- Overview
- Getting started
- Runtime dependencies
- Running from the sources
- Installation from the sources
- Installation
- Configuration
- Translations
- Usage
- Use weather data in Conky
meteo-qt is an application to display weather information in desktop panels, desktop notifications and its own window.
Weather data is taken from OpenWeatherMap. The application is based on Python 3 and Qt 5. It is licensed under the GNU General Public License version 3 (GPLv3).
After satisfying some runtime dependencies meteo-qt can be run right from the source tree. Installing
is possible as well and relying on on a file setup.py as commonly used in Python. This enables
every regular user to run the application and updates the translations comprised in the code. Also,
some binary packages are available.
The following sections will describe all three approaches stating some major Linux distributions as
example.
These are PyQt, SIP and lxml which can be installed as follows:
Arch Linux
# pacman -S python-pyqt5 python-sip python-lxml
Debian, Derivatives
# apt-get install python3-pyqt5 python3-sip python3-lxml
Fedora
# dnf install python3-qt5 python3-sip python3-lxml
openSUSE Leap
# zypper install python3-qt5 python3-sip python3-lxml
(SIP packages stated for the sake of completeness only. In fact they all are a dependency of the respective PyQt packages.)
Once the runtime dependencies stated above are met the application can be run from its sources by invoking
$ python3 /path/to/meteo-qt/meteo_qt/meteo_qt.py
In addition to the runtime dependencies stated above binariespylupdate5 of PyQt and lrelease of
Qt Linguist are needed.
Binary lrelease still comes as Qt 5 and 4 version in all major distributions so it must be ensured
the former is used.
This document describes how to achieve this by tweaking the system-wide settings of
qtchooser which is available on Arch Linux, Debian and
Fedora while a manual approach has to be taken on openSUSE. The corresponding changes may or may not
be reverted after installing meteo-qt depending on the needs of the respective system.
To test whether lrelease is configured properly run $ lrelease -version which should output the
desired Qt version like 5.5.1.
Arch Linux Install package
# pacman -S qt5-tools
This will pull in package qtchooser which has the usual link /etc/xdg/qtchooser/default.conf point to
/etc/xdg/qtchooser/5.conf making Qt 5 the default.
Debian, Derivatives Install packages
# apt-get install pyqt5-dev-tools qttools5-dev-tools
To make Qt 5 the default version either install package qt5-default in addition or create a symbolic
link
# ln -s /usr/share/qtchooser/qt5-x86_64-linux-gnu.conf /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qtchooser/default.conf
where the architecture, here x86_64-linux-gnu, may have to get adjusted to the current system.
Fedora Install packages
# dnf install python3-qt5-devel qt5-linguist qtchooser
To make Qt 5 default run
# update-alternatives --config qtchooser-default
follow the instructions and log out and in again.
(Fedora is handling qtchooser by the Debian Alternatives System,
see $ ls -l /etc/alternatives/qtchooser-* /etc/xdg/qtchooser/. The binaries handled by qtchooser are
placed at a location that's usually outside $PATH and added to the latter by files in /etc/profiles.d/,
hence the need to log out and in again.)
openSUSE Leap Install packages
# zypper install python3-qt5-devel libqt5-linguist
Make sure package libqt4-linguist which is the only package providing binary lrelease in $PATH isn't installed
or move /usr/bin/lrlease to another location and run
# ln -s /usr/bin/lrelease-qt5 /usr/bin/lrelease
To install run
# python3 setup.py install
in the source tree. Adding switch --help displays additional options.
After installing that way a binary meteo-qt will be placed in $PATH, a
desktop entry file meteo-qt.desktop
in $XDG_DATA_DIRS/applications making the application available in the usual panel main menus.
AUR package meteo-qt is providing the
latest stable release, package meteo-qt-git the latest checkout
of branch master.
Package meteo-qt is providing stable releases.
After installation you will be prompted to do a right click on the system tray icon to configure the cities, units and other settings for the weather informations and the application.
You can contribute in a current translation or add a missing language in the Weblate platform.

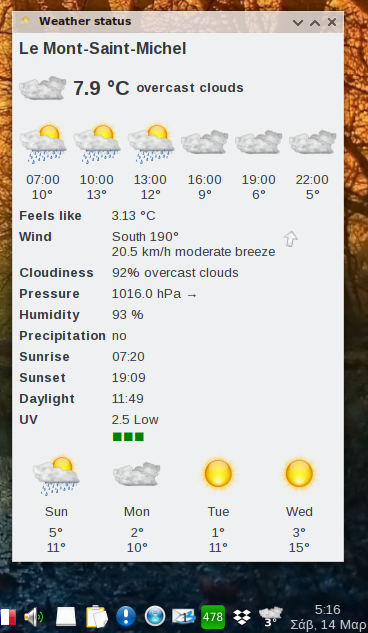
Not much to say. The window providing verbose information as depicted above will display upon left clicking the panel icon, a context menu coming up on right-click is providing several configuration options all of which should be pretty self-explanatory.
You can read the weather data from the log file. Here is an example how to extract them (see #137):
[dglent@localhost meteo-qt]$ pwd
/home/dglent/.config/meteo-qt
[dglent@localhost meteo-qt]$ awk '/EXPORT_START/{ f=1;r=""; next }f && /EXPORT_END/{f=0} f{ r=(r=="")? $0: r RS $0 }END{ print r }' meteo-qt.log
City,Paris, FR
Temperature,18.61 °C
Feels like,18.88 °C
Wind, 1 Bft. calm
Cloudiness,100% overcast clouds
Humidity,90 %
Visibility,10.0 km
Comfort,Alright
Precipitation,no
Sunrise,07:16
Sunset,20:21
Daylight,13:05
Air quality,Fair
UV,4.66 Moderate