Part of Weather Nowcasting - Weather prediction on an NVIDIA jetson with a CI/CD pipeline on the cloud. Shows how Terraform can be used to set up our Snowflake resources. On top of that, we present how to load in near-real-time the content of an Azure container into a Snowflake table.
This is part of the graduation project of the rootsacademy of March 2022. An application to predict weather up to 4 hours in the future based on measurements obtained from a sensor installed on the roof of Dataroots' building. These predictions will be based on real-time measurements of the temperature, humidity, pressure, light, sound and a camera pointed towards the sky. We also wanted to exercise building the CI/CD pipeline and connection between the edge device and the cloud. More information can also be found here.
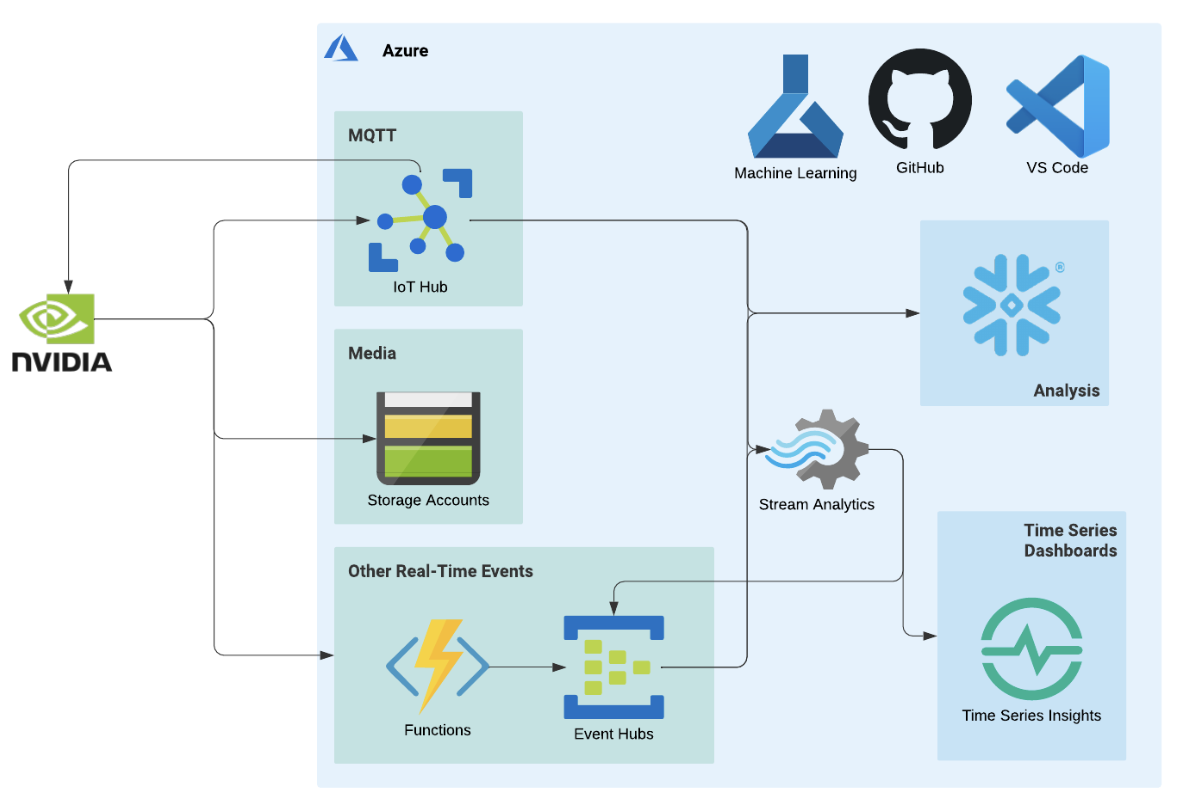
Here's an overview of our cloud architecture:
- Provisioning the required resources and environments
- Managing the flow of sensor data from the edge device into the IoT hub on Azure
- Connecting the IoT endpoint (blob container) to Snowflake using Azure Event Grid
- Managing the flow of images from the device into a blob storage container on Azure and from the storage container into the ML workspace
- Developing a CI/CD pipeline that automates the build and deployment of a model on an edge device
Snowflake
- Database
- Warehouse
- Schema
- Tables
- One for sensor information
- One for predictions
- File format
- Storage & notification integration
- Pipes (one for each of the tables)
- Stages (one for each of the tables)
Edge & ML resources:
- IoT hub, along with its dependencies, e.g. azure container registry
- Storage accounts
- One for storing the images sent from the IoT device
- One for storing the sensor data
- One for storing the predictions
- Machine learning workspace, along with its dependencies, e.g. key vault, application insights
In this project we validate and plan our Terraform code as part of a Github workflow; more specifically, we execute the following 4 steps:
- Init command:
terraform init -backend-config backend/staging.tfvars - Format command:
terraform fmt -check -recursive - Validate command:
terraform validate - Plan command:
terraform plan
The above actions get triggered on a pull-request; whenever the pull-request is reviewed, approved and closed, a new workflow will run and everything gets executed in production: terraform apply -var-file vars/prod.tfvars
We explain everything in our blog post. Briefly, you can do the following:
- Find out the Snowflake's account locator and region id
- Create RSA key
- Create service user for authentication to Terraform
- Set up the resources
- Grant access to storage containers
- Verify/apply changes
Special thanks go to our supervisors at Dataroots for guiding us throught this project.