A Slack bot and set of scripts for exporting history (and something more) from public channels, private channels and direct messages (DMs), using Slack's new Conversations API.
A similar service is provided by Slack for workspace admins at https://my.slack.com/services/export (where my can be replaced with your full workspace name to refer to a workspace different than your default). However, it can only access public channels, while pyslacker can retrieve data from any channel accessible to your user account.
Based on sebseager/slack-exporter
There are two ways to use pyslacker (detailed below). Both require a Slack API token to be able to communicate with your workspace.
- Visit https://api.slack.com/apps/ and sign in to your workspace.
- Click
Create New App, enter a name (e.g.,Slack Exporter), and select your workspace. - In prior versions of the Slack API, OAuth permissions had to be specified manually. Now, when prompted for an App Manifest, just paste in the contents of the
slack.yamlfile in the root of this repo. - Select
Install to Workspaceat the top of that page (orReinstall to Workspaceif you have done this previously) and accept at the prompt. - Copy the
OAuth Access Token(which will generally start withxoxpfor user-level permissions)
Wrapper script dump-history.sh can create an archive of all accessible conversation history with all replies in your workspace.
-
Either add
SLACK_USER_TOKEN = xoxp-xxxxxxxxxxxxx...to a file named
.envin repo's root (runcp .env.dist .envif it doesn't exist) or run the following in your shell (replacing the value with the user token you obtained in the Authentication with Slack section above).export SLACK_USER_TOKEN=xoxp-xxxxxxxxxxxxx... -
Run
./warmup-cache.sh. This script will download and cache channels and users from your workspace (this step is optional, but recommended). -
Type all channels you want to save as comma-separated list and run:
./dump-history.sh channel1,channel2; -
... or run
./dump-history-from-json.shwhich will usechannel.jsonin repo's root as a source of channels to export (runcp channel.dist.json channel.jsonif file doesn't exist and add channels to copied file). If you skipped step 2, channel/user lists will be downloaded before actual export starts, but this needs to be done only once.
dump-emoji.shcan be used to download all emojis defined in a workspace (but as for now it requires some additional manual work).- To interact with history export script directly, use:
venv/bin/python -m pyslacker --help(this will list available options).
pyslacker/bot.py is a Slack bot that responds to "slash commands" in Slack channels (e.g., /export-channel). To connect the bot to the Slack app generated in Authentication with Slack, add the following line to a file named .env in repo's root (run cp .env.dist .env if it doesn't exist) :
SLACK_USER_TOKEN = xoxp-xxxxxxxxxxxxx...
After that run the Flask app such that the application is exposed to the Internet. This can be done via a web server (e.g., Heroku), as well as via the ngrok service, which assigns your localhost server a public URL.
To use the ngrok method:
-
Download the appropriate binary.
-
Run
./start-bot.sh -
Run the ngrok binary with
path/to/ngrok http 5000, where5000is the port on which the Flask application (step 2) is running. Copy the forwarding HTTPS address provided. -
Create the following slash commands will be created (one for each applicable Flask route):
Command Request URL Arguments Example Usage /export-channel https:// [host_url]/slack/export-channeljson | text /export-channel text /export-replies https:// [host_url]/slack/export-repliesjson | text /export-replies json To do this, clone
slack.dist.yamlasslack.yaml, uncomment theslash-commandssection inslack.yamland replaceYOUR_HOST_URL_HEREwith something likehttps://xxxxxxxxxxxx.ngrok.io(if using ngrok). Then navigate back toOAuth & Permissionsand click(Re)install to Workspaceto add these slash commands to the workspace (ensure the OAuth token in your.envfile is still correct).
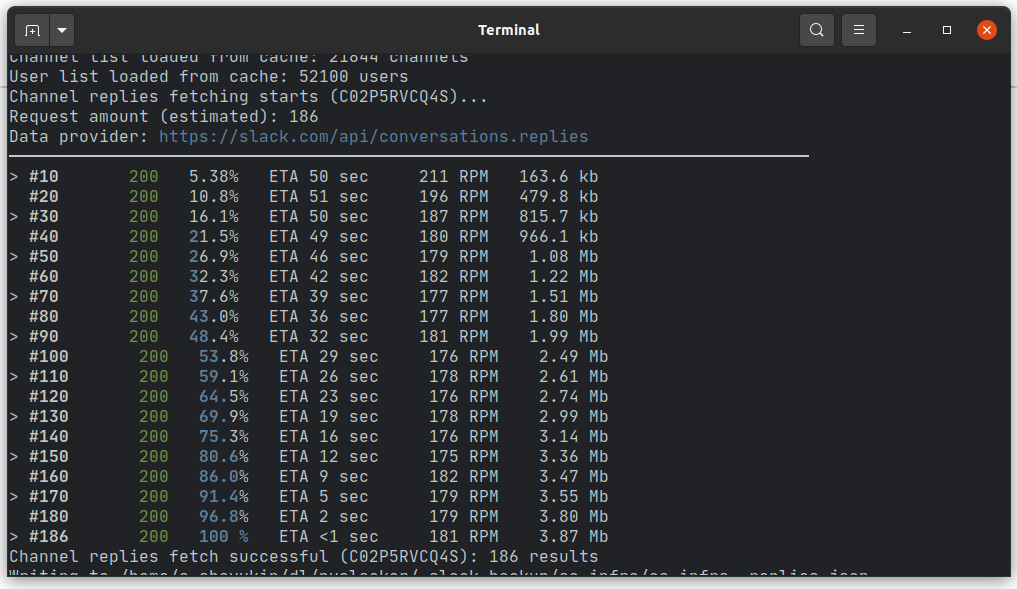
Example of channel history export completed in 186 requests (all thumbnails are clickable):
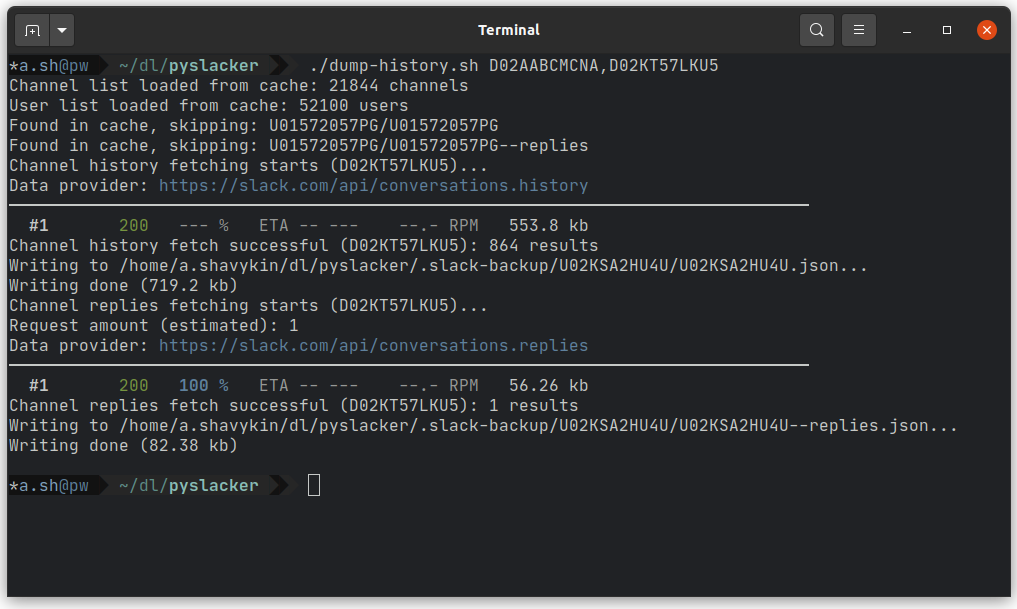
Running wrapper script with two channels specified:
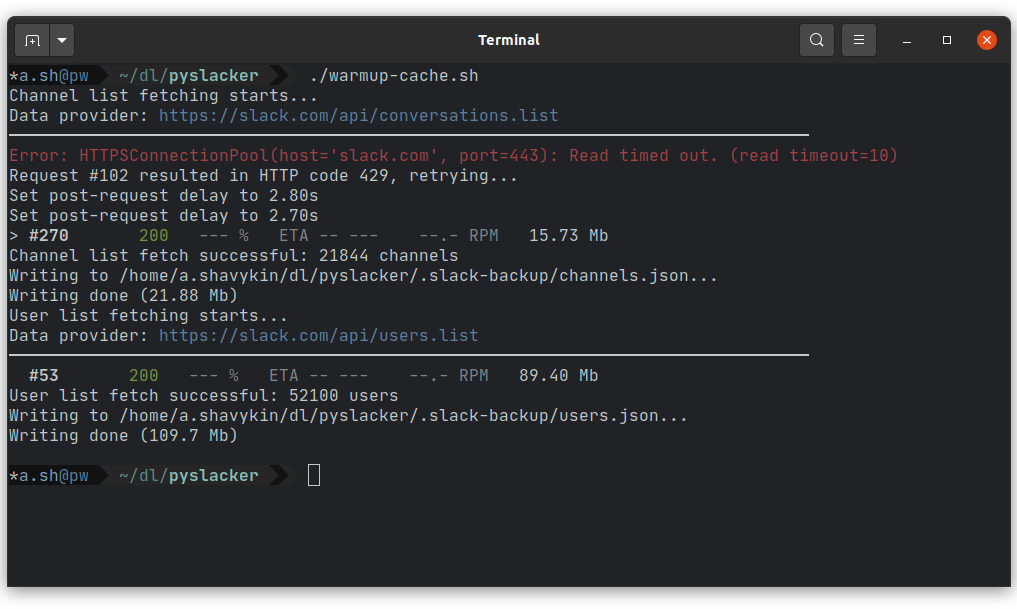
Running preparation script warmup-cache.sh which downloads full channel list and full user list. This is optional, because these lists will be loaded anyway before actual export starts; but in that case this will be done within export command, which might be confusing.
- Seb Seager (original scripts)
- Aleksandr Shavykin (refactoring, detailed output, more exporters)
- Mikhail Shipov (enchancements, fixes)
This software is available under the GPL.