A Dataset for Multi-hop Explainable Fact Verification
ACL 2024 (Findings)

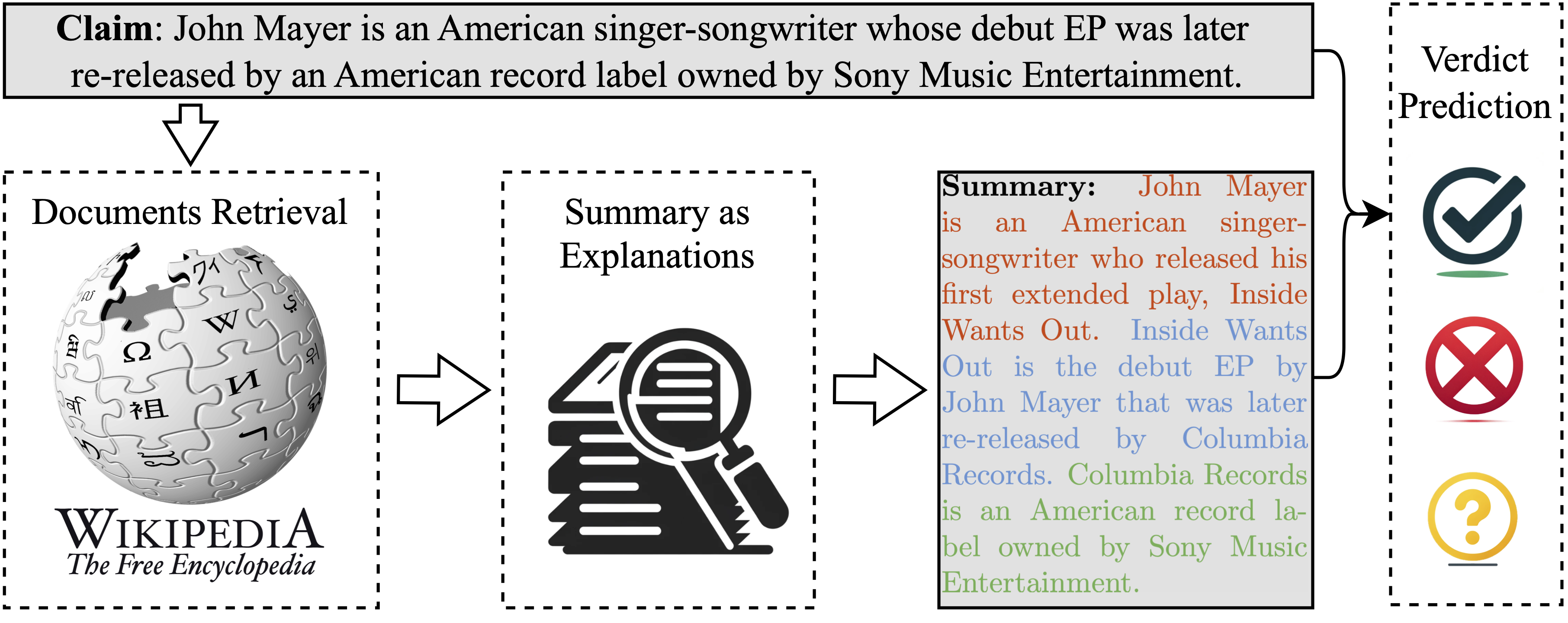
A sample in the proposed dataset EX-FEVER. The textual explanation in different colors refers to the information in different documents.
The baseline system comprises three stages: document retrieval, summary generation as explanations, and verdict prediction. The system produces two main outputs: a veracity label indicating whether the claim is 'SUPPORT'ed, 'REFUTE'd, or there is 'NOT ENOUGH INFO', and a summary that serves as an explanation for the prediction.
First, install drqa
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/DrQA.git
cd DrQA; pip install -r requirements.txt; python setup.py developpip install -r requirementsDownload wikipedia dumps provided by HOVER https://nlp.cs.unc.edu/data/hover/wiki_wo_links.db
We first use TF-IDF retrieval to yield the top-200 relevant Wikipedia documents.
python scripts/build_tfidf.py data/wiki_wo_links.db resultspython scripts/exfc_tfidf.py results/wiki_db-tfidf-ngram=2-hash=16777216-tokenizer=simple.npz resultsAdd tfidf rank and score to train/dev/test and save it to an additional csv file
Then the neural-based Document Retrieval Model. Implement by HOVER
python scripts/prepare_data_for_fcdoc_retrieval.py --data_split=dev --doc_retrieve_range=200
python scripts/prepare_data_for_doc_retrieval.py --data_split=train --doc_retrieve_range=200Training the neural-based document retrieval model
./scripts/train_doc_retrieval.shAnd a multi-hop design retrieval model Multi-Hop Dense Text Retrieval (MDR)
We fine tune a bart model through transformer library
We use a bert model and GEAR model respectively
Finetune a bert model through transformer library
Train the Gear model through https://github.com/thunlp/GEAR
In this section, we conduct preliminary investigations into using Large Language Models (LLMs) for fact-checking in two ways:
- Directly using LLMs as an actor.
- Using LLMs as a planner.
We evaluate both the verdict accuracy and the ability of LLMs to generate explanations.
We will use a mini test dataset and the OpenAI API to utilize the GPT-3.5 Turbo model for claim verification. To do this, you need to add your OpenAI API key by modifying the following code:
openai.api_key = 'your_api_key'Run the script using the command:
python scripts/openai_api.py claim_onlyYou can choose from the following prompt templates:
w_expclaim_onlywo_expw_exp_doc1w_exp_doc3json
The test results are saved to the results folder.
We use LLMs as a planner through ProgramFC.
| Hops | SUP | REF | NEI | Claim | EXP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
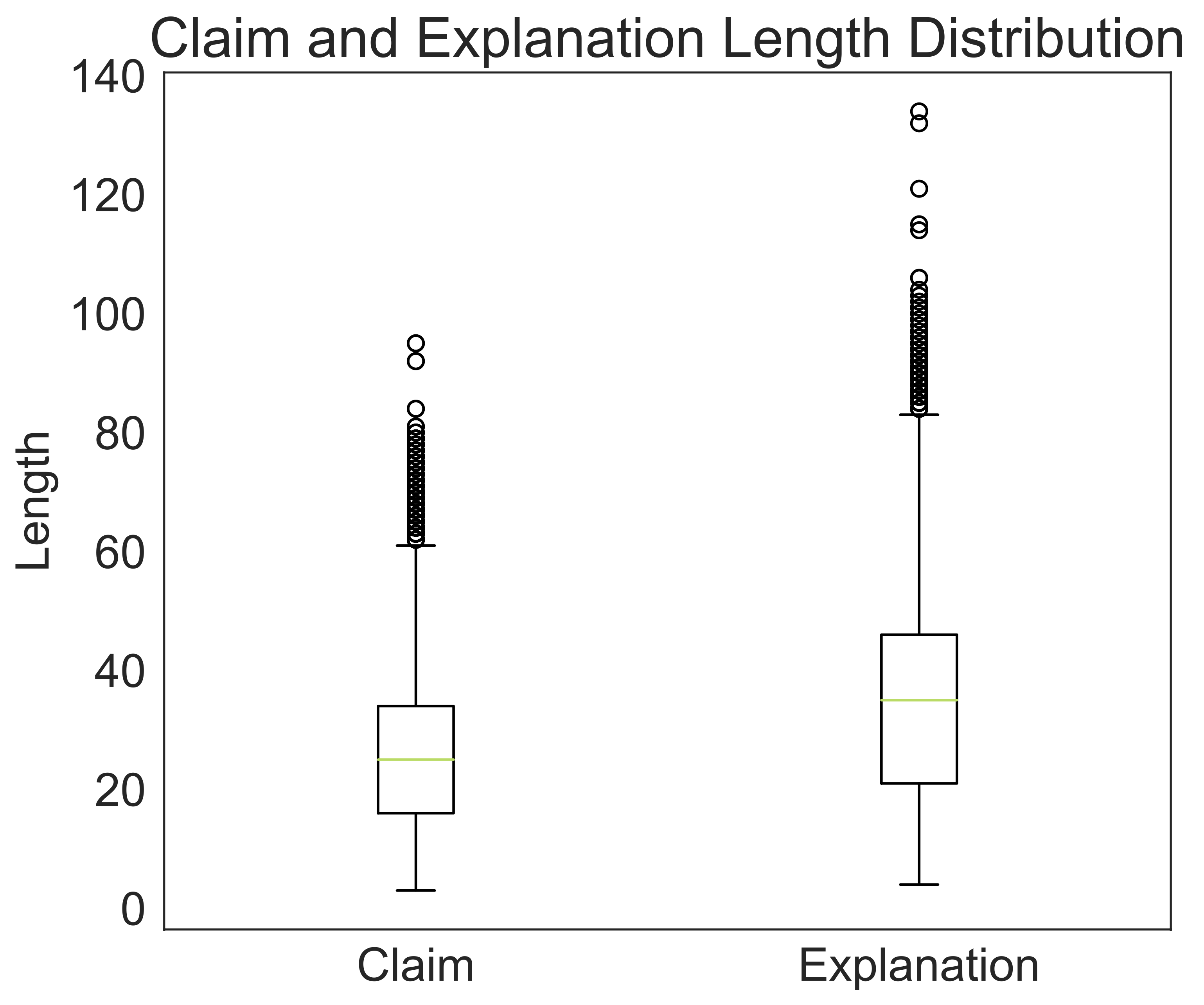
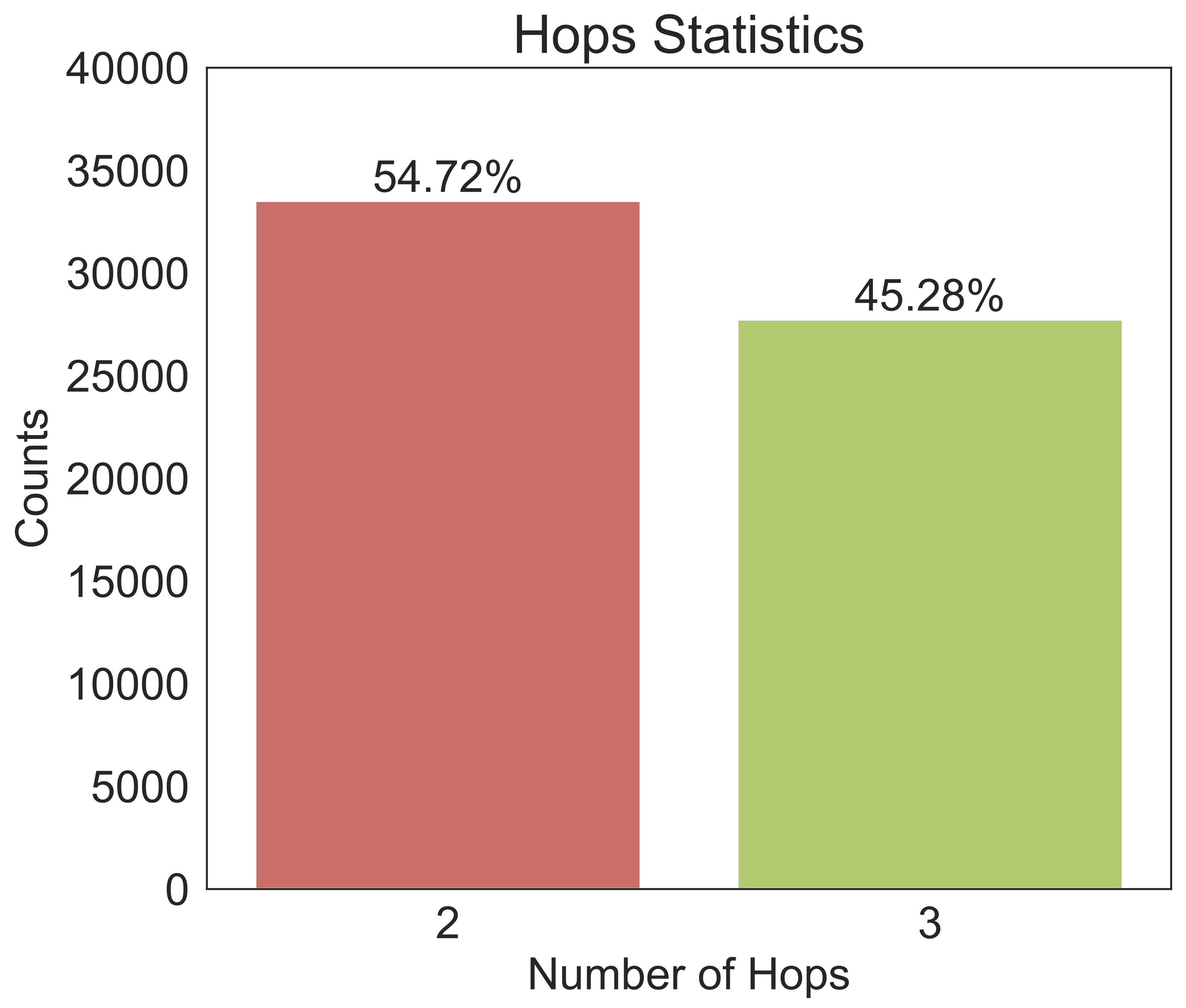
| 2 Hops | 11053 | 11059 | 11412 | 21.63 | 28.39 |
| 3 Hops | 9337 | 9463 | 8941 | 30.69 | 43.45 |
| Total | 20390 | 20522 | 20353 | 25.73 | 35.21 |
If you use this dataset, please cite the following paper:
@inproceedings{ma-etal-2024-ex,
title = "{EX}-{FEVER}: A Dataset for Multi-hop Explainable Fact Verification",
author = "Ma, Huanhuan and
Xu, Weizhi and
Wei, Yifan and
Chen, Liuji and
Wang, Liang and
Liu, Qiang and
Wu, Shu and
Wang, Liang",
editor = "Ku, Lun-Wei and
Martins, Andre and
Srikumar, Vivek",
booktitle = "Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024",
month = aug,
year = "2024",
address = "Bangkok, Thailand",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.findings-acl.556/",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2024.findings-acl.556",
pages = "9340--9353",
abstract = "Fact verification aims to automatically probe the veracity of a claim based on several pieces of evidence. Existing works are always engaging in accuracy improvement, let alone explainability, a critical capability of fact verification systems.Constructing an explainable fact verification system in a complex multi-hop scenario is consistently impeded by the absence of a relevant, high-quality dataset. Previous datasets either suffer from excessive simplification or fail to incorporate essential considerations for explainability. To address this, we present EX-FEVER, a pioneering dataset for multi-hop explainable fact verification. With over 60,000 claims involving 2-hop and 3-hop reasoning, each is created by summarizing and modifying information from hyperlinked Wikipedia documents. Each instance is accompanied by a veracity label and an explanation that outlines the reasoning path supporting the veracity classification. Additionally, we demonstrate a novel baseline system on our EX-FEVER dataset, showcasing document retrieval, explanation generation, and claim verification, and validate the significance of our dataset. Furthermore, we highlight the potential of utilizing Large Language Models in the fact verification task. We hope our dataset could make a significant contribution by providing ample opportunities to explore the integration of natural language explanations in the domain of fact verification."
}@article{ma2023exfever,
title={Ex-fever: A dataset for multi-hop explainable fact verification},
author={Ma, Huanhuan and Xu, Weizhi and Wei, Yifan and Chen, Liuji and Wang, Liang and Liu, Qiang and Wu, Shu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.09754},
year={2023}
}