An production ready demo analytics application framework built over IUDX. Some of the demo dashboards can be found here.
This app demonstrates the implementation of a scalable and big-data ready architecture based on IUDX datasources based completely on open-source components.
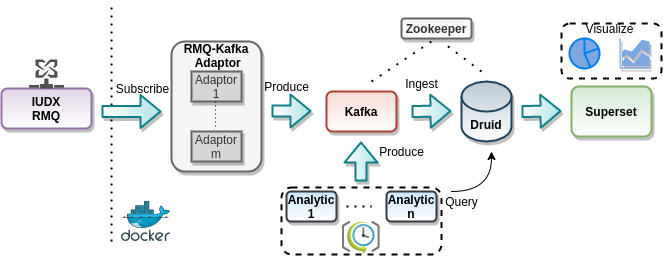
The components involved are
- RMQ-Kafka Adaptor - The main consumer of IUDX data. Publishes into Kafka for consumption of the database and analytic blocks.
- Kafka - Application internal event streaming. Primarily serves as a log store for database ingestion and publishing of processed data from the analytic blocks.
- Druid - The workhorse of this application. It's high ingestion rate and fast queries make it an ideal candidate for high ingestion rate datasources (like GTFS).
- Zookeeper - Cenralized server for maintaining configurations and synchronizations.
- Superset - Visualization engine with large scale distribution capabilities.
Setting this application will require multiple servers and of different configurations depending on the scale and number of datasources.
- Druid: Minimum: 2CPUs and 16GB RAM, single node deployments may need multiple vms for different datasources depending on the retention policy
- Zookeeper: Minimum: 1CPU and 2GB RAM
- Kafka: Minimum: 2CPUs and 8GB RAM
- Superset: Minimum: 2CPUs and 8GB RAM
Zookeeper -> Kafka -> Druid -> Adaptors -> Superset -> Apps
Build necessary docker images
cd ./scripts/
./build_all.sh
Usual deployments will have
- Ingestion - Zookeeper + Kafka + Druid + Adaptors in one VM
- Consumption - Superset + Apps in another VM.
This setup takes care of setting the ingestion pipeline, i.e, bringing up Zookeeper, Kafka, Druid and setting up the adaptors. You will need access to streaming data from IUDX. This involves registration and consent from providers of the datasources. Please contact us for support on this.
- Add a configuration file in
./configs/config.jsonwith IUDX subscription secrets - Execute the ingestion script
cd ./scripts && ./setup_ingestion.sh - Execute the database script
cd ./scripts && ./setup_db.sh
This setup takes care of bringing up superset configured to the datasources ingested previously.
- Add the DB url in
./configs/backend_config.sh cd ./scripts/./setup_app.sh
cd ./setup/zookeeper- Edit zookeeper settings as required in
./setup/zookeeper/docker-compose.ymlanddocker-compose up -d
- Ensure
zookeeperis visible in the docker network cd ./setup/kafka/- Edit configuration in
docker-compose.ymlsuch as zookeeper service name and address, andKAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERSfor visibility outside the container. docker-compose up -d
- Ensure
zookeeperis visible in the docker network cd ./setup/druid- Edit
./setup/druid/environmentfor common java properties - Edit
./setup/druid/*.envfor druid component specific jvm properties - Edit
./setup/druid/docker-compose.ymlwith proper env variables, network settings etc. - Bring up different druid services in different vms if required (especially
historical) or in a single vmdocker-compose up -d
Check the group ownership of all configuration files, environment files and `storage` folder. Make sure they are not root.
- Apache airflow based orchestration
- Fully configurable apps (frontend) based on single configuration file
- Swarm/Kubernets based setup
Please contact us for any support.