An automated way on troubleshooting Kubernetes deployments. This tool is based on visual guide on troubleshooting Kubernetes deployment.
-
python3 and packages
-
pip3needs to be installed to get required packages. You need to install above packages with command:xpip3 install -r requirements.txt
-
KUBECONFIG for the cluster needs to be exported as env. It is read by kube-wrench to connect to the cluster to get details.
Once above pre-requisites are installed and configured, you are ready to run kube-wrench as below after cloning the repo:
-
Change dir:
cd kube-wrench
-
Run script:
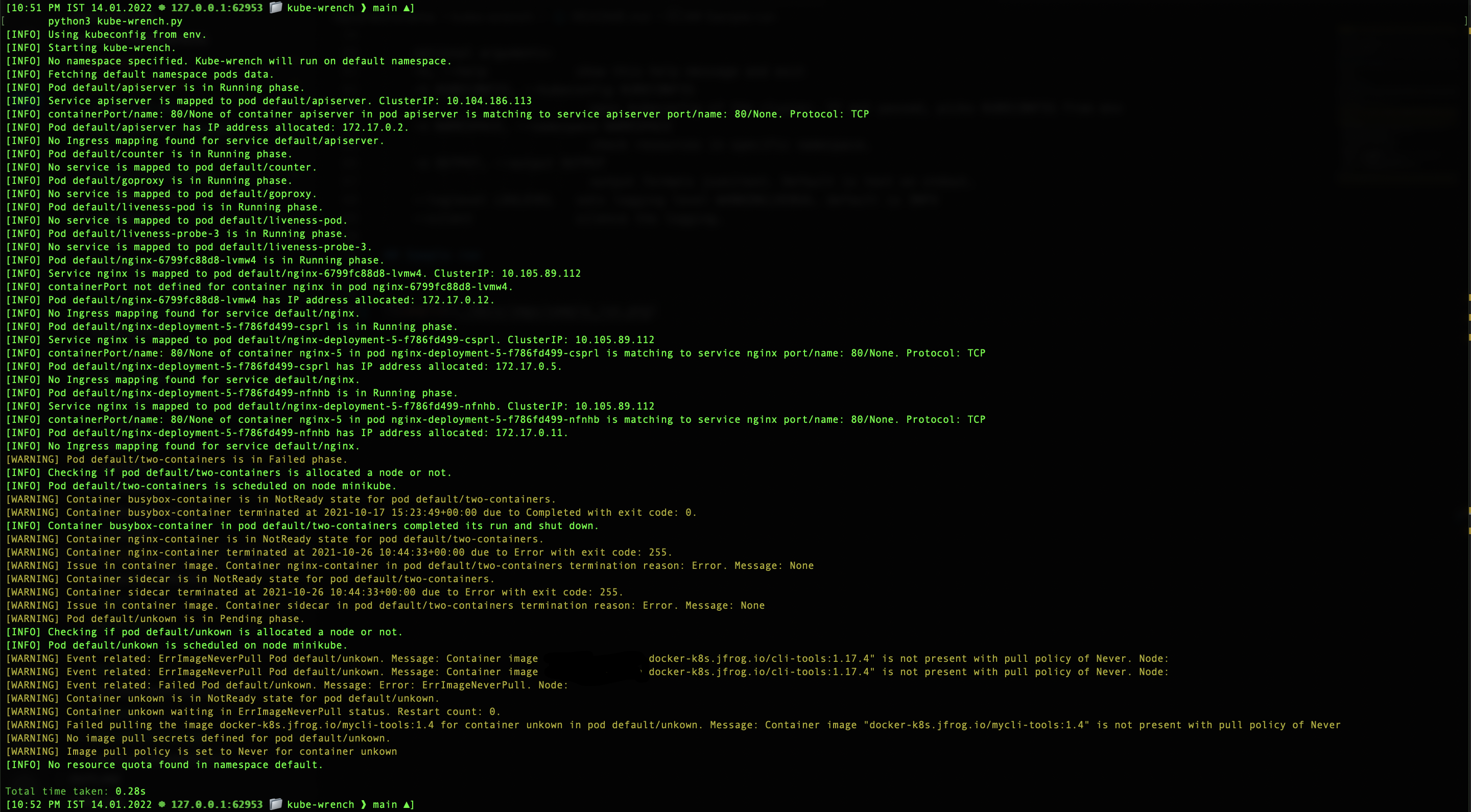
python3 kube-wrench.py
Running through docker image would be much easier than installing dependencies on your machine. The docker image being used is based on python:3.8-slim-buster which is a very light weight version of python in docker.
If you want a ready-made env to run kube-wrench, please check dguyhasnoname/kube-wrench for latest image.
Pulling docker image:
docker pull docker.io/dguyhasnoname/kube-wrench:0.1.0
Running the docker image:
docker run -it --rm -v ~/k8sconfig/ct/:/app/k8sconfig/ -e KUBECONFIG=/app/k8sconfig/kubeconfig.yaml docker.io/dguyhasnoname/kube-wrench:0.1.0
python3 kube-wrench.py -h
usage: kube-wrench.py [-h] [-k KUBECONFIG] [-n NAMESPACE] [-o OUTPUT] [--loglevel LOGLEVEL] [--silent]
This script can be debug issues in a namespace in a Kubernetes cluster.
Before running script export KUBECONFIG file as env:
export KUBECONFIG=<kubeconfig file location>
e.g. export KUBECONFIG=/Users/dguyhasnoname/kubeconfig
ALternatively kubeconfig can be passed as argument.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-k KUBECONFIG, --kubeconfig KUBECONFIG
pass kubeconfig of the cluster. If not passed, picks KUBECONFIG from env
-n NAMESPACE, --namespace NAMESPACE
check resources in specific namespace.
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
output formats json|text. Default is text on stdout.
--loglevel LOGLEVEL sets logging level WARNING|DEBUG. default is INFO
--silent silence the logging.