A Fastify plugin for serving Swagger UI.
Supports Fastify versions 4.x.
npm i @fastify/swagger-ui
Add it with @fastify/swagger to your project with register, pass it some options, call the swagger API, and you are done!
const fastify = require('fastify')()
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger'))
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger-ui'), {
routePrefix: '/documentation',
uiConfig: {
docExpansion: 'full',
deepLinking: false
},
uiHooks: {
onRequest: function (request, reply, next) { next() },
preHandler: function (request, reply, next) { next() }
},
staticCSP: true,
transformStaticCSP: (header) => header,
transformSpecification: (swaggerObject, request, reply) => { return swaggerObject },
transformSpecificationClone: true
})
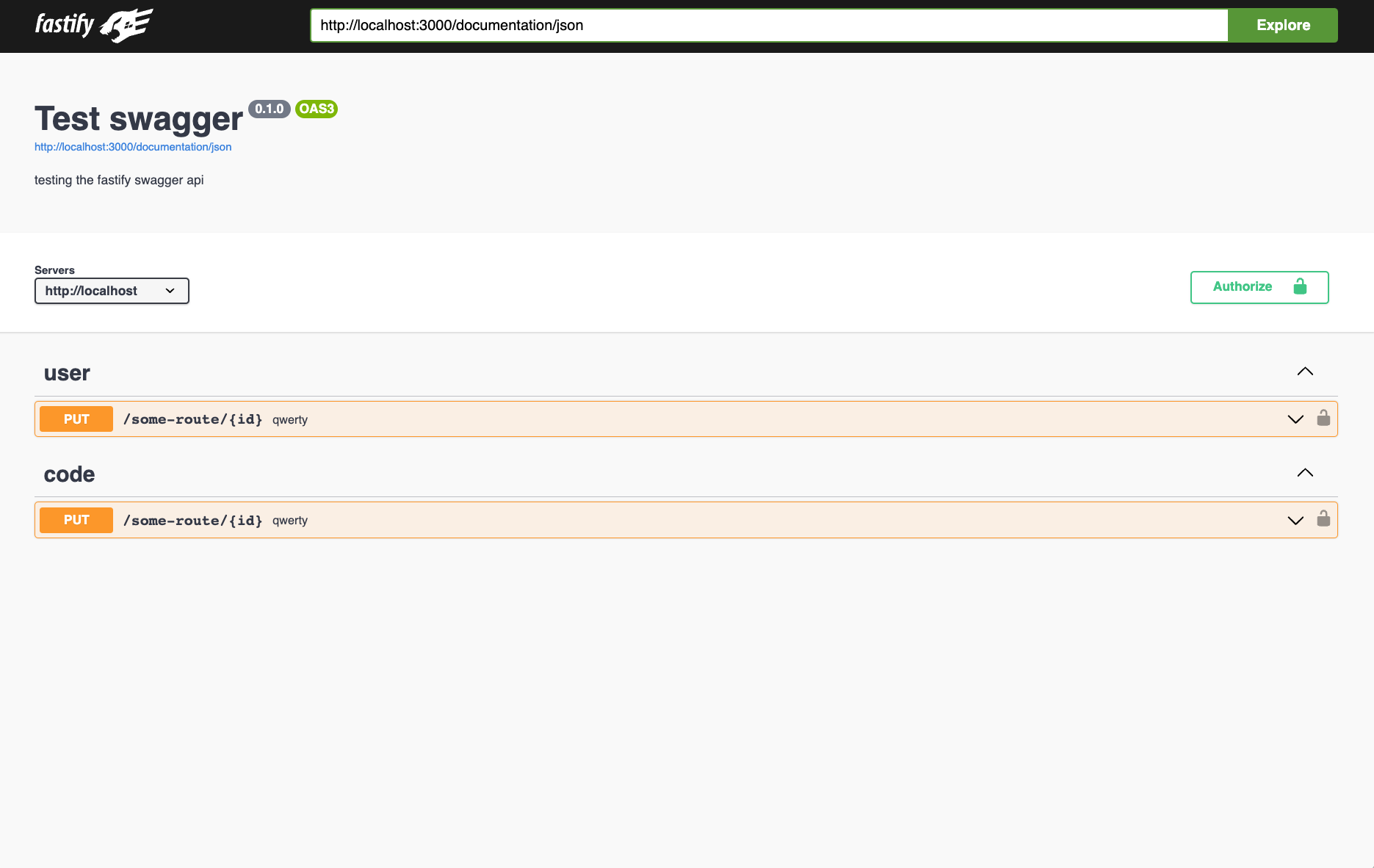
fastify.put('/some-route/:id', {
schema: {
description: 'post some data',
tags: ['user', 'code'],
summary: 'qwerty',
params: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
id: {
type: 'string',
description: 'user id'
}
}
},
body: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
hello: { type: 'string' },
obj: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
some: { type: 'string' }
}
}
}
},
response: {
201: {
description: 'Successful response',
type: 'object',
properties: {
hello: { type: 'string' }
}
},
default: {
description: 'Default response',
type: 'object',
properties: {
foo: { type: 'string' }
}
}
},
security: [
{
"apiKey": []
}
]
}
}, (req, reply) => {})
await fastify.ready()| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| baseDir | undefined | Specify the directory where all spec files that are included in the main one using $ref will be located. By default, this is the directory where the main spec file is located. Provided value should be an absolute path without trailing slash. |
| initOAuth | {} | Configuration options for Swagger UI initOAuth. |
| routePrefix | '/documentation' | Overwrite the default Swagger UI route prefix. |
| staticCSP | false | Enable CSP header for static resources. |
| transformStaticCSP | undefined | Synchronous function to transform CSP header for static resources if the header has been previously set. |
| transformSpecification | undefined | Synchronous function to transform the swagger document. |
| transformSpecificationClone | true | Provide a deepcloned swaggerObject to transformSpecification |
| uiConfig | {} | Configuration options for Swagger UI. |
| uiHooks | {} | Additional hooks for the documentation's routes. You can provide the onRequest and preHandler hooks with the same route's options interface. |
| theme | {} | Add custom JavaScript and CSS to the Swagger UI web page |
| logLevel | info | Allow to define route log level. |
The plugin will expose the documentation with the following APIs:
| URL | Description |
|---|---|
'/documentation/json' |
The JSON object representing the API |
'/documentation/yaml' |
The YAML object representing the API |
'/documentation/' |
The swagger UI |
'/documentation/*' |
External files that you may use in $ref |
To configure Swagger UI, you need to modify the uiConfig option.
It's important to ensure that functions are self-contained. Keep in mind that
you cannot modify the backend code within the uiConfig functions, as these
functions are processed only by the browser. You can reference the Swagger UI
element using ui, which is assigned to window.ui.
const fastify = require('fastify')()
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger'))
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger-ui'), {
uiConfig: {
onComplete: function () {
alert('ui has type of ' + typeof ui) // 'ui has type of object'
alert('fastify has type of ' + typeof fastify) // 'fastify has type of undefined'
alert('window has type of ' + typeof window) // 'window has type of object'
alert('global has type of ' + typeof global) // 'global has type of undefined'
}
}
})There can be use cases, where you want to modify the swagger definition on request. E.g. you want to modify the server definition based on the hostname of the request object. In such a case you can utilize the transformSpecification-option.
const fastify = require('fastify')()
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger'))
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger-ui'), {
transformSpecification: (swaggerObject, req, reply) => {
swaggerObject.host = req.hostname
return swaggerObject
}
})By default fastify.swagger() will be deepcloned and passed to the transformSpecification-function, as fastify.swagger() returns a mutatable Object. You can disable the deepcloning by setting transformSpecificationClone to false. This is useful, if you want to handle the deepcloning in the transformSpecification function.
const fastify = require('fastify')()
const LRU = require('tiny-lru').lru
const rfdc = require('rfdc')()
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger'))
const swaggerLru = new LRU(1000)
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger-ui'), {
transformSpecificationClone: false,
transformSpecification: (swaggerObject, req, reply) => {
if (swaggerLru.has(req.hostname)) {
return swaggerLru.get(req.hostname)
}
const clonedSwaggerObject = rfdc(swaggerObject)
clonedSwaggerObject.host = req.hostname
swaggerLru.set(req.hostname, clonedSwaggerObject)
return clonedSwaggerObject
}
})You can add custom JavaScript and CSS to the Swagger UI web page by using the theme option.
const fastify = require('fastify')()
fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger'))
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger-ui'), {
theme: {
title: 'My custom title',
js: [
{ filename: 'special.js', content: 'alert("client javascript")' }
],
css: [
{ filename: 'theme.css', content: '* { border: 1px red solid; }' }
],
favicon: [
{
filename: 'favicon.png',
rel: 'icon',
sizes: '16x16',
type: 'image/png',
content: Buffer.from('iVBOR...', 'base64')
}
]
}
})You can add custom JavaScript and CSS to the Swagger UI web page by using the theme option.
It's possible to override the logo displayed in the top bar by specifying:
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger-ui'), {
logo: {
type: 'image/png',
content: Buffer.from('iVBOR...', 'base64')
},
theme: {
favicon: [
{
filename: 'favicon.png',
rel: 'icon',
sizes: '16x16',
type: 'image/png',
content: Buffer.from('iVBOR...', 'base64')
}
]
}
})
You can protect your documentation by configuring an authentication hook.
Here is an example using the @fastify/basic-auth plugin:
const fastify = require('fastify')()
const crypto = require('node:crypto')
fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger'))
// perform constant-time comparison to prevent timing attacks
function compare (a, b) {
a = Buffer.from(a)
b = Buffer.from(b)
if (a.length !== b.length) {
// Delay return with cryptographically secure timing check.
crypto.timingSafeEqual(a, a)
return false
}
return crypto.timingSafeEqual(a, b)
}
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/basic-auth'), {
validate (username, password, req, reply, done) {
let result = true
result = compare(username, validUsername) && result
result = compare(password, validPassword) && result
if (result) {
done()
} else {
done(new Error('Access denied'))
}
},
authenticate: true
})
await fastify.register(require('@fastify/swagger-ui', {
uiHooks: {
onRequest: fastify.basicAuth
}
})To ensure that models are correctly rendered at the bottom of the Swagger UI page, it's important to define your schemas using $refs through fastify.addSchema. Directly embedding JSON schemas within the schema property of your route definitions in Fastify may lead to them not being displayed in Swagger UI.
SwaggerUI can automatically validate the given specification using an online validator.
To enable this behavior you can pass the validatorUrl option
to this plugin which will be forwarded to SwaggerUI.
fastify.register('@fastify/swagger-ui', {
validatorUrl: 'https://validator.swagger.io/validator'
})Note that this behavior is disabled by default in @fastify/swagger-ui.
Licensed under MIT.