This project is forked from microservices-demo at commit id ab601665d17cf697ef79b5e00b88d21ca4860b81.
The purpose of this project is to demonstrate OpenCensus tracing and monitoring capabilities.
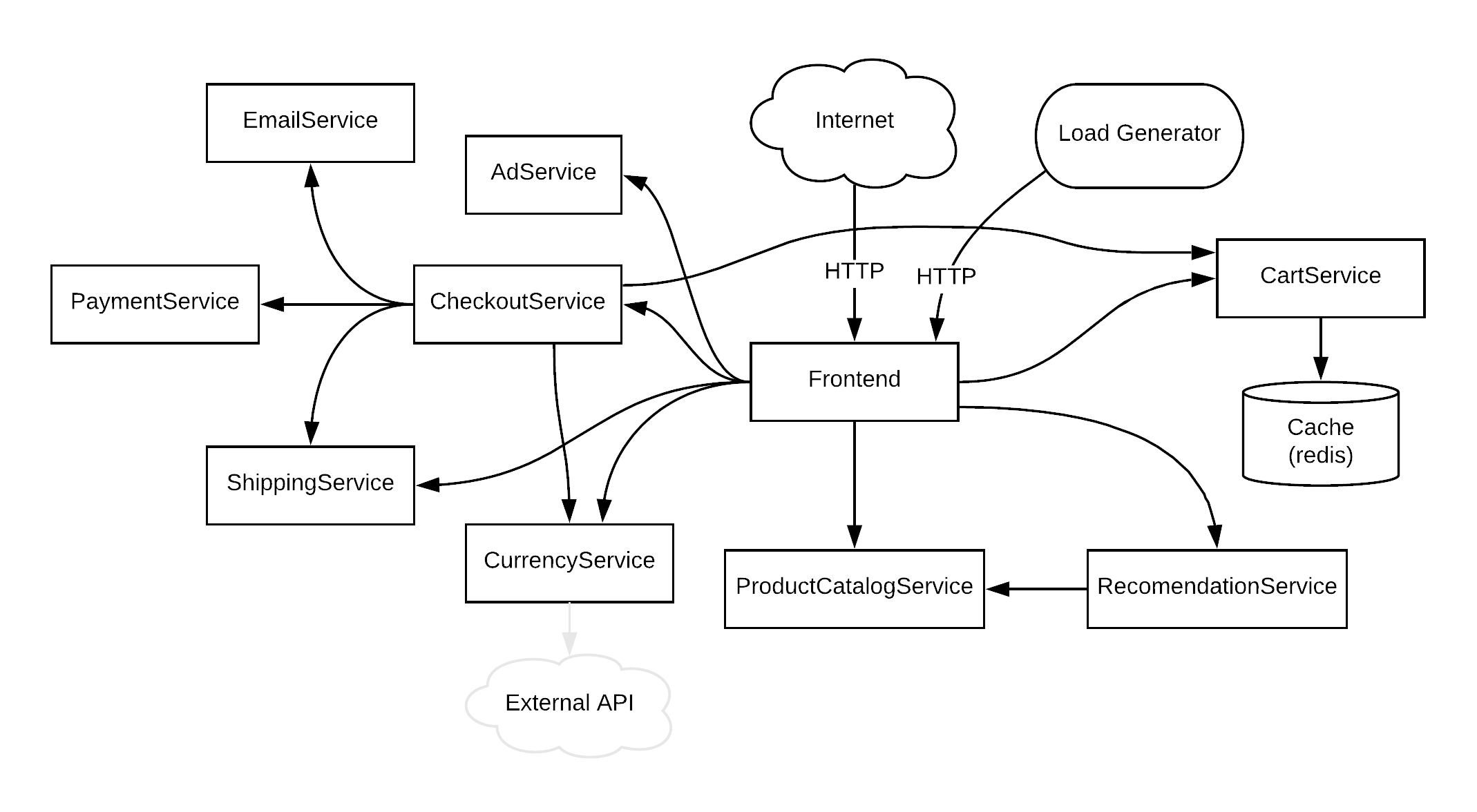
This project contains a 10-tier microservices application. The application is a web-based e-commerce app called “Hipster Shop” where users can browse items, add them to the cart, and purchase them.
| Home Page | Checkout Screen |
|---|---|
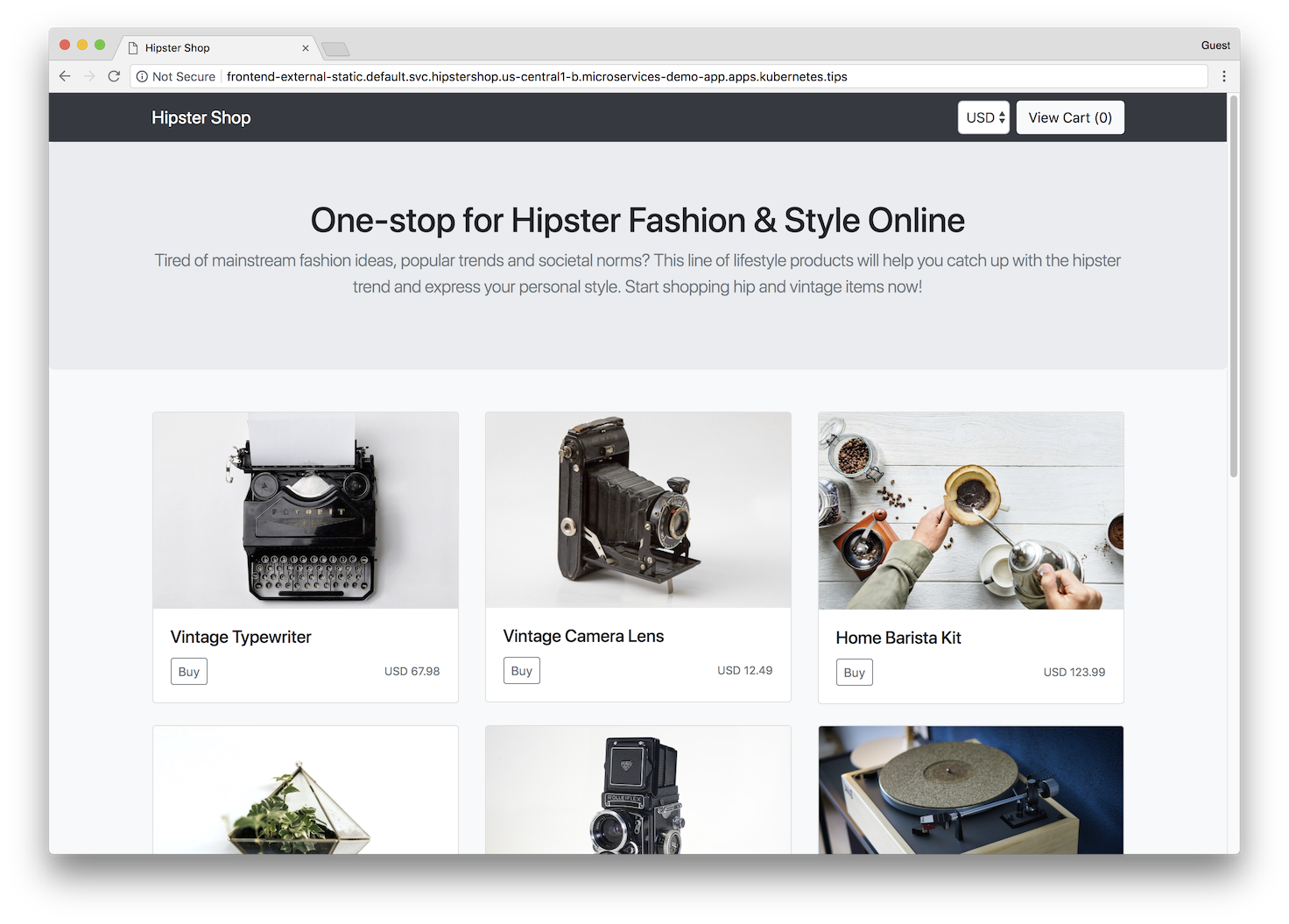 |
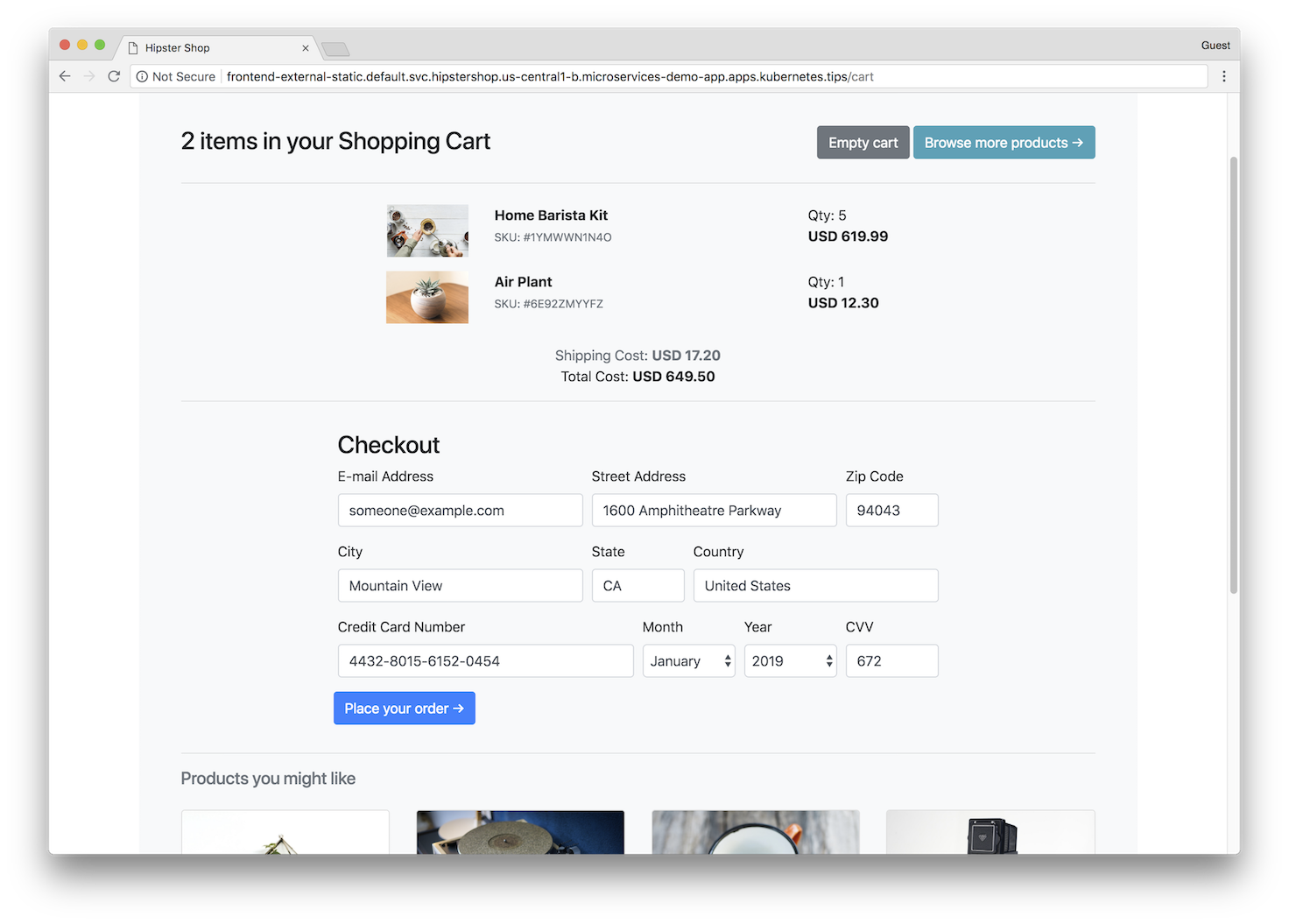 |
Hipster Shop is composed of many microservices written in different languages that talk to each other over gRPC.
Find Protocol Buffers Descriptions at the ./pb directory.
| Service | Language | Description |
|---|---|---|
| frontend | Go | Exposes an HTTP server to serve the website. Does not require signup/login and generates session IDs for all users automatically. |
| cartservice | C# | Stores the items in the user's shipping cart in Redis and retrieves it. |
| productcatalogservice | Go | Provides the list of products from a JSON file and ability to search products and get individual products. |
| currencyservice | Node.js | Converts one money amount to another currency. Uses real values fetched from European Central Bank. It's the highest QPS service. |
| paymentservice | Node.js | Charges the given credit card info (hypothetically😇) with the given amount and returns a transaction ID. |
| shippingservice | Go | Gives shipping cost estimates based on the shopping cart. Ships items to the given address (hypothetically😇) |
| emailservice | Python | Sends users an order confirmation email (hypothetically😇). |
| checkoutservice | Go | Retrieves user cart, prepares order and orchestrates the payment, shipping and the email notification. |
| recommendationservice | Python | Recommends other products based on what's given in the cart. |
| adservice | Java | Provides text ads based on given context words. |
| loadgenerator | Python/Locust | Continuously sends requests imitating realistic user shopping flows to the frontend. |
- Kubernetes/GKE: The app is designed to run on Kubernetes (both locally on "Docker for Desktop", as well as on the cloud with GKE).
- gRPC: Microservices use a high volume of gRPC calls to communicate to each other.
- Istio: Application works on Istio service mesh.
- OpenCensus Tracing: Most services are instrumented using OpenCensus trace interceptors for gRPC/HTTP.
- Stackdriver APM: Many services are instrumented with Profiling, Tracing and Debugging. In addition to these, using Istio enables features like Request/Response Metrics and Context Graph out of the box. When it is running out of Google Cloud, this code path remains inactive.
- Skaffold: Application is deployed to Kubernetes with a single command using Skaffold.
- Synthetic Load Generation: The application demo comes with a background job that creates realistic usage patterns on the website using Locust load generator.
- Prometheus/Grafana APM: Frontend(Go) and AdService(Java) are instrumented to export metrics to Prometheus. Grafana service scraps metrics data from Prometheus and is pre-configured with a Dashboard to show OpenCensus metrics.
- Jaeger: Jaeger collects OpenCensus traces exported by microservices. This traces are presented on Jaeger UI.
Note: that the first build can take up to 20-30 minutes. Consequent builds will be faster.
💡 Recommended if you're planning to develop the application.
-
Install tools to run a Kubernetes cluster locally:
- kubectl (can be installed via
gcloud components install kubectl) - Docker for Desktop (Mac/Windows): It provides Kubernetes support as noted here.
- skaffold
- kubectl (can be installed via
-
Launch “Docker for Desktop”. Go to Preferences and choose “Enable Kubernetes”.
-
Run
kubectl get nodesto verify you're connected to “Kubernetes on Docker”. -
Run
skaffold run(first time will be slow, it can take ~20-30 minutes). This will build and deploy the application. If you need to rebuild the images automatically as you refactor he code, runskaffold devcommand. -
Run
kubectl get podsto verify the Pods are ready and running. The application frontend should be available at http://localhost:80 on your machine. -
Check Grafana at http://localhost:3000/ to view pre-configured Dashboard. username/password is admin/admin
-
Check Jaeger UI at http://localhost:16686 to view traces collected by Jaeger.
💡 Recommended for demos and making it available publicly.
-
Install tools specified in the previous section (Docker, kubectl, skaffold)
-
Create a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster and make sure
kubectlis pointing to the cluster.gcloud services enable container.googleapis.com gcloud container clusters create demo --enable-autoupgrade \ --enable-autoscaling --min-nodes=3 --max-nodes=10 --num-nodes=5 kubectl get nodes -
Enable Google Container Registry (GCR) on your GCP project and configure the
dockerCLI to authenticate to GCR:gcloud services enable containerregistry.googleapis.com gcloud auth configure-docker -q -
Set your project ID on image names:
-
Edit
skaffold.yaml, update theimageName:fields that look likegcr.io/[PROJECT_ID]with your own GCP project ID. -
Similarly, edit all Kubernetes Deployment manifests in the
./kubernetes-manifestsdirectory. Find theimage:fields withgcr.io/[...]and change them to your own GCP project ID.
-
-
Run
skaffold runfrom the root of this repository. This command:- builds the container images
- pushes them to GCR
- applies the
./kubernetes-manifestsdeploying the application to Kubernetes.
-
Find the IP address of your application, then visit the application on your browser to confirm installation.
kubectl get service frontend-external
Note: you followed GKE deployment steps above, run
skaffold deletefirst to delete what's deployed.
-
Create a GKE cluster.
-
Install Istio without mutual TLS option. (Istio mTLS is not yet supported on this demo.)
-
Install the automatic sidecar injection (annotate the
defaultnamespace with the label):kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled -
Apply the manifests in
./istio-manifestsdirectory.kubectl apply -f ./istio-manifestsThis is required only once.
-
Deploy the application with
skaffold run. -
Run
kubectl get podsto see pods are in a healthy and ready state. -
Find the IP address of your istio gateway Ingress or Service, and visit the application.
INGRESS_HOST="$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')" echo "$INGRESS_HOST" curl -v "http://$INGRESS_HOST"
This is not an official Google project.