This is the pytorch implementation of Paper: Image Inpainting With Learnable Bidirectional Attention Maps (ICCV 2019) paper suppl
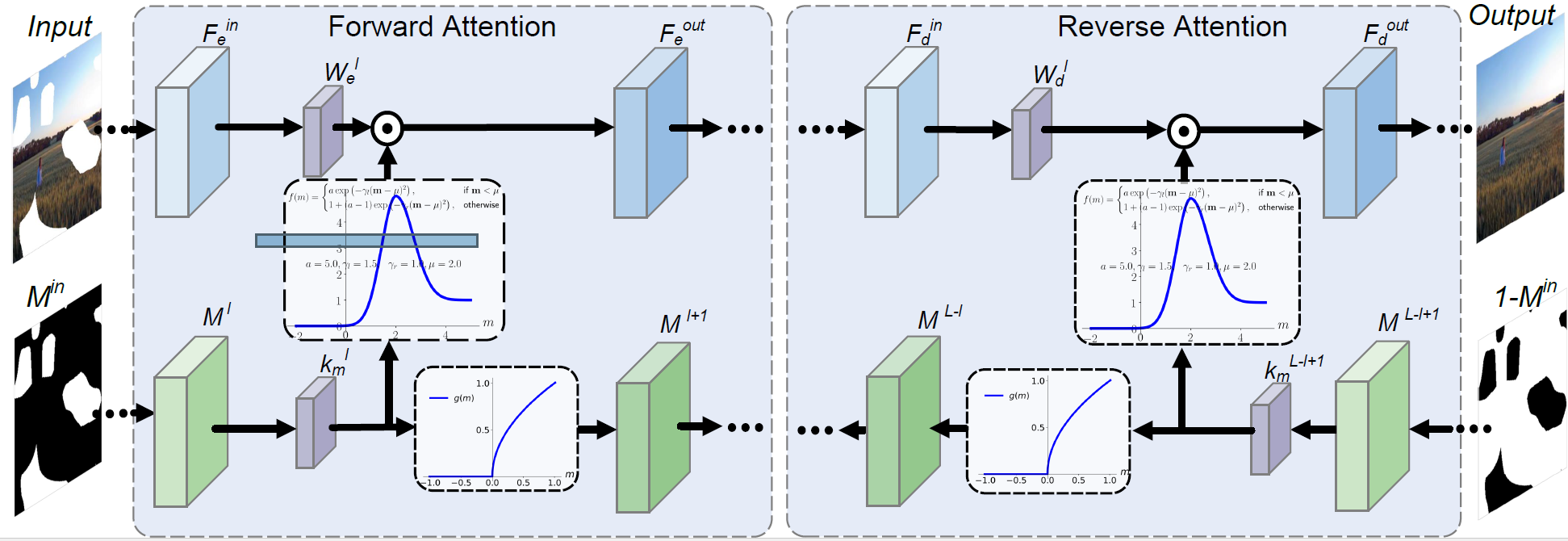
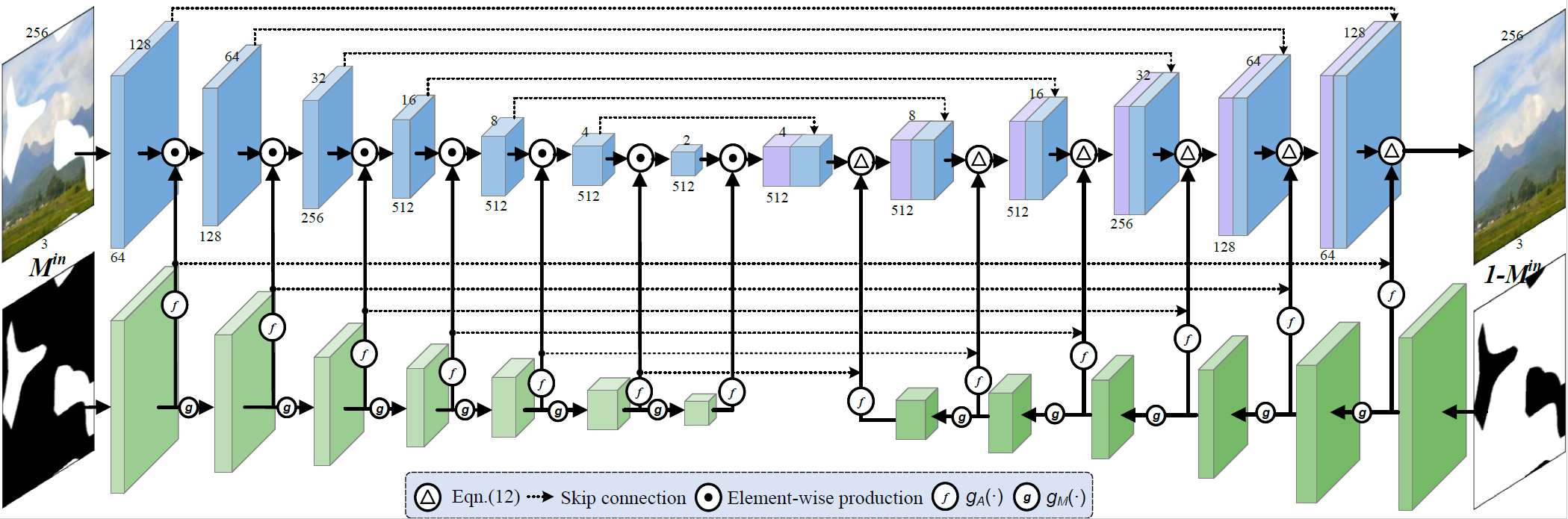
We propose a Bidirectional Attention model based on the U-Net architecture.
- Python 3.6
- Pytorch >= 1.0 (tested on pytorch version 1.0.0, 1.2.0, 1.3.0)
- CPU or NVIDIA GPU + Cuda + Cudnn
To train the LBAM model:
python train.py --batchSize numOf_batch_size --dataRoot your_image_path \
--maskRoot your_mask_root --modelsSavePath path_to_save_your_model \
--logPath path_to_save_tensorboard_log --pretrain(optional) pretrained_model_pathTo test the model:
python test.py --input input_image --mask your_mask --output output_file_prefix --pretrain pretrained_model_pathTo test with random batch with random masks:
python test_random_batch.py --dataRoot your_image_path
--maskRoot your_mask_path --batchSize numOf_batch_size --pretrain pretrained_model_path
We suggest that you train our model with a large batch size (>= 48 or so). We re-train our model with batch size 10, the results degrades a little bit, I guess it may be due to the batch-normalization opreation (I would try removing bn from LBAM and see how it affects).
The pretrained model can be found at google drive, or baidu cloud with extract code: mvzh. I made a slight change by setting the bn to false and modify the last tanh from absolute value to (tanh() + 1) / 2.
Here are some inpainting results that we train with batch size of 10 on Paris StreetView dataset:
| Input | Results | Ground-Truth |
|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Please cite our paper
@InProceedings{Xie_2019_ICCV,
author = {Xie, Chaohao and Liu, Shaohui and Li, Chao and Cheng, Ming-Ming and Zuo, Wangmeng and Liu, Xiao and Wen, Shilei and Ding, Errui},
title = {Image Inpainting With Learnable Bidirectional Attention Maps},
booktitle = {The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
month = {October},
year = {2019}
}
We benifit a lot from NVIDIA-partialconv and naoto0804-pytorch-inpainting-with-partial-conv, thanks for their excellent work.