A comprehensive guide to understanding Apache Kafka, including its architecture, installation steps, and a practical use case demonstration.
Kafka is a message broker using a commit log, often associated with infrastructure data, microservices, and event-driven architectures.
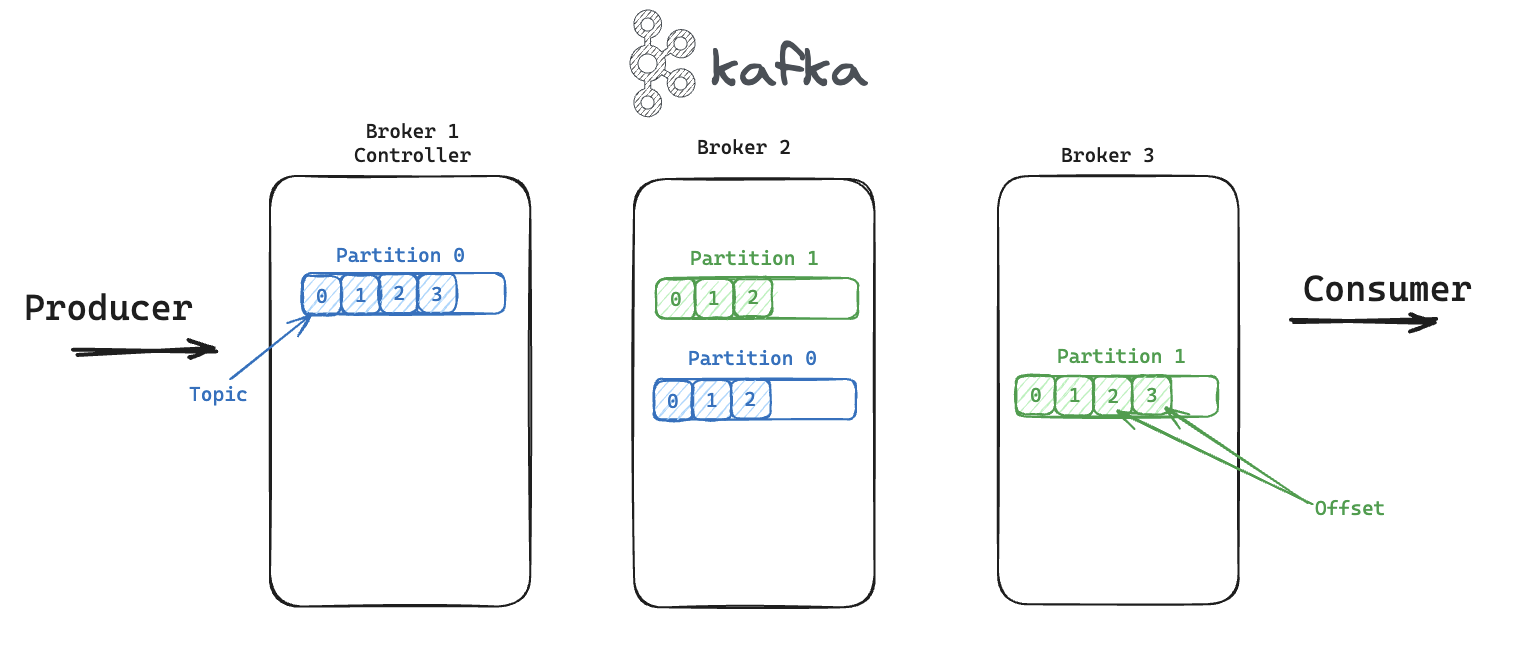
- Broker: Acts as a node with SSD storage.
- Partition: Ensures high availability and fault tolerance of data. We could have multiple partitions replicated across brokers (Leader and Followers).
- Topic: Similar to a table in a database, it defines a data stream.
- Offset: The unique identifier for a message/event within a topic.
- Producer: Publishes messages to Kafka.
- Consumer: Reads messages from a topic.
- Consumer Group: Multiple instances of the same application (e.g., App C with 3 instances) can consume messages from specific partitions with coordination.
- Replications: Ensures data redundancy and availability.
- Partitions: Allows for data distribution and parallel processing.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to handle large volumes of data.
- Performance: Optimized for high-throughput and low-latency message processing.
Kafka operates asynchronously, and consumers can reread messages since events are stored with offsets.
Partitions logically divide topics and are distributed across the cluster. Each message within a partition is associated with a unique key.
- RabbitMQ
- ActiveMQ
- ZeroMQ
Instructions for installing Kafka using Kubernetes will be provided in this section.
Tracking a bus to see its real-time position using Flask, JavaScript, and leafletjs .