This repository contains various demonstrations to highlight features and configuration in Consul Service Mesh.
NOTE: All service registration and central config is automatically applied when running these examples.
To apply configuration manually you can comment out the CENTRAL_CONFIG environment variable in the docker-compose.yml files:
web_envoy:
image: nicholasjackson/consul-envoy:v1.6.0-v0.10.0
environment:
CONSUL_HTTP_ADDR: 10.5.0.2:8500
CONSUL_GRPC_ADDR: 10.5.0.2:8502
SERVICE_CONFIG: /config/web_v1.json
# CENTRAL_CONFIG: "/central_config/web-defaults.hcl;/central_config/api-defaults.hcl;/central_config/api-v1-defaults.hcl;/central_config/api-v2-defaults.hcl;/central_config/api-router.hcl"
volumes:
- "./service_config:/config"
- "./central_config:/central_config"
command: ["consul", "connect", "envoy","-sidecar-for", "web-v1"]
network_mode: "service:web"Config can then be manually applied using the following command once you have started the example with docker-compose up:
$ consul config write config_file.hcl
All central config is stored in the central_config folder in each example.
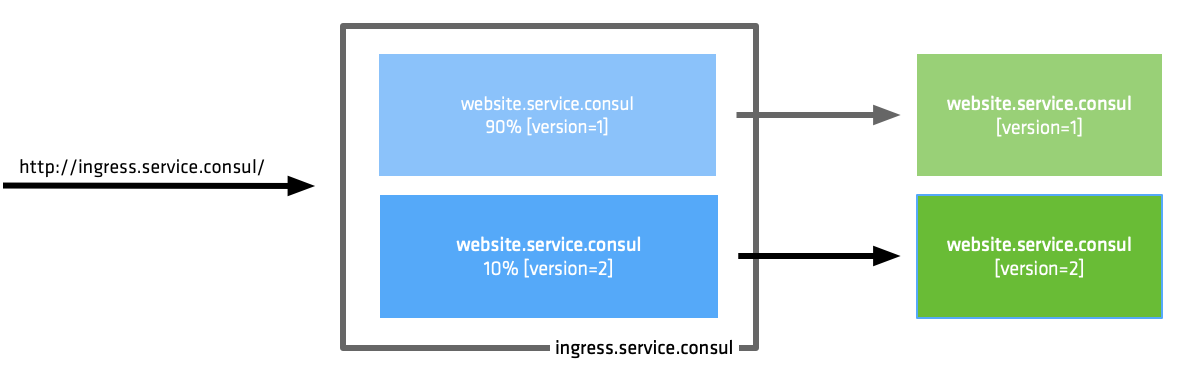
This demonstration shows how traffic can be split between two service instances. This feature could be used for a Canary or Dark deployment testing strategy.
This demonstration shows how upstream traffic can be routed between two services using HTTP paths.
This demonstration shows how to configure Consul Service Mesh for Observability.
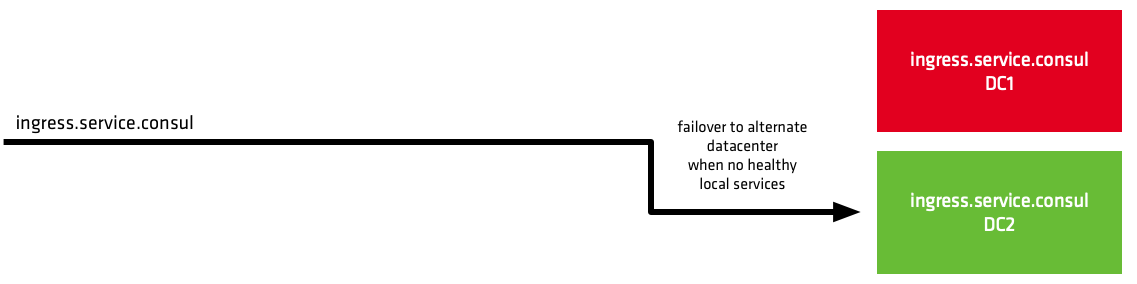
This demonstration shows how to failover upstream services to a different datacenter. This feature could be used to main uptime during a partial or regional service outage.
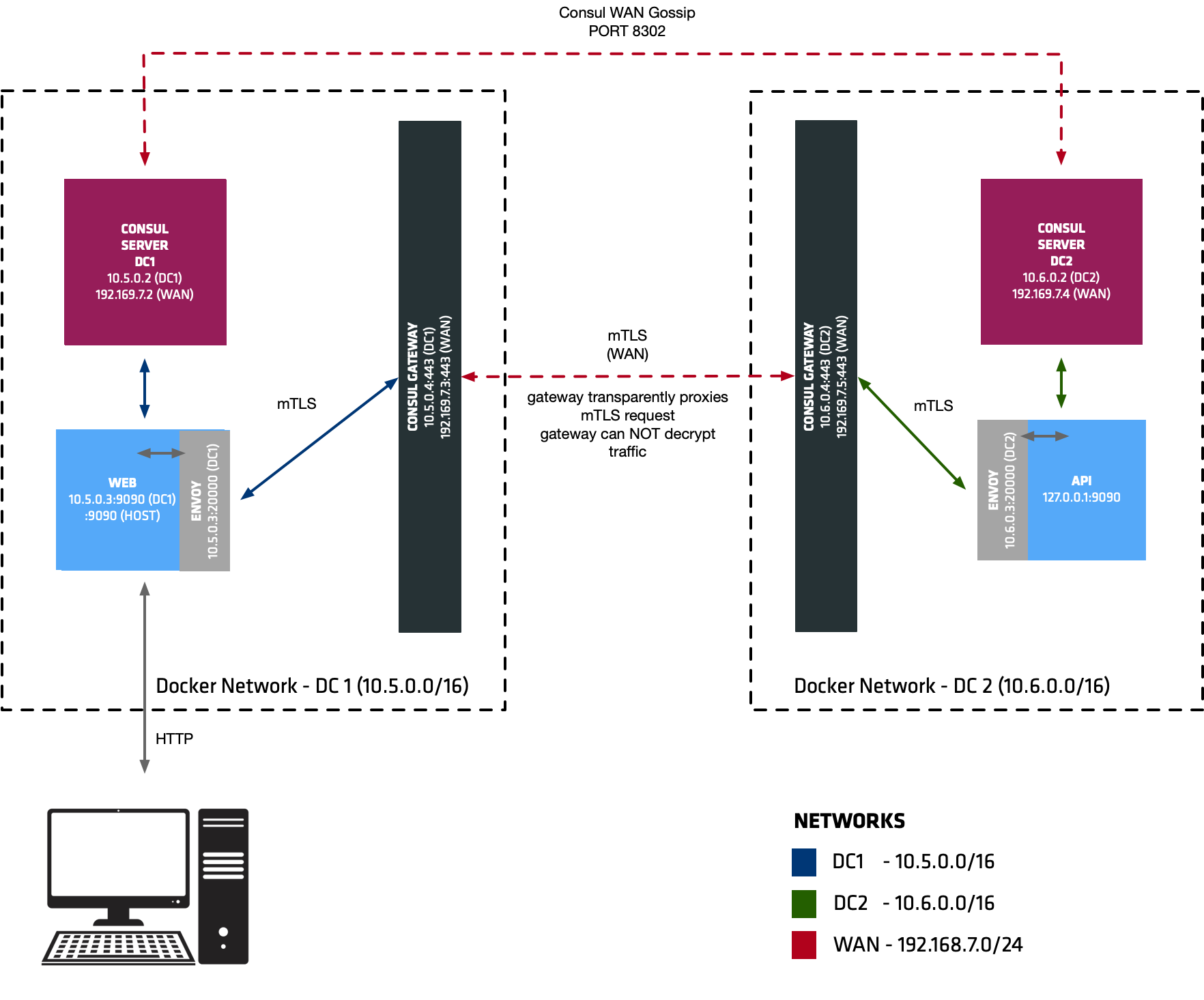
This demonstration shows how to route traffic to a second Consul Datacenter using Consul Gateways. This feature could be used to route traffic between Virtual Machines and Kubernetes.