Spectral–Spatial Adversarial Multidomain Synthesis Network for Cross-Scene Hyperspectral Image Classification (TGRS2024)
Paper web page:Spectral–Spatial Adversarial Multidomain Synthesis Network for Cross-Scene Hyperspectral Image Classification.
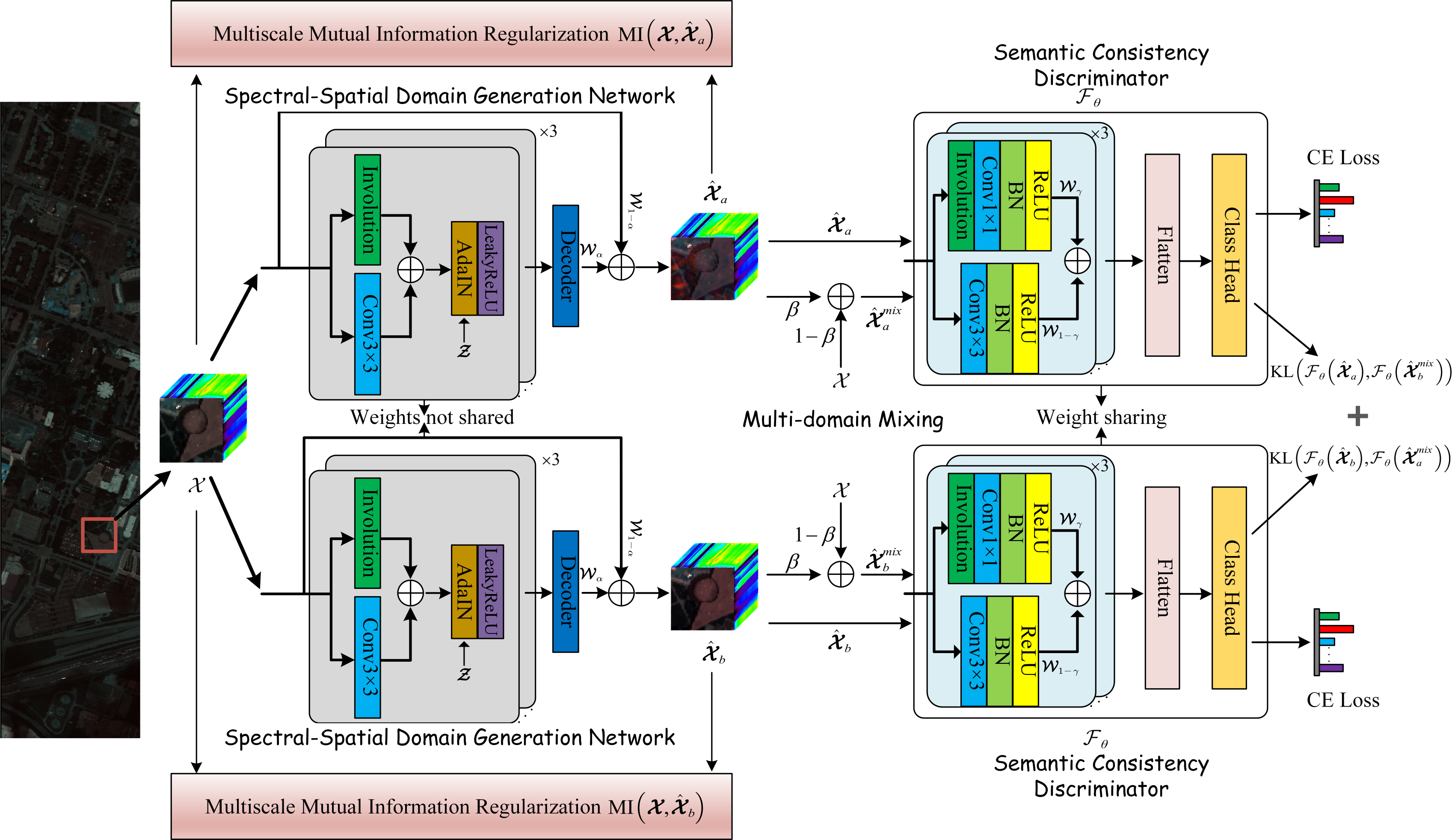
Cross-scene hyperspectral image (HSI) classification has received widespread attention due to its practicality. However, domain adaptation (DA)-based cross-scene HSI classification methods are typically tailored for a specific target scene involved in model training and require retraining for new scenes. We instead propose a novel spectral–spatial adversarial multidomain synthetic network (
Please cite us if our project is helpful to you!
@ARTICLE{10531019,
author={Chen, Xi and Gao, Lin and Zhang, Maojun and Chen, Chen and Yan, Shen},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing},
title={Spectral–Spatial Adversarial Multidomain Synthesis Network for Cross-Scene Hyperspectral Image Classification},
year={2024},
volume={62},
number={},
pages={1-16},
doi={10.1109/TGRS.2024.3401231}}
1. torch==1.11.0+cu113
2. python==3.8.3
3. mmcv==1.3.0
4. cupy-cuda110==8.5.0
The dataset can be downloaded from here: HSI datasets. We greatly appreciate their outstanding contributions.
The dataset directory should look like this:
datasets
Houston
├── Houston13.mat
├── Houston13_7gt.mat
├── Houston18.mat
└── Houston18_7gt.mat
Houston datasets:
python main.py --source_name Houston13 --target_name Houston18 --patch_size 13 --training_sample_ratio 0.8