -o output.fastq input.fastq
Once all trimming had been run, re-pair the read 1 and read 2 files so they contain matching reads as denoted by their headers for each read. The repair.sh tool from BBTools is used to perform this step. e.g.
repair.sh in1=broken1.fq in2=broken2 out1=fixed1.fq out2=fixed2.fq outs=singletons.fq repair
Usw the McCarrol DropSeq Tools FastqToSam to run the concersion to a BAM file. The files are now ready to run through the standard DropSeq Tools protocol.
Contact Russell Hamilton (darogan@gmail.com)