A Python-based open-source package that can be used to perform two-dimensional model fitting of optical and near-infrared images to characterize the light distribution of galaxies with components including a disk, bulge, bar and quasar.
$ git clone https://github.com/dartoon/galight <desired location>
$ cd <desired location>
$ python setup.py install --user
Alternatively, galight can be installed through pip:
$ pip install galight --user
The example notebook allows the user to quickly go through a fitting task on a HST observed AGN at z~1.5.
Some other notebooks of demonstrating how to use galight with more features can be found in:
https://github.com/dartoon/galight_notebooks
The data used in the example notebook can be found here.
For more information, an online documentation can be found in ReadtheDocs: https://galight.readthedocs.io/
galight helps the user to execute model fitting with ease based on, but not limited to, automated features as listed as follows:
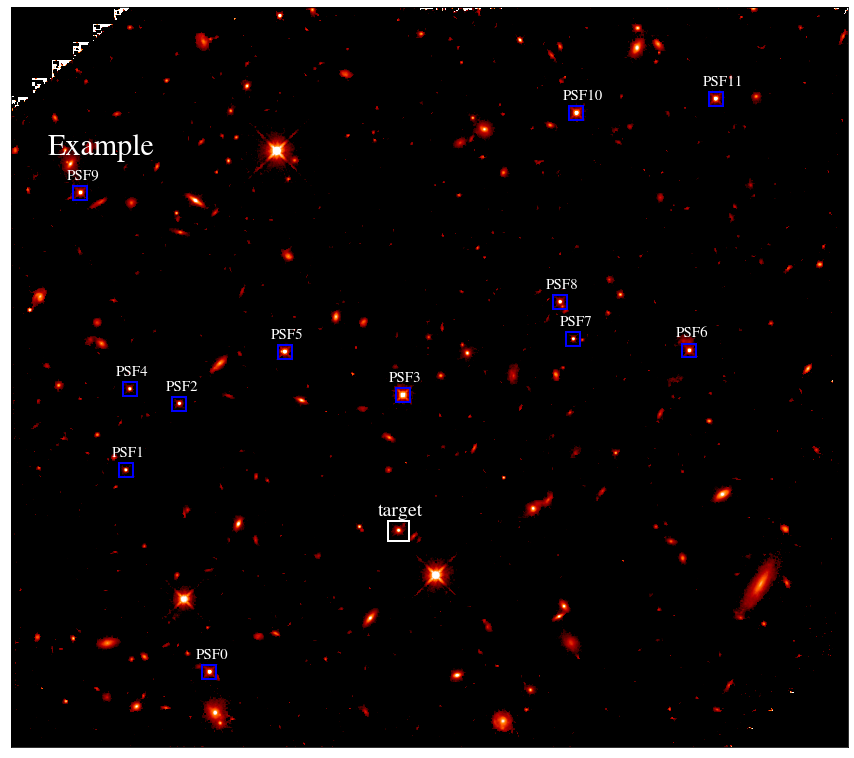
- Search PSF stars in the FOV.
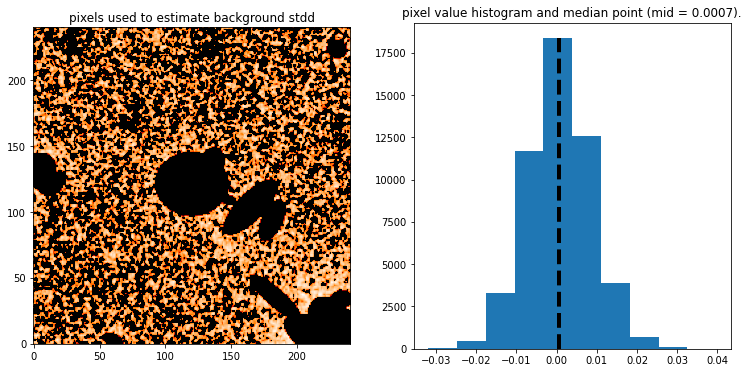
- Automatically Estimate the background noise level.
- Cutout the target object galaxies (QSOs) and prepare the materials to model the data.
- Detecting objects in the cutout stamp and quickly create Sersic keywords (in
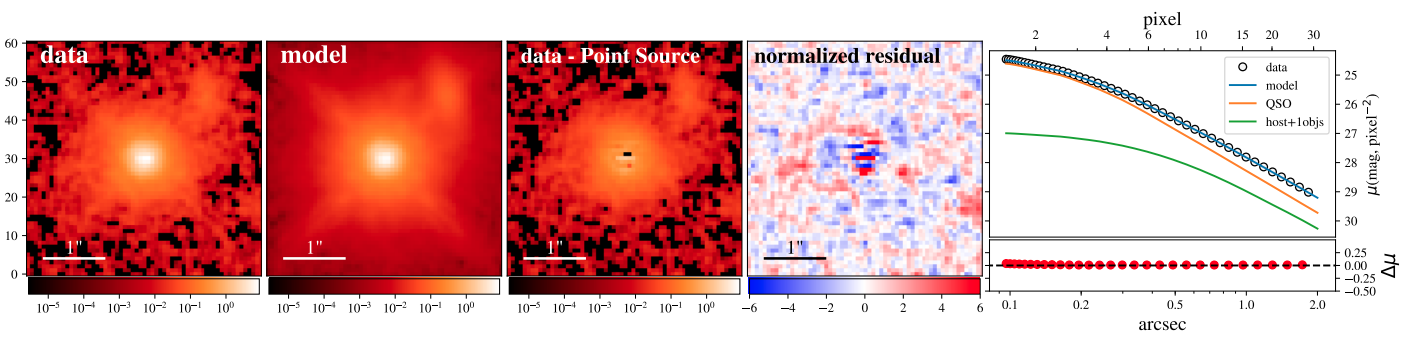
lenstronomytype) to model them. - Model them QSOs and galaxies using 2D Sersic profile and scaled point source, based on
lenstronomy.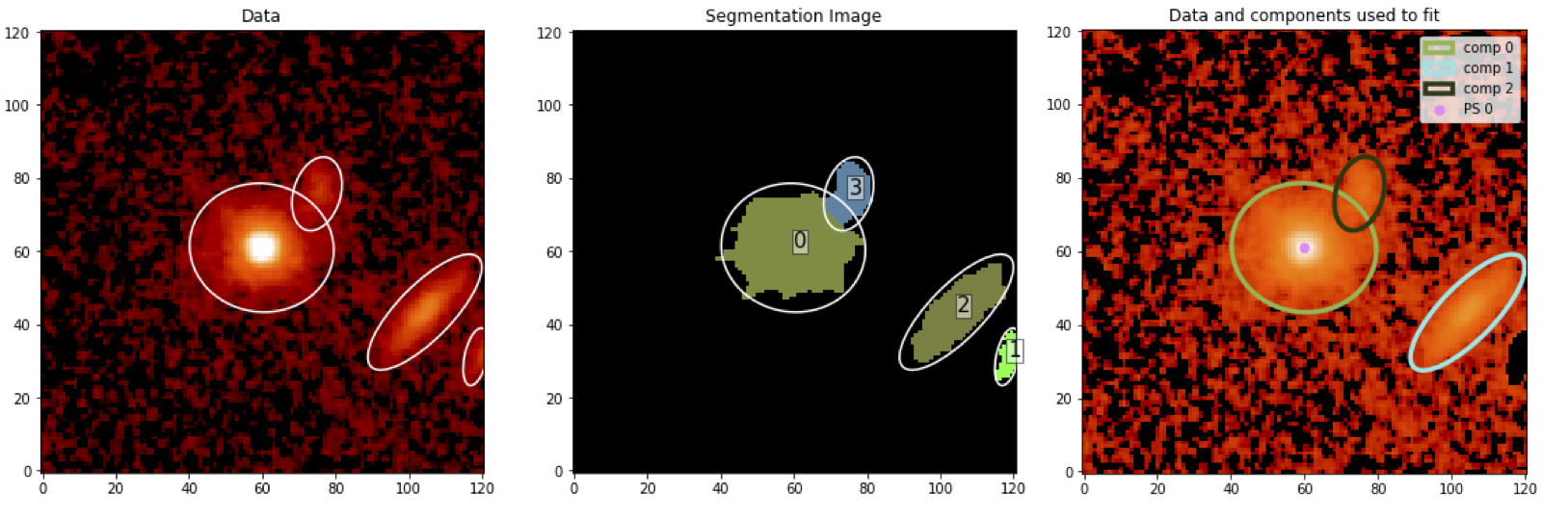
Galight utilizes the image modeling capabilities of lenstronomy while redesigning the user interface for the analysis of large samples of extragalactic sources.
packages requirements can be found here.
@ARTICLE{2020ApJ...888...37D,
author = {{Ding}, Xuheng and {Silverman}, John and {Treu}, Tommaso and {Schulze}, Andreas and {Schramm}, Malte and {Birrer}, Simon and {Park}, Daeseong and {Jahnke}, Knud and {Bennert}, Vardha N. and {Kartaltepe}, Jeyhan S. and {Koekemoer}, Anton M. and {Malkan}, Matthew A. and {Sanders}, David},
title = "{The Mass Relations between Supermassive Black Holes and Their Host Galaxies at 1 < z < 2 HST-WFC3}",
journal = {\apj},
keywords = {Galaxy evolution, Active galaxies, 594, 17, Astrophysics - Astrophysics of Galaxies},
year = 2020,
month = jan,
volume = {888},
number = {1},
eid = {37},
pages = {37},
doi = {10.3847/1538-4357/ab5b90},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
eprint = {1910.11875},
primaryClass = {astro-ph.GA},
adsurl = {https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020ApJ...888...37D},
adsnote = {Provided by the SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System}
}
@ARTICLE{2021JOSS....6.3283B,
author = {{Birrer}, Simon and {Shajib}, Anowar and {Gilman}, Daniel and {Galan}, Aymeric and {Aalbers}, Jelle and {Millon}, Martin and {Morgan}, Robert and {Pagano}, Giulia and {Park}, Ji and {Teodori}, Luca and {Tessore}, Nicolas and {Ueland}, Madison and {Van de Vyvere}, Lyne and {Wagner-Carena}, Sebastian and {Wempe}, Ewoud and {Yang}, Lilan and {Ding}, Xuheng and {Schmidt}, Thomas and {Sluse}, Dominique and {Zhang}, Ming and {Amara}, Adam},
title = "{lenstronomy II: A gravitational lensing software ecosystem}",
journal = {The Journal of Open Source Software},
keywords = {image simulations, Python, gravitational lensing, dynamics, astronomy, Ruby, Astrophysics - Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics, Astrophysics - Astrophysics of Galaxies, Astrophysics - Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics},
year = 2021,
month = jun,
volume = {6},
number = {62},
eid = {3283},
pages = {3283},
doi = {10.21105/joss.03283},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
eprint = {2106.05976},
primaryClass = {astro-ph.CO},
adsurl = {https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021JOSS....6.3283B},
adsnote = {Provided by the SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System}
}