This environment is under construction!!
Always use the released versions because in these all examples are tested and the API documentation is consistent. The master branch may contain inconsistencies because this environment is currently under development. See the Travis CI tag above to know the status of this repository.
- CMSIS 5.4.0 (Core and DSP). CMSIS_5 Repository.
- LPCOpen v3.02 LPCOpen Software Development Platform LPC43XX NXP website.
- LPCUSBlib. LPCUSBlib documentation
- sAPI v0.5.2. sAPI API Reference (spanish).
- Elm-Chan FatFS R0.13b. FatFS documentation. Generic FAT Filesystem module with support for SD Card (SSP) and Pendrive (USB MSD) disks.
- FreeRTOS Kernel V10.0.1. FreeRTOS_Reference_Manual_V10.0.0.pdf.
- gcc-arm-none-eabi
- Make sure you have an
arm-none-eabi-*toolchain configured in yourPATH. If you don't have it, download GCC ARM Embedded. - Make sure you have an
openocdconfigured in yourPATH.
- Create a
board.mktext file inside this folder. - Define
BOARDvariable inboard.mkaccording to the board you want to compile.
board.mk example default values:
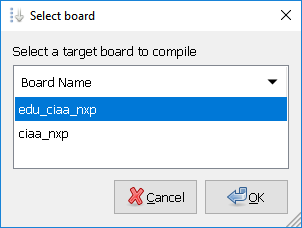
BOARD = edu_ciaa_nxpNote: If you have zenity installed (included in CIAA Software), you can use:
make select_boardto select graphically a target board.
This will create automaticaly a board.mk text file inside this folder with the selected board.
- Create a
program.mktext file inside this folder. - Define
PROGRAM_NAMEandPROGRAM_PATHvariables inprogram.mkaccording to the program you want to compile (PROGRAM_PATH is relative to this folder, leave void if the program is inside this folder).
program.mk example default values:
PROGRAM_PATH = examples/c
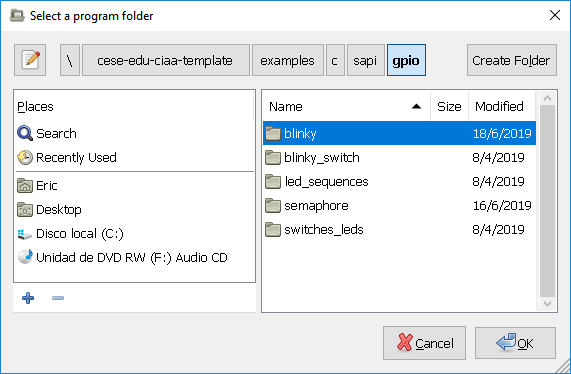
PROGRAM_NAME = appNote: If you have zenity installed, you can use:
make select_programto select graphically a program.
This will create automaticaly a program.mk text file inside this folder with the selected program.
- Compile with
make. - Download to target via OpenOCD with
make download. - Clean compilation with
make clean.
Each program consist in a folder (with a non-spaces name) that includes inside 2 folders, one named src (here go, .c, .cpp or .s source code files), and another one named inc (here go, .h or .hpp source header files).
program.c example:
#include "sapi.h"
int main( void )
{
boardInit();
while(1){
gpioToggle(LED);
delay(200);
}
}program.h example:
#ifndef __ARCHIVO_H_
#define __ARCHIVO_H_
// Your public declarations...
#endifAlso you can use a file named config.mk, where you may configure which libraries you include and compiler options.
config.mk example and default values:
# Compile options
VERBOSE=n
OPT=g
USE_NANO=y
SEMIHOST=n
USE_FPU=y
# Libraries
USE_LPCOPEN=y
USE_SAPI=yProgram complete structure is:
+program
+--config.mk
+--+src
| +--program.c
+--+inc
+--program.h
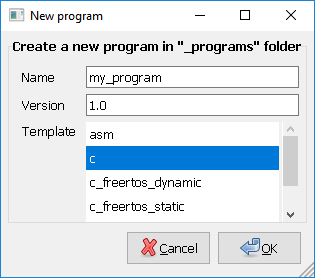
Note: If you have zenity installed, you can use:
make new_programto create graphically a program using program templates.
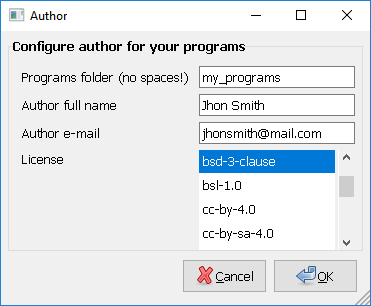
First time will ask you for your user preferences:
The libs folder include libraries that can be used fom any program (global libraries).
The Makefile allow you to include 2 types of libraries:
- Simple library. Consist in a folder (with a non-spaces name) that includes inside 2 folders, one named
src(here go .c, .cpp or .s source code files), and another one namedinc(here go .h or .hpp header files). This kind of library compiles automaticaly by the Makefile. - Advanced library. Consist in a library with a complex folder and files structure, i.e. LibUSB. This case require make your own makefile. You can inspire from sAPI makefile to do that.
Included examples are:
asm_lpc_open: assembler with LPC Open libraryasm_sapi: assembler with sAPI library
- sAPI library
- Bare metal:
adc_dac: ADC and DAC example.- bluetooth
hm10_uart_bridge: Bluettoth HM10 module AT, tx and rx example.
cycles_counter: clock cycles counter functions, only work in debug mode. Allows execution time trazability.dht11_temp_humidity: humidity and temperature sensor.- gpio
gpio_01_switches_leds: each switch drives the upper led.gpio_02_blinky: the simply led blinky with a blocking delay.gpio_03_blinky_switch: led blinky with a with a non-blocking delay, to allow you to respond to a switch at the same time.gpio_04_led_sequences: led sequences by using a non-blocking delay.
hcsr04_ultrasonic_sensor: HC-SR04 utrasonic distance sensor.- i2c:
- IMUs
mpu9250: MPU9250 IMU 9DOF (Gyroscope, Accelerometer and Magnetometer) + Temperature.
- magnetometers. In Chinese GY-273 module you can have one of this magnetometers, that have the same pinout but different register map. To difference them see the chip, ignore the board serigraphy.
hmc5883l: HMC5883L magnetometer.qmc5883l: QMC5883L magnetometer.
- IMUs
keypad_7segment: Drives a keypad and 7 segment display.lcd: Drives a LCD display.- pwm
pwm_01: PWM applied to LEDs.pwm_02_rgb_controller_uart: RGB LED example.
rtc: RTC peripheral to have date and time clock.sapi_basic_example: a basic sAPI library exampleservo: angular servomotor PWM control example.- spi_sd_card
spi_sd_card_01_wite_file: Wite a text file in a SD/MicroSD Card (SPI connected) by using a FAT File System (Elm-Chan FAT FS).spi_sd_card_02_log_time_stamp: Wite a text file in a SD/MicroSD Card (SPI connected) by using a FAT File System (Elm-Chan FAT FS) add time-stamp in samples.spi_sd_card_03_list_files: List files in a SD/MicroSD Card (SPI connected) by using a FAT File System (Elm-Chan FAT FS). Show results in UART.
tick_hook: periodic tick function (interrupt-based) with periodic callback.- uart
uart_01_echo: UART echo, it respond the same that you send from PC.uart_02_receive_string_blocking: waits until receive a certain pattern String in a UART or timeout expire (blocking code). Don't save received string.uart_03_receive_string: waits until receive a certain pattern String in a UART or timeout expire (non-blocking code). Don't save received string.
- wifi_esp8266
wifi_esp8266_01_uart_bridge: use this to send AT commands directly to ESP01 module.wifi_esp8266_02_thingspeak: send data to thingspeak dashboards.
- usb
usb_device_01_hid_keyboard: USB Device. Board as USB Keyboard.usb_device_02_cdc_virtualSerialPort: USB Device. Using USB OTG as a virtual serial port.
- Operating Systems:
- rtos_cooperative (see M.J. Pont's book at https://www.safetty.net/publications/pttes )
scheduler_01_seos: first cooperative schedulerscheduler_02_seos_background_foreground: second cooperative schedulerseos_pont_2014_01_first_app: third cooperative scheduler
- rtos_freertos
- dynamic_mem
freeRTOS_01_blinkyfreeRTOS_03_ChanFatFS_SPI_SdCard_ADC_log: ADC logging in a SD/MicroSD Card (SPI connected) by using a FAT File System (ChanFS), freeRTOS and sAPI.
- static_mem
freeRTOS_01_blinky
- dynamic_mem
- rtos_cooperative (see M.J. Pont's book at https://www.safetty.net/publications/pttes )
- Bare metal:
- LPC Open library
- bare_metal
blinkyblinky_inputblinky_ramblinky_ritbooti2clpc_open_basic_examplempupwm
- operating_systems
freertos_blinky
- statecharts
statechart
- bare_metal
newlib_printf_scanfwithout_libs
cpp_sapi_basic_example: a C++ basic example with sAPI library.