A highly optimized and auto-upgradable, HA-able & Load-Balanced, Kubernetes cluster powered by k3s-on-k3os deployed for peanuts on Hetzner Cloud 🤑 🚀
Hetzner Cloud is a good cloud provider that offers very affordable prices for cloud instances, with data center locations in both Europe and the US. The goal of this project is to create an optimal and highly optimized Kubernetes installation that is easily maintained, secure, and automatically upgrades. We aimed for functionality as close as possible to GKE's auto-pilot.
Please note that we are not affiliated to Hetzner, this is just an open source project striving to be an optimal solution for deploying and maintaining Kubernetes on Hetzner Cloud.
- Lightweight and resource-efficient Kubernetes powered by k3s on k3os nodes.
- Maintenance free with auto-upgrade to the latest version of k3os, k3s, Hetzner CCM and CSI.
- Proper use of the underlying Hetzner private network to remove the need for encryption and make the cluster both fast and secure.
- Automatic HA with the default setting of two control-plane and agents nodes.
- Ability to add or remove as many nodes as you want while the cluster stays running.
- Automatic Traefik ingress controller attached to a Hetzner load balancer with proxy protocol turned on.
It uses Terraform to deploy as it's easy to use, and Hetzner provides a great Hetzner Terraform Provider.
Follow those simple steps, and your world's cheapest Kube cluster will be up and running in no time.
First and foremost, you need to have a Hetzner Cloud account. You can sign up for free here.
Then you'll need to have terraform and kubectl cli installed. The easiest way is to use the gofish package manager to install them.
gofish install terraform
gofish install kubectlThe Hetzner cli hcloud is also useful to have, mainly for debugging without having to use the Hetzner website. See how to install it here.
- Create a project in your Hetzner Cloud Console, and go to Security > API Tokens of that project to grab the API key. Take note of the key! ✅
- Generate an ssh key pair for your cluster, unless you already have one that you'd like to use (ed25519 is the ideal type). Take note of the respective paths of your private and public keys! ✅
- Copy
terraform.tfvars.exampletoterraform.tfvars, and replace the values from steps 1 and 2. ✅ - (Optional) There are other variables in
terraform.tfvarsthat could be customized, like Hetzner region, and the node counts and sizes.
terraform init
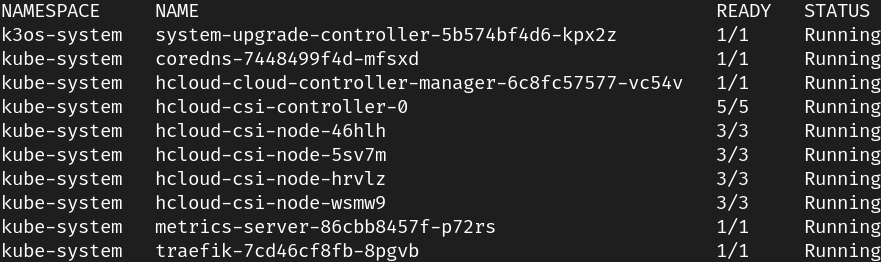
terraform apply -auto-approveIt will take around 12 minutes to complete, and then you should see a green output with the IP addresses of the nodes. Then you can immediately kubectl into it (using the kubeconfig.yaml saved to the project's directory after the install).
Just using the command kubectl --kubeconfig kubeconfig.yaml would work, but for more convenience, either create a symlink from ~/.kube/config to kubeconfig.yaml, or add an export statement to your ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc file, as follows (you can get the path of kubeconfig.yaml by running pwd):
export KUBECONFIG=/<path-to>/kubeconfig.yamlWhen the cluster is up and running, you can do whatever you wish with it! 🎉
You can scale the number of nodes up and down without any issues or even disruption! Just edit these variables in terraform.tfvars and re-apply terraform with terraform apply -auto-approve.
For instance:
servers_num = 2
agents_num = 3- List your nodes IPs, with either of those:
terraform outputs
hcloud server list- See the Hetzner network config:
hcloud network describe k3s-net- Log into one of your nodes (replace the location of your private key if needed):
ssh rancher@xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=noBy default, k3os and its embedded k3s instance get upgraded automatically on each node, thanks to its embedded system upgrade controller.
You can also choose to automatically kustomize the Hetzner CCM and CSI to set their container images to "latest" with an imagePullPolicy of "Always". That means that when the nodes upgrade, these container images will be automatically upgraded too. For more info on this, see terraform.tfvars.example.
If you wish to turn off automatic upgrade on a specific node, you need to take out the label k3os.io/upgrade=latest. It can be done with the following command:
kubectl label node <nodename> 'k3os.io/upgrade'-If you want to takedown the cluster, you can proceed as follows:
kubectl delete -k hetzner/csi
kubectl delete -k hetzner/ccm
hcloud load-balancer delete traefik
terraform destroy -auto-approveAlso, if you had a full-blown cluster in use, it would be best to delete the whole project in your Hetzner account directly as operators or deployments may create other resources during regular operation.
Any contributions you make are greatly appreciated.
- Fork the Project
- Create your Branch (
git checkout -b AmazingFeature) - Commit your Changes (
git commit -m 'Add some AmazingFeature') - Push to the Branch (
git push origin AmazingFeature) - Open a Pull Request
- Karim Naufal - @mysticaltech
- Dennis Hoppe - @dhoppe
- k-andy was the starting point for this project. It wouldn't have been possible without it.
- Best-README-Template that made writing this readme a lot easier.
- k3os-hetzner was the inspiration for the k3os installation method.
- Hetzner Cloud for providing a solid infrastructure and terraform package.
- Hashicorp for the amazing terraform framework that makes all the magic happen.
- Rancher for k3s and k3os, robust and innovative technologies that are the very core engine of this project.