fastapi-pagination is a Python library designed to simplify pagination in FastAPI applications.
It provides a set of utility functions and data models to help you paginate your database queries
and return paginated responses to your clients.
With fastapi-pagination, you can easily define pagination parameters in your FastAPI endpoint functions,
and use them to generate paginated responses that include the requested subset of your data.
The library supports a variety of pagination strategies, including cursor-based pagination and page-based pagination.
fastapi-pagination is built on top of the popular fastapi library, and it works with a wide range
of SQL and NoSQL databases frameworks. It also supports async/await syntax and is compatible with Python 3.8 and higher.
Features:
- Simplifies pagination in FastAPI applications.
- Supports a variety of pagination strategies, including cursor-based pagination and page-based pagination
- Works with a wide range of SQL and NoSQL databases frameworks, including
SQLAlchemy,Tortoise ORM, andPyMongo. - Supports async/await syntax.
- Compatible with Python 3.8 and higher.
For more information on how to use fastapi-pagination, please refer to the official documentation.
pip install fastapi-paginationAll you need to do is to use Page class as a return type for your endpoint and call paginate function
on data you want to paginate.
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
# import all you need from fastapi-pagination
from fastapi_pagination import Page, add_pagination, paginate
app = FastAPI() # create FastAPI app
class UserOut(BaseModel): # define your model
name: str = Field(..., example="Steve")
surname: str = Field(..., example="Rogers")
users = [ # create some data
# ...
]
@app.get('/users')
async def get_users() -> Page[UserOut]: # use Page[UserOut] as return type annotation
return paginate(users) # use paginate function to paginate your data
add_pagination(app) # important! add pagination to your appPlease, be careful when you work with databases, because default paginate will require to load all data in memory.
For instance, if you use SQLAlchemy you can use paginate from fastapi_pagination.ext.sqlalchemy module.
from sqlalchemy import select
from fastapi_pagination.ext.sqlalchemy import paginate
@app.get('/users')
def get_users(db: Session = Depends(get_db)) -> Page[UserOut]:
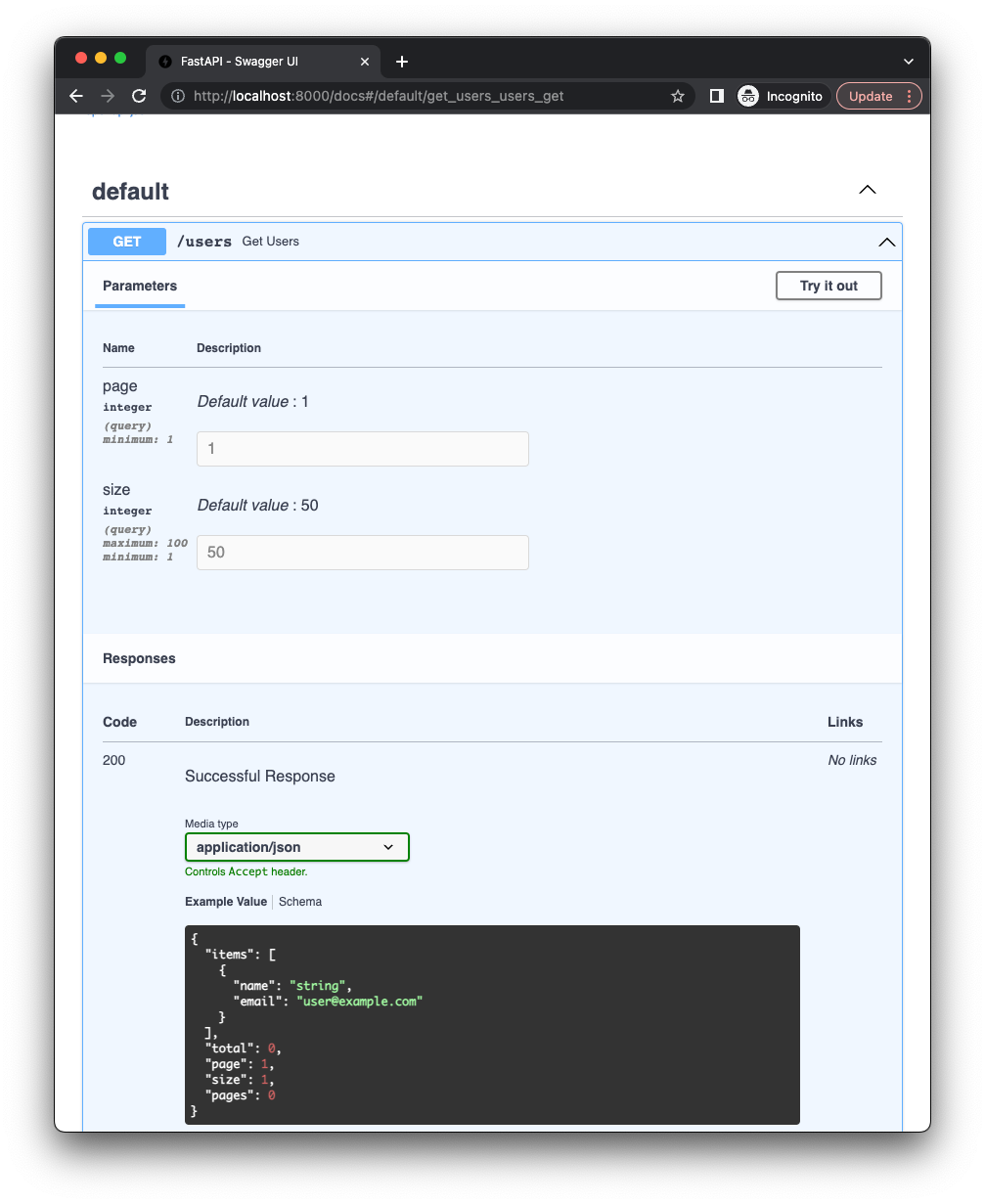
return paginate(db, select(User).order_by(User.created_at))Code from Quickstart will generate OpenAPI schema as bellow: