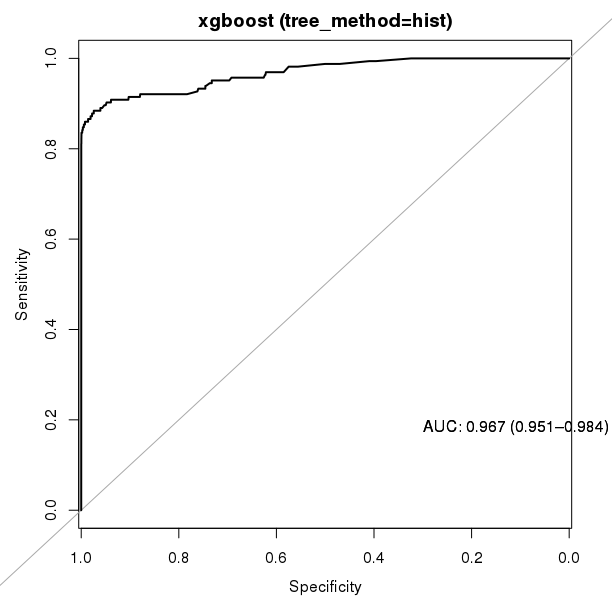
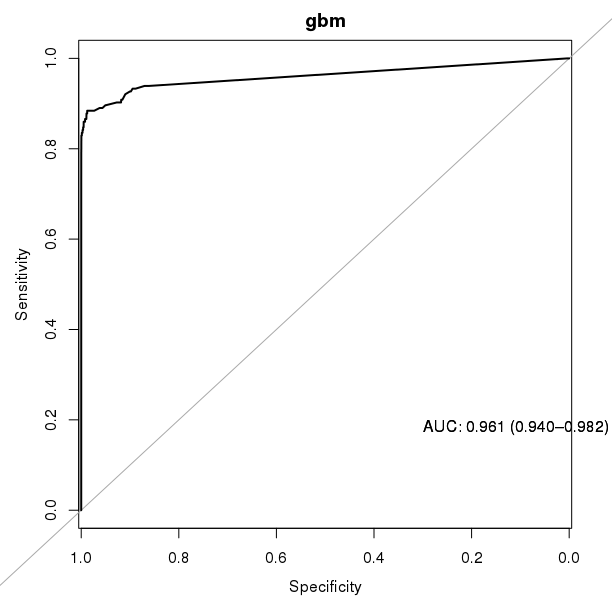
Anonymized credit card transactions labeled as fraudulent or genuine.
- 27 core, 71 processors (Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU @ 2.10GHz)
- 528g total memory
- Gbm (v‘2.1.3’) vs XGBboost(v‘0.81.0.1’)
- Total dataset = 284,807 x 31 with last column being binary outcome.
- 70% training and 30% testing.
- baseline gbm vs three variations of xgboost
gbm: 4 mins
xgboost: 74s-76s
Conclusion: xgboost is clear winner.
gbm: 0.961
xgboost: 0.9644-0.967
Conclusion: xgboost is sightly better.
Feature gbm_fi
1: V12 52.470465
2: V14 27.048769
3: V17 6.237203
4: V10 4.884359
5: V20 3.527659
6: V9 1.245999
7: V4 1.071521
Feature Gain Cover Frequency
1: V14 0.416218440 0.354986648 0.33766234
2: V10 0.246135716 0.176385012 0.12337662
3: V12 0.165018774 0.126950350 0.09090909
4: V17 0.111386539 0.190137506 0.07142857
5: V4 0.059261483 0.149853021 0.32467532
6: V3 0.001180491 0.000687422 0.02597403
7: V11 0.000798557 0.001000042 0.02597403
Context
It is important that credit card companies are able to recognize fraudulent credit card transactions so that customers are not charged for items that they did not purchase.
Content
The datasets contains transactions made by credit cards in September 2013 by european cardholders. This dataset presents transactions that occurred in two days, where we have 492 frauds out of 284,807 transactions. The dataset is highly unbalanced, the positive class (frauds) account for 0.172% of all transactions.
It contains only numerical input variables which are the result of a PCA transformation. Unfortunately, due to confidentiality issues, we cannot provide the original features and more background information about the data. Features V1, V2, ... V28 are the principal components obtained with PCA, the only features which have not been transformed with PCA are 'Time' and 'Amount'. Feature 'Time' contains the seconds elapsed between each transaction and the first transaction in the dataset. The feature 'Amount' is the transaction Amount, this feature can be used for example-dependant cost-senstive learning. Feature 'Class' is the response variable and it takes value 1 in case of fraud and 0 otherwise.
Inspiration
Identify fraudulent credit card transactions.
Given the class imbalance ratio, we recommend measuring the accuracy using the Area Under the Precision-Recall Curve (AUPRC). Confusion matrix accuracy is not meaningful for unbalanced classification.
Acknowledgements
The dataset has been collected and analysed during a research collaboration of Worldline and the Machine Learning Group (http://mlg.ulb.ac.be) of ULB (Université Libre de Bruxelles) on big data mining and fraud detection. More details on current and past projects on related topics are available on https://www.researchgate.net/project/Fraud-detection-5 and the page of the DefeatFraud project