Casbin-Mesh (hereinafter referred to as: application) is intended to provide users with an out-of-the-box permission control application that supports multi-tenancy. you can quickly deploy a high-performance and scalable Casbin application through Helm, docker-compose and other tools, without worrying about which persistent storage Adapter are used.
This application will use the Raft[0] consensus algorithm to synchronize the memory data in multiple nodes, and use the Embedded Database to store the Raft Log persistently, and support recovery the application states from the locally persistently stored Log or Snapshots. The application structure can be divided into two parts, Server (that is, responding to requests initiated by users), and Client (that is, users use Client libraries to initiate requests to the server. For example, initiating Enforcer requests, performing RBAC Management operations, etc.).
In this draft, we consider using Hashicorp/Raft[1]'s Raft implementation and bboltDB[2] to implement persistent storage. We will not repeat some of the basic features of Raft (such as Tolerating failure, Snapshots (Log compaction), etc.), we will try to focus on some of the features at the application layer.
In the case of a larger number of requests, the external interface using non-JSON serialization (and non-HTTP 1.X) protocol can achieve better performance, and can use long links to reduce context (for example, reduce database access permissions The check. Will be specifically explained in the Security Section) switch. From the perspective of interface versatility, we will use gRPC in the external interface and provide HTTP API at the same time.
Backup and recovery are mainly divided into two types: Snapshot and Log. The main difference is that Log can support limited rollback (for example, in transaction operations that may be supported in the future, data in one production environment is backed up to another through Log backup. In the production environment, the application can still cancel the submission of the existing Log to roll back the data).
Let us imagine the following situation, we have a Casbin cluster, query data from the follower (secondary) node. When the following situations occur, we may read some old data (stale read). The node is still part of the cluster, but it has fallen behind the leader in updating memory data. The node is no longer part of the cluster, and no longer applies (Apply) Logs from the Leader.
The above problems can be solved by: Forcing data to be read from the Leader (possibly) can ensure read consistency. (For example, when a request is received, query from the local State whether it is currently a Leader node, if it is not a redirection or an error.) (In the case of relatively low requirements for read consistency) Check the current time of the current node and the interval at which the last heartbeat packet from the Leader was received. If the interval is higher than the given threshold, a read failure (expired) error will be returned. .
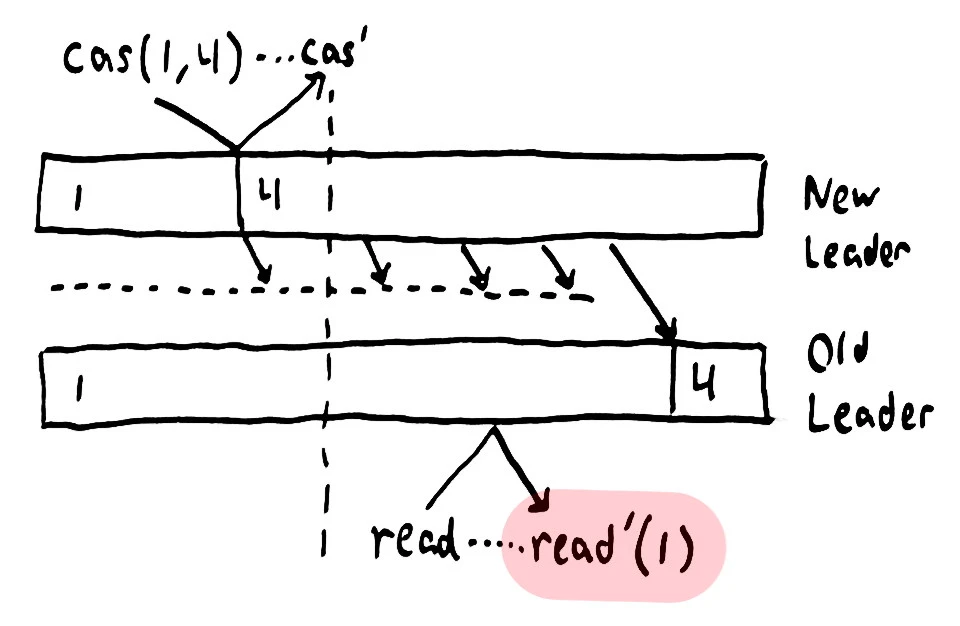
Let us imagine another situation, we have a Casbin cluster, although we have requested to query data from the Leader, in some extreme cases, the query may still return some old data (stale read). The communication of the Old Leader was interrupted, and the New Leader was selected from the remaining nodes, but the Old Leader was still in the term of office and received (and responded to) the query request (Split-brain).
In Image-0[3], New Leader has changed the value from 1 to 4, and at the same time, the user initiated a request that requested only can be responded to by the Leader node, but still, read the old data (stale).
The above problems can be solved by: Ask other (most) nodes in the Raft cluster whether the current node is still the Leader node.
Here we introduce the definition of rqlite[4] to read consistency query Level[5].
Level is defined as follows: -None: Respond to query from local memory -Weak: Read data from Leader and check whether it is Leader from local memory -Strong: Read data from the Leader, and ask (most) nodes in the cluster whether the current node is the Leader
As mentioned above, permission control is a model that reads more and writes less. We increase the read performance of the cluster by supporting the addition of Read-only nodes without increasing the write delay (that is, subscribe to Logs from the Leader and accept a certain write delay). Read-only nodes do not participate in the Raft consensus system, nor do they participate in voting (the number of nodes is not counted in the total number of voting nodes). Read the data in the Read-only node, by setting the query Level = None, and setting the threshold of data staleness. In the query, it is determined whether the current query is valid by comparing the given threshold and the time difference between the current time and the last heartbeat packet received from the Leader (that is, the time difference is greater than the threshold, indicating that the data is too old).
As mentioned above, this is an application that supports multi-tenancy. This also means that we need to verify the permissions of the user's read and write requests (of course, the user can also choose to turn off the requested permission authentication). At the same time, the security mechanism is divided into the following two types: sending authentication information through the SSL/TLS channel, or using the SCRAM [6] mutual authentication mechanism.
-Raft[0]: Raft: In Search of an Understandable Consensus Algorithm -Hashicorp/Raft[1]: https://github.com/hashicorp/raft -bboltDB[2]: https://github.com/etcd-io/bbolt -Image-0[3]: Kyle Kingsbury's article on linearizability and stale reads in Raft systems -rqlite[4] :https://github.com/rqlite/rqlite -Level [5]: https://github.com/rqlite/rqlite/blob/master/DOC/CONSISTENCY.md -SCRAM[6]: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5802