remoteAudio is a cross plattform audio streaming application, built for Amateur Radio purposes. The most typical use case for this software is the remote operation of an amateur radio station. remoteAudio is written in Go.
remoteAudio supports multiple users and multiple audio sources (e.g. radios). This means that with a single click a user can switch between audio sources. At any time multiple clients can listen simultaneously on the same radio, although remoteAudio only allows one user to transmit.
ADVICE: This project is under development. The parameters, ICD and the behaviour is still not stable and subject to change.
- OPUS
- extensible for other codecs (e.g. PCM)
RemoteAudio has been tested on the following CPU architectures:
- AMD64
- i386
- ARMv7 (e.g. Raspberry Pi 2)
- ARMv8 (e.g. Raspberry Pi 3)
and the following operating Systems:
- Linux (Ubuntu, Raspian, Armbian)
- MacOS
- Windows (7 and 10)
Users have reported performance issues with remoteAudio on single core ARMv6 SoCs, in particular the Raspberry Pi 1. Usage of the Raspberry Pi 1 is therefore not recommended.
You can download a tarball / zip archive with the compiled binary for MacOS, Linux (ARM/AMD64) and Windows from the releases page. remoteAudio is just a single exectuable.
remoteAudio depends on some 3rd party libraries which can be installed on Linux and MacOS with the respective packet managers. On Windows the 3rd party libraries are included in the zip archive.
$ sudo apt-get install -y pkg-config libsamplerate0 libopus0 libopusfile0 libportaudio2$ brew update
$ brew install pkg-config opus opusfile portaudio libsamplerateIn order to operate remoteAudio you need to either run your own NATS Broker which can be downloaded here for a lot of platforms & operating systems.
If you are not sure about the name of your audio devices and their parameters, you can easily list the available devices:
$ remoteAudio enumerateBy default the standard input / output devices defined in your OS will be used.
You can find further tips about configuring your audio devices in the Wiki.
Both, the server and the client provide extensive configuration possibilities,
either through a configuration file (TOML|YAML|JSON), typically located in
your home directory /home/your_user/.remoteAudio.toml. or through pflags.
An example configuration file named .remoteAudio.tomlis included in the
repository.
All parameters can be set through pflags. The following example shows the options for
$ remoteAudio server nats --helpNATS Server for bi-directional audio streaming
Usage:
remoteAudio server nats [flags]
Flags:
-p, --broker-port int Broker Port (default 4222)
-u, --broker-url string Broker URL (default "localhost")
-h, --help help for nats
-P, --password string NATS Password
-Y, --radio string radio name to which this audio server belongs (e.g. 'ts480')
-U, --username string NATS Username
Global Flags:
-f, --audio-frame-length int Amount of audio samples in one frame (default 480)
--config string config file (default is $HOME/.remoteAudio.yaml)
--input-device-channels int Input Channels (default 1)
--input-device-latency duration Input latency (default 5ms)
-i, --input-device-name string Input device (default "default")
--input-device-samplerate float Input device sampling rate (default 48000)
--opus-application string profile for opus encoder (default "restricted_lowdelay")
--opus-bitrate int Bitrate (bits/sec) generated by the opus encoder (default 32000)
--opus-complexity int Computational complexity of opus encoder (default 9)
--opus-max-bandwidth string maximum bandwidth of opus encoder (default "wideband")
--output-device-channels int Output Channels (default 2)
--output-device-latency duration Output latency (default 5ms)
-o, --output-device-name string Output device (default "default")
--output-device-samplerate float Output device sampling rate (default 48000)
-R, --rx-buffer-length int Buffer length (in frames) for incoming Audio packets (default 10)
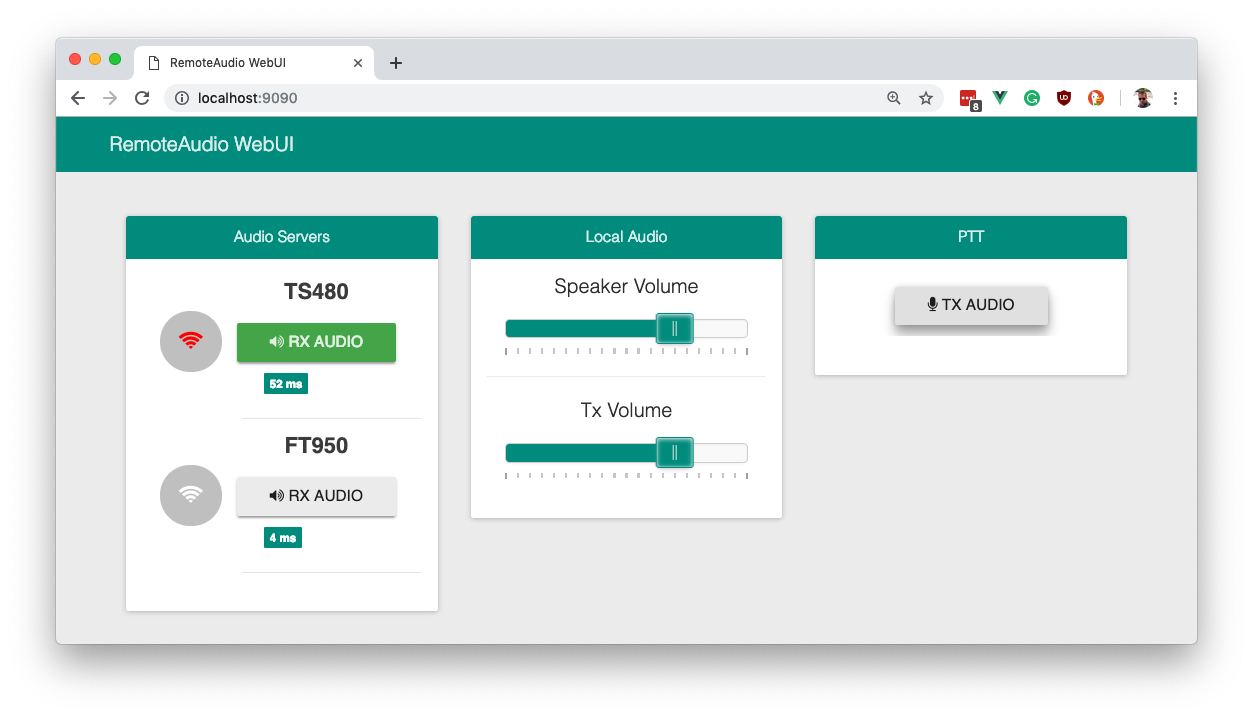
$ remoteAudio server nats$ remoteAudio client natsThe Client provides a minimal Web Interface for basic control of the client and server side audio streams. Open a Webbrowser at: http://localhost:9090 to access the WebUI.
The Wiki contains detailed instructions on how to build remoteAudio from source code on Linux, MacOS and Windows.
The remoteAudio client can be fully controlled through a REST API. Check the Wiki for more details.
remoteAudio does it's best to check if your sound hardware is compatible with the parameters you have set. However it's not entirely possible to check all the Settings.
Inexpensive (USB) Soundcards usually operate at 48kHz. They play the audio in Stereo and Record the Audio in MONO.
The Wiki contains a Troubleshooting section.
Feel free to open an issue if you encounter problems.