A Cobalt Strike Beacon Object File (BOF) project which uses direct system calls to enumerate processes for specific modules or process handles.
- Use direct systems calls within Beacon Object files to enumerate processes for specific loaded modules (e.g. winhttp.dll, amsi.dll or clr.dll).
- Use direct systems calls within Beacon Object files to enumerate processes for specific process handles (e.g. lsass.exe).
- Avoid using the Windows and Native APIs as much as possible (to avoid userland hooks).
- Execute this code within the beacon process using Beacon object files to avoid fork&run.
Utilizing direct systems calls via inline assembly in BOF code provides a more opsec safe way of interacting with the system. Using direct system calls avoids AV/EDR software intercepting user-mode API calls.
-
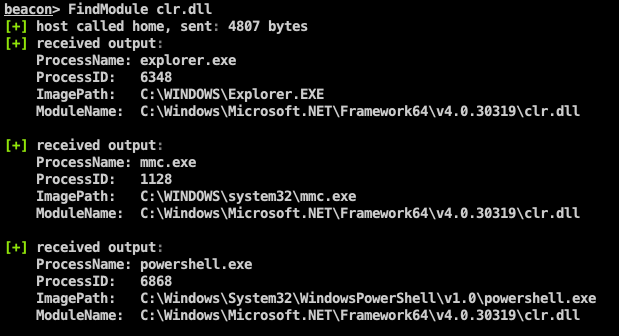
The
FindModulebof can be used to identify processes which have a certain module loaded, for example the .NET runtimeclr.dllor thewinhttp.dllmodule. This information can be used to select a more opsec safe spawnto candidate when using Cobalt Strike'sexecute-assemblyor before injecting an exfill beacon shellcode using theshinjectcommand. -
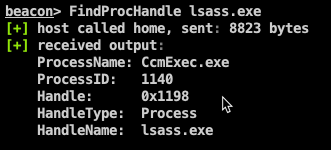
The
FindProcHandlebof can be used to identify processes with a specific process handle in use, for example processes using a handle to thelsass.exeprocess. If there's a process within the system with alsass.exeprocess handle, we could use this existing process/handle to read or write memory without opening a new process handle. This bypasses certain AV/EDR's capabilities of detecting and blocking LSASS process/memory access.
We will not supply compiled binaries. You will have to do this yourself:
- Clone this repository.
- Make sure you have the Mingw-w64 compiler installed. On Mac OSX for example, you can use the ports collection to install Mingw-w64 (
sudo port install mingw-w64). - Run the
makecommand to compile the Beacon object file. - Within Cobalt Strike use the
Script Managerto load the FindObjects.cna script. - Within a Cobalt Strike beacon context use the
FindProcHandleorFindModulecommand with the required parameters (e.g. module or process name).