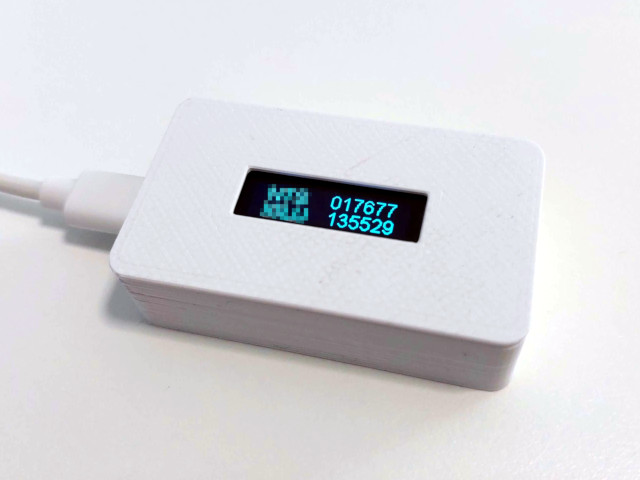
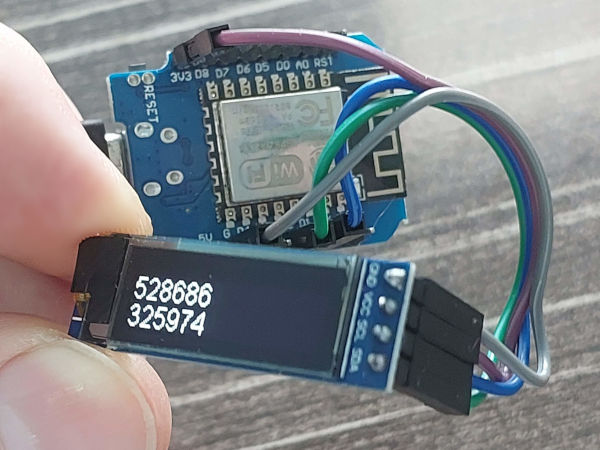
This repository contains an Arduino sketch for an ESP8266 module equipped with an I2C display. The sketch is designed to connect to a specified Wi-Fi network, synchronize the time with an NTP server, calculate a One-Time Password (OTP) based on a secret key, and display this OTP on the screen. This functionality is typically used in two-factor authentication systems.
A suitable case can be found here: Wemos D1 Case with Display on Thingiverse
- Connects to a predefined Wi-Fi network.
- Synchronizes time with a specified NTP server.
- Calculates and displays two Time-based One-Time Passwords (TOTP) on the I2C display.
-
Set up your ESP8266 environment: Ensure that your Arduino IDE is configured to program the ESP8266 and that all necessary libraries (
ESP8266WiFi,WiFiUdp,NTPClient,Wire,SSD1306Wire,TOTP) are installed. -
Configuring the sketch:
- Update the Wi-Fi credentials (
ssidandpassword) in the sketch with your network's details. - Set the NTP server address and the UTC offset in seconds for your time zone.
- Replace the placeholder for the
secret1andsecret2byte arrays with your actual OTP secret keys. - Replace the labels "OTP1" and "OTP2" if needed.
- Update the Wi-Fi credentials (
-
Uploading the sketch:
- Connect your ESP8266 to your computer and select the correct board and port in the Arduino IDE.
- Upload the sketch to the ESP8266.
If your OTP secret key is in Base32 format (common with many authentication systems), you'll need to convert it to a byte array format to use in this sketch. You can use the following Python script to do this:
import base64
def base32_to_byte_array(base32_string):
# Decode the Base32 string into bytes
decoded_bytes = base64.b32decode(base32_string, casefold=True)
return [byte for byte in decoded_bytes]
# Example usage
base32_secret = "YOUR_BASE32_SECRET" # Replace with your actual Base32 secret
byte_array = base32_to_byte_array(base32_secret)
# Print the byte array in hexadecimal format
print("Decoded bytes in hex format:", ', '.join('0x{:02x}'.format(byte) for byte in byte_array))