Git a Version Control Software (VCS) which allows you to take a snapshot of a project whenever it's in a working state.
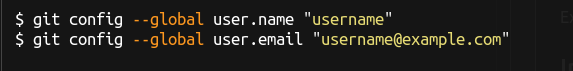
Git keeps track of who makes changes to a project, even when only one person is working on the project. It requires username and email.
Example:
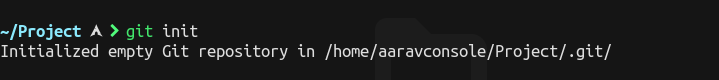
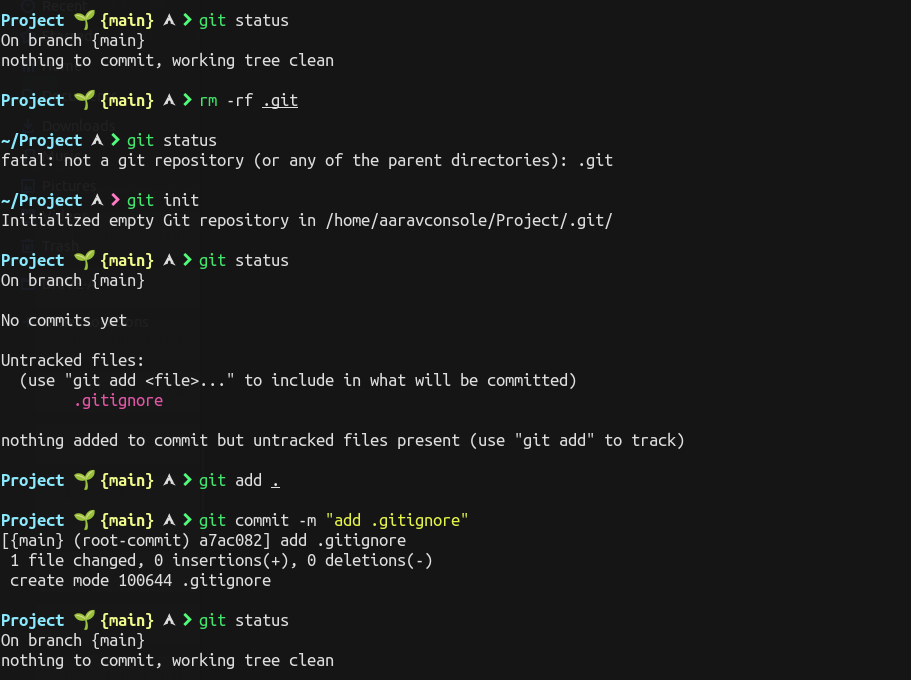
To Initializing a Repository you need to first select the directory and then type git init in git console.
Example:
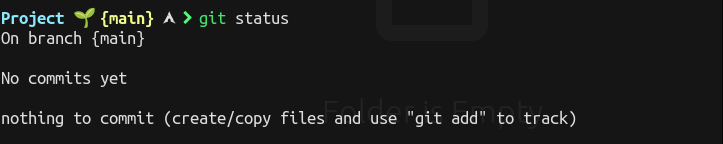
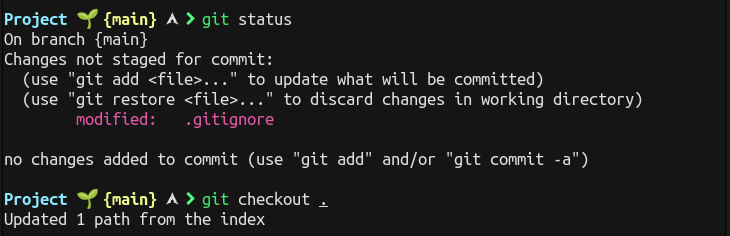
You can track the status of your working project or untracked files by git status.
Example:
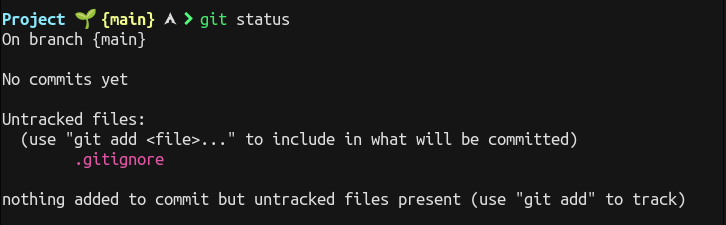
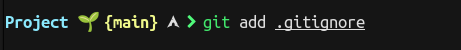
For the Files you don't want to take track off, you can simply write the path of those files in file with extension .gitignore.
Example:
To add files to commit (staging) one can use command git add . to add all the files in the working directory
to add specific file the commmand is git add filename.
Example:
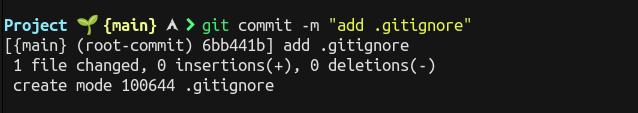
To make a commit on staged files (ready to commit) the command is git commit -m "commit message" or git commit -am "commit message".
The -a flag tells Git to add all modified files in the repository to the current commit.
The commit message should be short, descriptive and in imperative, present tense.
The -m flag in the command tells Git to record a message in the log for this commit.
Example:
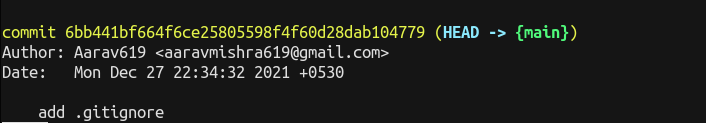
Git keeps a log of all commits made to the files or projects. Dedicated command to log details is git log.
Example:
Each time commit is made, Git generates a unique, 40-character refrence ID. As we don't always need all of this information there is simpler version to log entries git log --pretty=oneline.
Example:
Now Let'a take a look at how to abandon a change and revert back to the previous working state of the project or files.
Example:
The command git checkout . allows you to work with any previous commit. It abandons any changes made since the last commit and restores the files in last committed state.
To delete a Repository type rm -rf .git in git console. Afterwards, you'll need to start over with a fresh repository to start tracking your changes again. Here's the look how this entire process looks like in terminal session.