Type-safe polymorphic binary search tree (BST) implementation using Java 17
This is an exercise to implement a type-safe polymorphic (unbalanced) BST in a thread-safe way using Java Generics, Optional, and Record. Being a BST, the time complexity for searching, insertion and deletion are as follows:
- average case: O(h) where h is the height of the tree
- worst case: O(n) where n is the number of nodes
Using both iterative and recursive approaches, the tree implements the following methods:
- Add item; the item is discarded if it already exists.
- Remove item
- Maximum item
- Minimum item
- Height
- In-order depth-first traversal
- Pre-order depth-first traversal
- Post-order depth-first traversal
- Breadth-first traversal
The only requirement for data to be stored being the item class must implement the Java Comparable interface.
You need to have Java 17 installed to build the project. Go to the project folder and type ./gradlew build.
To run a quick demo, type ./gradlew run or java -jar build/libs/binary-tree.jar.
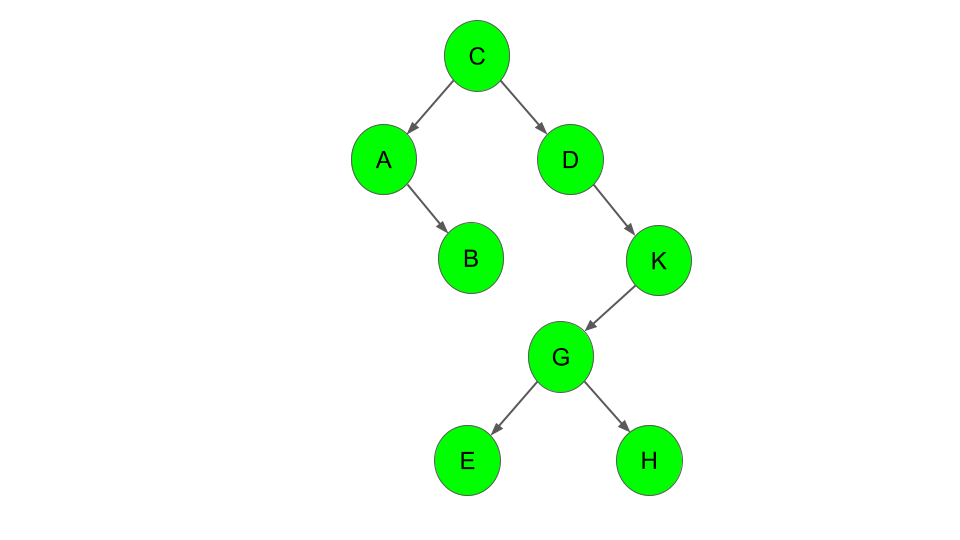
The demo builds the tree as per the following snippet:
tree = add(tree, "C");
tree = add(tree, "D");
tree = add(tree, "A");
tree = add(tree, "B");
tree = add(tree, "A");
tree = add(tree, "K");
tree = add(tree, "G");
tree = add(tree, "E");
tree = add(tree, "H");The sequence above yields the following tree: