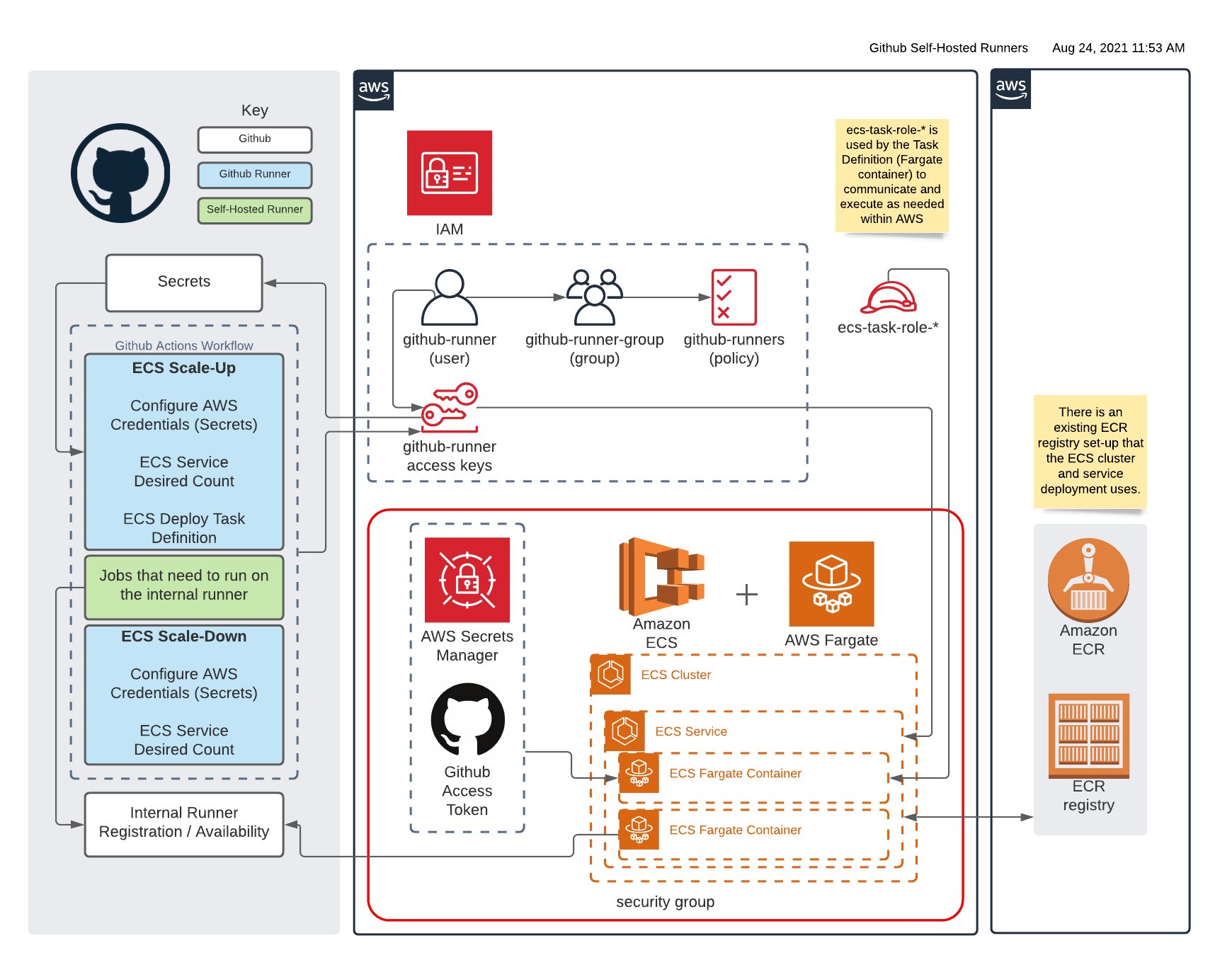
This repository contains the Dockerfile for a self-hosted GitHub Actions runner and an associated Terraform module which can be run in your environment to provision:
- ECS Cluster
- ECS Service
- ECS Fargate task definition to spin up an instance of this runner per job in your GitHub Actions workflow
This module uses an existing ECR repository in AWS, and so does not provision one.
- Create and request access for a Github robot user.
- Create EUA account for robot user
- Create Github account for robot user
- Request permission for the robot user within Github
- Create an access token for the robot user within Github
- Store the access token in AWS Secrets Manager
- The secret's name must start with
github-runnerdue to IAM restrictions on the ecs-task-role
- The secret's name must start with
- Set up an IAM user in AWS with the necessary permissions to support the docker-build.yml workflow script included. See
IAM User Permissionssection below for details.- Once you have your user, be sure to add the access key details to your repository's Secrets
- Provision the Terraform module in this repository.
- You should now be able to push images to the org level ECR repository via a push to your main branch or a new release. An ECS Cluster and Service should be set up for you.
- See the documentation on usage of the runner on how to deploy runners to your service.
Creation of the IAM user, group, and attached policy should be submitted via CMS Jira to the Cloud Support team.
For the IAM user needed for Github to interact with AWS (specifically ECR and ECS):
- the username should be
github-runner - the user should be a part of the group
github-runner-group - the permissions policy (
github-runners) should be attached to the group to follow best practices
In the IAM policy, the following variables should be updated to be the appropriate account ID and region for your deployment:
$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID$AWS_REGION
All of the specified resources in the IAM policy do not have to exist prior to the policy being created.
github-runners IAM policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "IAMActions",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"iam:GetRole",
"iam:PassRole"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/ecs-task-role-*"
},
{
"Sid": "ECRTokenAndECSTaskActions",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecs:RegisterTaskDefinition",
"ecr:GetAuthorizationToken",
"ecs:DescribeTaskDefinition"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "ECSClusterActions",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecs:DescribeServices",
"ecs:UpdateService"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:ecs:$AWS_REGION:$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:cluster/gh-runner-*",
"arn:aws:ecs:$AWS_REGION:$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:service/gh-runner-*"
]
}
]
}
Should you decide to populate the optional path variable in this module, ensure that the Resource the iam:GetRole and PassRole are enabled on includes the path you specify. e.g. "arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/path/you/specified/ecs-task-role-*"
This is strictly for testing purposes. These steps help test a Github token by running the docker image and enabling you to manually trigger the entrypoint.sh script locally via Docker. This does not require any AWS infrastructure deployed.
The entrypoint.sh script is what sets-up the docker image to act as a runner, including registration with the repository specified.
- Clone this repository to your machine.
- Ensure your environment variables are populated:
PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN- Your github personal access token with repository permissions.REPO_OWNER- The name of the repository owner, e.g.CMSgovREPO_NAME- The name of the repository you are configuring the runners for
- Build and run the image.
./entrypoint.shshould register the runner with your repository and start listening for jobs. - In one of the workflows in the target repository, change the
runs-onvalue toself-hosted. This will make the workflow use the registered self-hosted runner to complete its task, after which it will shut down.
This repository contains a Terraform module to deploy an ECS cluster, ECS service, and log to Cloudwatch in support of automating deployment of ephemeral self-hosted Github Actions runners within AWS.
This module supports the following features:
- Optionally pass an existing ECS Cluster, and if not, create one
- Set default desired count for ECS Service (default is 0, assuming it will be managed by Github Actions workflow)
module "github-actions-runner-aws" {
source = "github.com/cmsgov/github-actions-runner-aws?ref=v2.0.0"
# ECS variables
environment = "${environment}"
ecs_vpc_id = "${vpc.id}"
ecs_subnet_ids = "${vpc.private_subnets.id}"
# GitHub Runner variables
personal_access_token_arn = "${secretsmanager.token.arn}"
github_repo_name = "${repo_name}"
}Some existing variable information can be looked-up in AWS via data sources. For example:
data "aws_secretsmanager_secret_version" "token" {
secret_id = "/github-runner-dev/token"
}Will let you then use the ARN of that data source in this way:
personal_access_token_arn = data.aws_secretsmanager_secret_version.token.arn| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| environment | Environment name (used in naming resources) |
| ecs_vpc_id | VPC ID to be used by ECS |
| ecs_subnet_ids | Subnet IDs for the ECS tasks. |
| personal_access_token_arn | AWS SecretsManager ARN for GitHub personal access token |
| github_repo_name | The Github repository name |
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cloudwatch_log_retention | 731 | Number of days to retain Cloudwatch logs |
| ecr_repo_tag | "latest" | The tag to identify and pull the image in ECR repo |
| ecs_desired_count | 0 | Sets the default desired count for task definitions within the ECS service |
| assign_public_ip | "false" | Choose whether to assign a public IP address to the Elastic Network Interface |
| role_path | "/" | The path in which to create the assume roles and policies. Refer to the AWS docs for more |
| permissions_boundary | "" | ARN of the policy that is used to set the permissions boundary for the role |
| github_repo_owner | "CMSgov" | The name of the Github repo owner. |
| tags | {} | Additional tags to apply |
None.
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| terraform | >= 0.13 |
| aws | >= 3.0 |
None.