Author/Mantainer: Ignacio Heredia (CSIC)
Project: This work is part of the DEEP Hybrid-DataCloud project that has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 777435.
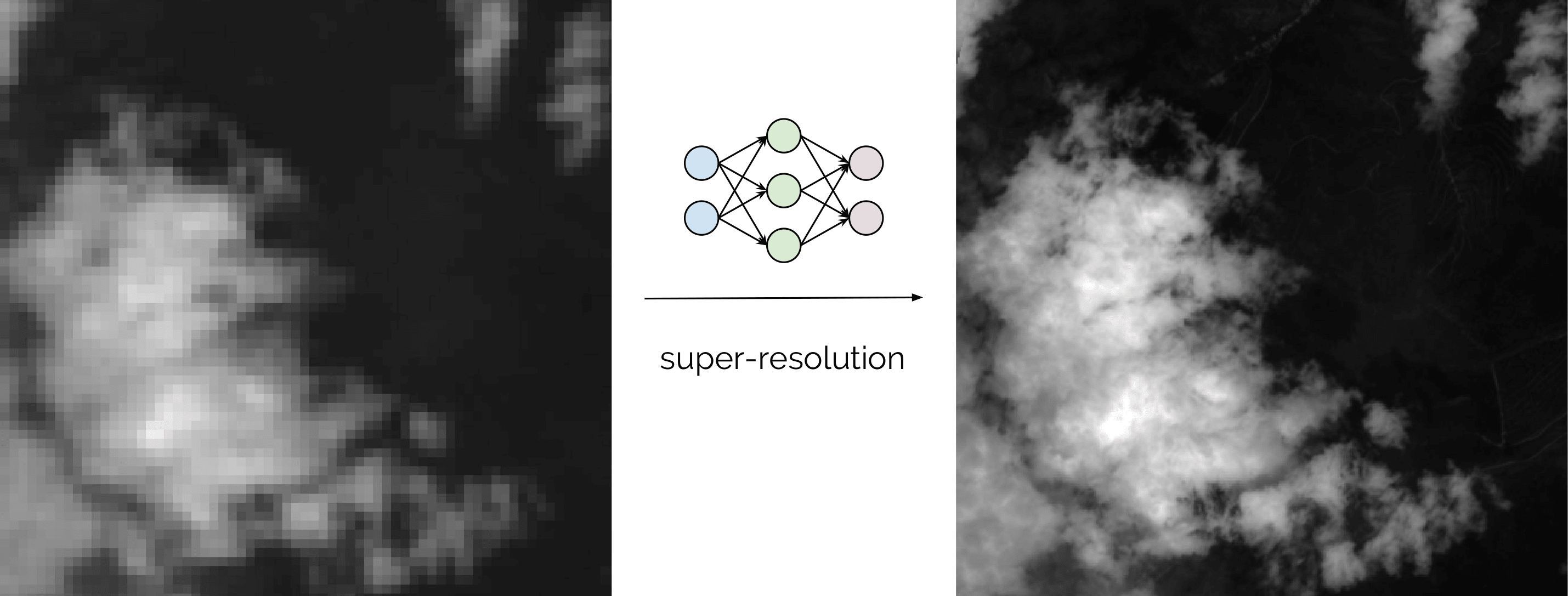
This is a plug-and-play tool to perform super-resolution on multi-spectral satellite imagery. It uses Deep Learning to provide a better performing alternative to classical pansharpening (more details in the paper mentioned below).
Right now we are supporting super-resolution for the following satellites:
More information on the satellites and processing levels that are supported can be found here along with some demo images of the super-resolutions performed in non-training data. If you want to perform super-resolution on another satellite, go to the training section to see how you can easily add support for additional satellites. We are happy to accept PRs! 🚀
You can find more information about it in the DEEP Marketplace.
Table of contents
Requirements
This project has been tested in Ubuntu 18.04 with Python 3.6.5. Further package requirements are described in the
requirements.txtfile.
It is a requirement to have Tensorflow>=1.14.0 installed (either in gpu or cpu mode). This is not listed in the
requirements.txtas it breaks GPU support.This package needs the
GDALlibrary (version >2.4.1). You can either install it withconda(withconda install gdal) or install it withpipafter having installed some additional external libraries. You can install those libraries in Linux with:sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:ubuntugis/ubuntugis-unstable sudo apt update sudo apt install -y gdal-bin python-gdal python3-gdal
To start using this framework clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/deephdc/image-classification-tf
cd image-classification-tf
pip install -e .now run DEEPaaS:
deepaas-run --listen-ip 0.0.0.0
and open http://0.0.0.0:5000/ui and look for the methods belonging to the satsr module.
We have also prepared a ready-to-use Docker container to run this module. To run it:
docker search deephdc
docker run -ti -p 5000:5000 -p 6006:6006 -p 8888:8888 deephdc/deep-oc-satsrNow open http://0.0.0.0:5000/ui and look for the methods belonging to the satsr module.
If you have images from a satellite that is not currently supported you can easily add support for your satellite.
Add Python files for your satellite
- Go to
./satsr/satellitesand create amynewsat.pyfile. This file should contains basic information like resolutions, bands names and functions for opening the bands. Check the./satsr/main_sat.pyfor a reference on what parameters and functions have to be defined. - Optional: You can also create another file like
mynewsat_download.pyto support downloading data directly with Python (see./satsr/data_download.py). - Link you newly created files with the satellite names by modifying the file
./satsr/main_sat.py.
Prepare your dataset
- Download training data (you can use the file
./satsr/data_download.pyfor convenience). - Create in
./data/dataset_filesatrain.txtfile with the tile names of the folders you want to train with. You can also create aval.txtif you want to use validation during training.
Train
-
Go to http://0.0.0.0:5000/ui and look for the
TRAINPOST method. Click on 'Try it out', change whatever training args you want and click 'Execute'. The training will be launched and you will be able to follow its status by executing theTRAINGET method which will also give a history of all trainings previously executed.If the module has some sort of training monitoring configured (like Tensorboard) you will be able to follow it at http://0.0.0.0:6006.
-
Rename the output timestamped folder in
./modelsto something likemynewsat_model_*m.
Now you proceed to the next section to use you newly trained model to perform super-resolution. If you are happy with the performance of your model we accept PRs to add it to the module's catalogue! In the near future we'll be happy to add support for additional Landsat and Sentinel missions, along with additional processing levels for satellites that are already supported, as well as any other satellite imagery in the public domain like ASTER or MeteoSat.
Go to http://0.0.0.0:5000/ui and look for the PREDICT POST method. Click on 'Try it out', change whatever test args
you want and click 'Execute'. You can either supply a:
- a
dataargument a path pointing to a compressed file (zipor tarball) containing your satellite tile.
OR
- an
urlargument with an URL pointing to a compressed file (zipor tarball) containing your satellite tile. Here is an example of such an url for the Sentinel-2 L2A that you can use for testing purposes. You can find other sample url for other satellites here.
The code in this project is based on the original repo by Charis Lanaras of the paper Super-Resolution of Sentinel-2 Images: Learning a Globally Applicable Deep Neural Network.
The main changes with respect to the original repo are that:
- most of the code has been either rewritten, restructured or cleaned up for better modularity, in order to make it plug-and-playable with other satellites (like LandSat).
- the code has been packaged into an installable Python package.
- it has been made compatible with the DEEPaaS API.
- some minor bugs have been corrected (and contributed back into the original repo in #5 and #6).
If you consider this project to be useful, please consider citing the DEEP Hybrid DataCloud project:
García, Álvaro López, et al. A Cloud-Based Framework for Machine Learning Workloads and Applications. IEEE Access 8 (2020): 18681-18692.
along with the original paper:
Lanaras, C., Bioucas-Dias, J., Galliani, S., Baltsavias, E., & Schindler, K. (2018). Super-resolution of Sentinel-2 images: Learning a globally applicable deep neural network. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 146, 305-319.